[1] MarketsandMarkets.com.Wound Care Market by Product (Foams, Hydrocolloids, Alginates, Antimicrobial Dressings, Assessment, NPWT Devices, Substitutes, Sutures, Staples, Tapes), Wound (Surgical, Trauma, Diabetic Ulcers, Burns), End-User, Region - Global Forecast to 2024. https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/wound-care-market-371.html
[2] BARROS SC, MARTINS JA, MARCOS JC, et al. Influence of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor-based peptides on elastase activity and their incorporation in hyaluronic acid hydrogels for chronic wound therapy. Biopolymers. 2012;98(6):576-590.
[3] VIG K, CHAUDHARI A, TRIPATHI S, et al. Advances in skin regeneration using tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4):789.
[4] WINTER GD. Formation of the scab and the rate of epithelisation of superficial wounds in the skin of the young domestic pig. J wound care. 1995;4(8):366-367.
[5] XU Q, A S, GAO Y, et al. A hybrid injectable hydrogel from hyperbranched PEG macromer as a stem cell delivery and retention platform for diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2018;75:63-74.
[6] WANG C, WANG M, XU T, et al. Engineering Bioactive Self-Healing Antibacterial Exosomes Hydrogel for Promoting Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing and Complete Skin Regeneration. Theranostics. 2019; 9(1):65-76.
[7] LIU R, DAI L, SI C, et al. Antibacterial and hemostatic hydrogel via nanocomposite from cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;195: 63-70.
[8] ZHANG L, MA Y, PAN X, et al. A composite hydrogel of chitosan/heparin/poly (gamma-glutamic acid) loaded with superoxide dismutase for wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;180:168-174.
[9] 韩颖,徐玉茵,田林奇,等.聚乙烯醇基水凝胶敷料的研究进展[J].中国医疗器械杂志,2018,42(6):437-439,443.
[10] YING H, ZHOU J, WANG M, et al. In situ formed collagen-hyaluronic acid hydrogel as biomimetic dressing for promoting spontaneous wound healing. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;101:487-498.
[11] HSIEH HT, CHANG HM, LIN WJ, et al. Poly-Methyl methacrylate/polyvinyl alcohol copolymer agents applied on diabetic wound dressing. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):9531.
[12] ZHENG C, LIU C, CHEN H, et al. Effective wound dressing based on poly (vinylalcohol)/dextran-aldehyde composite hydrogel. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;132:1098-1105.
[13] SHU M, LONG S, HUANG Y, et al. High strength and antibacterial polyelectrolyte complex CS/HS hydrogel films for wound healing. Soft Matter. 2019;15(38):7686-7694.
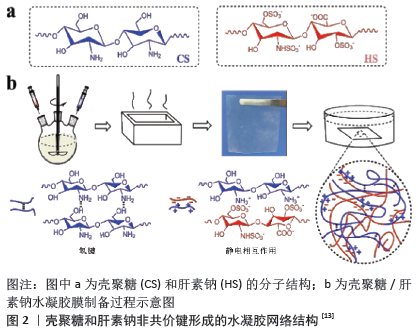
[14] STRACCIA MC, D’AYALA GG, ROMANO I, et al. Alginate hydrogels coated with chitosan for wound dressing. Mar Drugs. 2015;13(5):2890-2908.
[15] HOMANN HH, ROSBACH O, MOLL W, et al. A liposome hydrogel with polyvinyl-pyrrolidone iodine in the local treatment of partial-thickness burn wounds. Ann Plast Surg. 2007;59(4):423-427.
[16] Ouyang QQ, Hu Z, Lin ZP, et al. Chitosan hydrogel in combination with marine peptides from tilapia for burns healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;112:1191-1198.
[17] MOTAWEA A, ABD EL-GAWAD AEH, BORG T, et al. The impact of topical phenytoin loaded nanostructured lipid carriers in diabetic foot ulceration. Foot (Edinb). 2019;40:14-21.
[18] MAHMOUD NN, HIKMAT S, ABU GHITH D, et al. Gold nanoparticles loaded into polymeric hydrogel for wound healing in rats: Effect of nanoparticles’ shape and surface modification. Int J Pharm. 2019; 565:174-186.
[19] MASOOD N, AHMED R, TARIQ M, et al. Silver nanoparticle impregnated chitosan-PEG hydrogel enhances wound healing in diabetes induced rabbits. Int J Pharm. 2019;559:23-36.
[20] LI X, FAN R, TONG A, et al. In situ gel-forming AP-57 peptide delivery system for cutaneous wound healing. Int J Pharm. 2015;495(1): 560-571.
[21] ZHAI M, XU Y, ZHOU B, et al. Keratin-chitosan/n-ZnO nanocomposite hydrogel for antimicrobial treatment of burn wound healing: Characterization and biomedical application. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018;180:253-258.
[22] KONG L, WU Z, ZHAO H, et al. Bioactive Injectable Hydrogels Containing Desferrioxamine and Bioglass for Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(36):30103-30114.
[23] YASASVINI S, ANUSA RS, VEDHAHARI BN, et al. Topical hydrogel matrix loaded with Simvastatin microparticles for enhanced wound healing activity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;72:160-167.
[24] 凌建民,田爱玲,范鲁峰,等.脂肪间充质干细胞在功能化自组装纳米多肽水凝胶三维培养下旁分泌的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2018,35(2):250-252.
[25] KUO YR, WANG CT, CHENG JT, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing through the Induction of Autocrine and Paracrine Effects. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(1):71-81.
[26] XU H, HUANG S, WANG J, et al. Enhanced cutaneous wound healing by functional injectable thermo-sensitive chitosan-based hydrogel encapsulated human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;137:433-441.
[27] ALAPURE BV, LU Y, HE M, et al. Accelerate healing of severe burn wounds by mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-seeded biodegradable hydrogel scaffold synthesized from arginine-based poly(ester amide) and chitosan. Stem Cells Dev. 2018;27(23): 1605-1620.
[28] BURMEISTER DM, STONE R, WRICE N, et al. Delivery of allogeneic adipose stem cells in polyethylene glycol-fibrin hydrogels as an adjunct to meshed autografts after sharp debridement of deep partial thickness burns. Stem Cells Transmed. 2018;7(4):360-372.
[29] LOH EYX, MOHAMAD N, FAUZI MB, et al. Development of a bacterial cellulose-based hydrogel cell carrier containing keratinocytes and fibroblasts for fullthickness wound healing. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2875.
[30] SEMENIC D, CIRMAN T, ROZMAN P, et al. Regeneration of chronic wounds with allogeneic platelet gel versus hydrogel treatment: A prospective study. Acta Clin Croat. 2018;57(3):434-442.
[31] BABAVALIAN H, TEBYANIAN H, LATIFI AM, et al. The effect of synthetic alginate sulfate hydrogels with recombinant PDGF-BB on wound healing. BratislLek Listy. 2018;119(6):391-396.
[32] Xu HL, Chen PP, ZhuGe DL, et al. Liposomes with silk fibroin hydrogel core to stabilize bFGF and promote the wound healing of mice with deep second-degree scald. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(19). doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700344.
[33] KIM YH, TABATA Y. Recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages by dual release of stromal cell-derived factor-1 and a macrophage recruitment agent enhances wound closure. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(4):942-956.
[34] HUANG C, ORBAY H, TOBITA M, et al. Proapoptotic effect of control-released basic fibroblast growth factor on skin wound healing in a diabetic mouse model. Wound Repair Regen. 2016;24(1):65-74.
[35] LI W, GAO F, KAN J, et al. Synthesis and fabrication of a keratin-conjugated insulin hydrogel for the enhancement of wound healing. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;175:436-444.
[36] ZHANG S, LIU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Prostaglandin E2 hydrogel improves cutaneous wound healing via M2 macrophages polarization. Theranostics. 2018;8(19):5348-5361.
[37] SH AHMED A, TAHER M, MANDAL UK, et al. Pharmacological properties of Centella asiatica hydrogel in accelerating wound healing in rabbits. BMC Complement Alter Med. 2019;19(1):213.
[38] DAVOODI-ROODBORDEII F, AFSHAR M, HAJI ABAS TABRIZI F, et al. Topical hydrogel containing Fumaria vaillantii Loisel. extract enhances wound healing in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19(1):254.
[39] 王俊杰,王刚,益伟清,等.白及水凝胶敷料应用于Ⅰ Ⅱ期压疮的效果评价[J].中国药物与临床,2019,19(3):514-515.
[40] LAMMOGLIA-ORDIALES L, VEGA-MEMIJE ME, HERRERA-ARELLANO A, et al. A randomised comparative trial on the use of a hydrogel with tepescohuite extract (Mimosa tenuiflora cortex extract-2G) in the treatment of venous leg ulcers. Int Wound J. 2012;9(4):412-418.
[41] POH YUEN WEN A, HALIM AS, MAT SAAD AZ, et al. A prospective study evaluating wound healing with sea cucumber gel compared with hydrogel in treatment of skin graft donor sites. Complement Ther Med. 2018;41:261-266.
[42] JIJI S, UDHAYAKUMAR S, ROSE C, et al. Thymol enriched bacterial cellulose hydrogel as effective material for third degree burn wound repair. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;122:452-460.
[43] DANG LH, NGUYEN TH, TRAN HLB, et al. Injectable nanocurcumin-formulated chitosan-g-pluronic hydrogel exhibiting a great potential for burn treatment. J Healthc Eng. 2018;2018:5754890.
[44] KAMAR SS, ABDEL-KADER DH, RASHED LA. Beneficial effect of curcumin nanoparticls-hydrogel on excisional skin wound healing in type-I diabetic rat: Histological and immunohistochemical studies. Ann Anat. 2019;222:94-102.
[45] AMIN MA, ABDEL-RAHEEM IT. Accelerated wound healing and anti-inflammatory effects of physically cross linked polyvinyl alcohol-chitosan hydrogel containing honey bee venom in diabetic rats. Arch Pharm Res. 2014;37(8):1016-1031.
[46] 卫巍,刘燕飞,张玲,等.自组装短肽水凝胶:止血效应与机制研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(2):310-316.
[47] ZHAO X, GUO B, WU H, et al. Injectable antibacterial conductive nanocomposite cryogels with rapid shape recovery for noncompressible hemorrhage and wound healing. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):2784.
[48] LOKHANDE G, CARROW JK, THAKUR T, et al. Nanoengineered injectable hydrogels for wound healing application. Acta Biomater. 2018;70:35-47.
[49] YEGAPPAN R, SELVAPRITHIVIRAJ V, AMIRTHALINGAM S, et al. Carrageenan based hydrogels for drug delivery, tissue engineering and wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;198:385-400.
[50] 聂海英,李昆,张全英.湿性敷料在老年糖尿病足溃疡换药中的应用[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(13):3582-3584.
[51] BRITLAND S, SMITH A, FINTER W, et al. Recombinant Lucilia sericata chymotrypsin in a topical hydrogel formulation degrades human wound eschar ex vivo. Biotechnol Prog. 2011;27(3):870-874.
[52] EDWARDS J. Hydrogels and their potential uses in burn wound management. Br J Nurs. 2010;19:12-16.
[53] NALAMPANG K, PANJAKHA R, MOLLOY R, et al. Structural effects in photopolymerized sodium AMPS hydrogels crosslinked with poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate for use as burn dressings. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013;24(11):1291-1304.
[54] ZHU J, LI F, WANG X, et al. Hyaluronic Acid and Polyethylene Glycol Hybrid Hydrogel Encapsulating Nanogel with Hemostasis and Sustainable Antibacterial Property for Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(16):13304-13316.
[55] JIANG B, LARSON JC, DRAPALA PW, et al. Investigation of lysine acrylate containing poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels as wound dressings in normal and infected wounds. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;100(3):668-676.
[56] HASEEB MT, HUSSAIN MA, ABBAS K, et al. Linseed hydrogel-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial and wound-dressing applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:2845-2855.
[57] JIN SG, KIM KS, KIM DW, et al. Development of a novel sodium fusidate-loaded triple polymer hydrogel wound dressing: Mechanical properties and effects on wound repair. Int J Pharm. 2016;497(1-2):114-122.
[58] ZMEJKOSKI D, SPASOJEVIĆ D, ORLOVSKA I, et al. Bacterial cellulose-lignin composite hydrogel as a promising agent in chronic wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118(Pt A):494-503.
[59] DIMATTEO R, DARLING NJ , SEGURA T. In situ forming injectable hydrogels for drug delivery and wound repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;127:167-184.
[60] BURDICK JA, MAUCK RL, GERECHT S. To Serve and Protect: Hydrogels to Improve Stem Cell-Based Therapies. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;18(1):13-15.
|