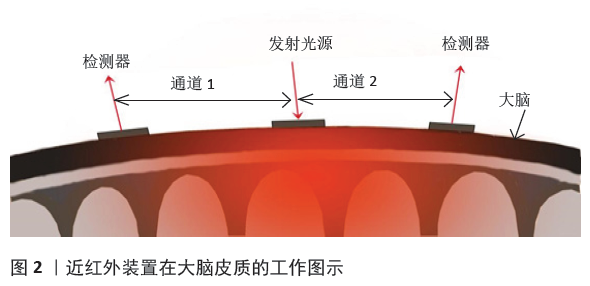
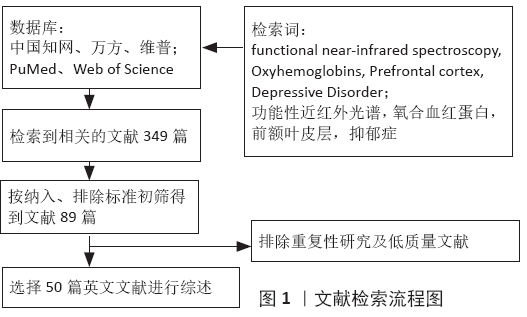
[1] CHOU PH, HUANG CJ, SUN CW, et al. The Potential Role of Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy as Clinical Biomarkers in Schizophrenia. Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(2):201-217.
[2] SAKATANI K, FUJII M, TAKEMURA N, et al. Effects of Acupuncture on Anxiety Levels and Prefrontal Cortex Activity Measured by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy: A Pilot Study. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;876:297-302.
[3] HUSAIN SF, TANG TB, YU R, et al. Cortical haemodynamic response measured by functional near infrared spectroscopy during a verbal fluency task in patients with major depression and borderline personality disorder. EBioMedicine. 2020;51:102586.
[4] OKADA F, TAKAHASHI N, TOKUMITSU Y, et al. Dominance of the ‘nondominant’ hemisphere in depression.J Affect Disord. 1996;37(1): 13-21.
[5] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[6] SOLOMON DA, KELLER MB, LEON AC, et al. Multiple recurrences of major depressive disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157(2):229-233.
[7] KESSLER RC, BERGLUND P, DEMLER O, et al. The epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication.JAMA. 2003;289(23):3095-3105.
[8] CUI X, BRAY S, BRYANT DM, et al. A quantitative comparison of NIRS and fMRI across multiple cognitive tasks. Neuroimage. 2011,54(4):2808-2821.
[9] KENNAN RP, KIM D, MAKI A, et al. Non-invasive assessment of language lateralization by transcranial near infrared optical topography and functionalMRI. Hum Brain Mapp. 2002;16(3):183-189.
[10] SCHECKLMANN M, EHLIS AC, PLICHTA M, et al. Altered frontal brain oxygenation in detoxified alcohol dependent patients with unaffected verbal fluency performance.Psychiat Res-neuroim. 2007;156(2): 129-138.
[11] ZANINOTTO L, SOLMI M, VERONESE NA, et al. meta-analysis of cognitive performance in melancholic versus non-melancholic unipolar depression.J Affect Disord.2016;201:15-24.
[12] ISMAIL Z, ELBAYOUMI H, FISCHER CE, et al. Prevalence of Depression in Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(1):58-67.
[13] ZHANG FF, PENG W, SWEENEY JA, et al. Brain structure alterations in depression: Psychoradiological evidence.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018; 24(11):994-1003.
[14] BEDNY M, HULBERT JC, THOMPSON-SCHILL SL, et al. Understanding words in context: the role of Broca’s area in word comprehension. Brain Res. 2007;1146:101-114.
[15] SIEGLE GJ, STEINHAUER SR, THASE ME, et al. Can’t shake that feeling: fMR assessment of sustained amygdala activity in response to emotional information in depressed individuals. Biol Psychiatry. 2002; 51(9):693-707.
[16] RAVNKILDE B, VIDEBECH P, ROSENBERG R, et al. Putative tests of frontal lobe function: a PET-study of brain activation during Stroop’s test and verbal fluency.J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2002;24(4):534-547.
[17] SUTO T, FUKUDA M, ITO M, et al. Multichannel near-infrared spectroscopy in depression and schizophrenia: cognitive brain activation study. Biol Psychiatry. 2004;55(5):501-511.
[18] KLUMPP H, DELDIN P. Review of brain functioning in depression for semantic processing and verbal fluency.Int J Psychophysiol. 2010;75(2): 77-85.
[19] OHTA H, YAMAGATA B, TOMIOKA H, et al. Hypofrontality in panic disorder and major depressive disorder assessed by multi-channel near-infrared spectroscopy. Depress. Anxiety. 2008;25(12):1053-1059.
[20] OKADA G, OKAMOTO Y, YAMASHITA H, et al. Attenuated prefrontal activation during a verbal fluency task in remitted major depression. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009;63(3):423-425.
[21] AKIYAMA T, KOEDA M, OKUBO Y, et al. Hypofunction of left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in depression during verbal fluency task: A multi-channel near-infrared spectroscopy study.J Affect Disord. 2018;231: 83-90.
[22] ROSE EJ, EBMEIER KP. Pattern of impaired working memory during major depression.J Affect Disord.2006;90(2-3):149-161.
[23] HARVEY PO, LE BASTARD G, POCHON JB, et al. Executive functions and updating of the contents of working memory in unipolar depression.J Psychiatr Res. 2004;38(6):567-576.
[24] HARVEY PO, FOSSATI P, POCHON JB, et al. Cognitive control and brain resources in major depression: an fMRI study using the n-back task. Neuroimage.2005;26:860-869.
[25] VASIC N, WALTER H, SAMBATARO F, et al. Aberrant functional connectivity of dorsolateral prefrontal and cingulate networks in patients with major depression during working memory processing.Psychol Med. 2009;39:977-987.
[26] WALTER H, VASIC N, HOSE A, et al. Working memory dysfunction in schizophrenia compared to healthy controls and patients with depression: evidence from event-related fMRI. Neuroimage. 2007; 35(4):1551-1561.
[27] SCHECKLMANN M, DRESLER T, BECK S, et al. Reduced prefrontal oxygenation during object and spatial visual working memory in unpolar and bipolar depression.Psychiatry Res. 2011;194(3):378-384.
[28] PU S, YAMADA T, YOKOYAMA K, et al. A multi-channel near-infrared spectroscopy study of prefrontal cortex activation during working memory task in major depressive disorder.Neurosci Res. 2011;70(1):91-97.
[29] MATSUO K, GLAHN DC, PELUSO MA, et al. Prefrontal hyperactivation during working memory task in untreated individuals with majordepressive disorder.Mol Psychiatry. 2007;12(2):158-166.
[30] FITZGERALD PB, SRITHIRAN A, BENITEZ J, et al. An fMRI study of prefrontal brain activation during multiple tasks in patients with majordepressive disorder. Hum Brain Mapp. 2008;29(4):490-501.
[31] WALSH ND, WILLIAMS SC, BRAMMER MJ, et al. A longitudinal functional magnetic resonance imaging study of verbal working memory in depression after antidepressant therapy. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;62(11):1236-1243.
[32] DAMASIO AR, GRABOWSKI TJ, BECHARA A, et al. Subcortical and cortical brain activity during the feeling of self-generated emotions.Nat Neurosci. 2000;3(10):1049-1056.
[33] YANG H, ZHOU Z, LIU Y, et al. Gender difference in hemodynamic responses of prefrontal area to emotional stress by near-infrared spectroscopy. Behav Brain Res. 2007;178(1):172-176.
[34] GLOTZBACH E, MÜHLBERGER A, GSCHWENDTNER K, et al. Prefrontal Brain Activation During Emotional Processing: A Functional Near Infrared Spectroscopy Study (fNIRS).Open Neuroimag J. 2011;5:33-39.
[35] MANELIS A, HUPPERT TJ, RODGERS E, et al. The role of the right prefrontal cortex in recognition of facial emotional expressions in depressedindividuals: fNIRS study.J Affect Disord.2019;258:151-158.
[36] OHAYON MM. Prevalence and correlates of nonrestorative sleep complaints. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(1):35-41.
[37] LI SX, LAM SP, CHAN JW, et al. Residual sleep disturbances in patients remitted from major depressive disorder: a 4-yearnaturalistic follow-up study. Sleep. 2012;35(8):1153-1161.
[38] SUDA M, SATO T, KAMEYAMA M, et al. Decreased cortical reactivity underlies subjective daytime light sleepiness in healthy subjects: a multichannel near-infrared spectroscopy study. Neurosci Res. 2008; 60(3):319-326.
[39] NISHIDA M, KIKUCHI S, MATSUMOTO K, et al. Sleep complaints are associated with reduced left prefrontal activation during a verbal fluencytask in patients with major depression: A multi-channel near-infrared spectroscopy study. J Affect Disord. 2017;207:102-109.
[40] MARZUK PM, HARTWELL N, LEON AC, et al. Executive functioning in depressed patients with suicidal ideation.Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2005; 112(4):294-301.
[41] PU S, NAKAGOME K, YAMADA T, et al. Suicidal ideation is associated with reduced prefrontal activation during a verbal fluency task in patients with major depressive disorder.J Affect Disord. 2015;181:9-17.
[42] BAIK SY, KIM JY, CHOI J, et al. Prefrontal Asymmetry during Cognitive Tasks and its Relationship with Suicide Ideation in Major Depressive Disorder: An fNIRS Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2019;9(4).pii: E193.
[43] KAMEYAMA M, FUKUDA M, YAMAGISHI Y, et al. Frontal lobe function in bipolar disorder: a multichannel near-infrared spectroscopy study.Neuroimage.2006;29(1):172-184.
[44] TAKIZAWA R, FUKUDA M, KAWASAKI S, et al. Neuroimaging-aided differential diagnosis of the depressive state.Neuroimage. 2014;85 Pt 1: 498-507.
[45] KINOU M, TAKIZAWA R, MARUMO K, et al. Differential spatiotemporal characteristics of the prefrontal hemodynamic response and their association with functional impairment in schizophrenia and major depression. Schizoph Res. 2013;150(2-3): 459-467.
[46] HUSAIN SF, TANG TB, YU R, et al. Cortical haemodynamic response measured by functional near infrared spectroscopy during a verbal fluency task in patients with major depression and borderline personality disorder. EBioMedicine. 2020;51:102586.
[47] ESCHWEILER GW, WEGERER C, SCHLOTTER W, et al. Left prefrontal activation predicts therapeutic effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in major depression.Psychiatry Res. 2000; 99(3):161-172.
[48] CURTIN A, TONG S, SUN J, et al. A Systematic Review of Integrated Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS) and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Studies.Front Neurosci. 2019;28;13:84.
[49] SHINBA T, KARIYA N, MATSUDA S, et al. Increase of frontal cerebral blood volume during transcranial magnetic stimulation in depressionis related to treatment effectiveness: A pilot study with near-infrared spectroscopy.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2018;72(8):602-610.
[50] LI H, ZHU N, KLOMPARENS EA, et al. Application of functional near-infrared spectroscopy to explore the neural mechanism of transcranial direct current stimulation for post-stroke depression.Neurol Res. 2019; 41(8):714-721.
|