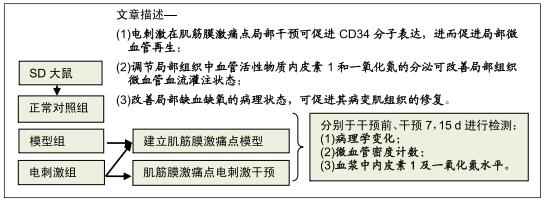
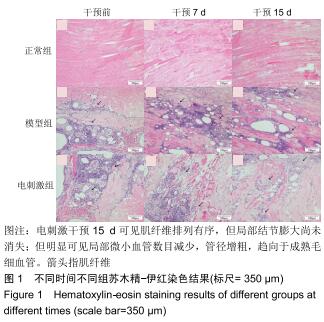
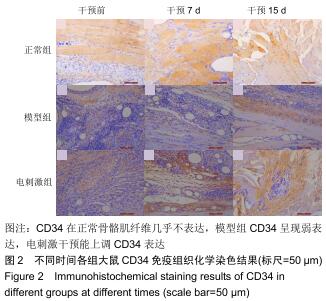
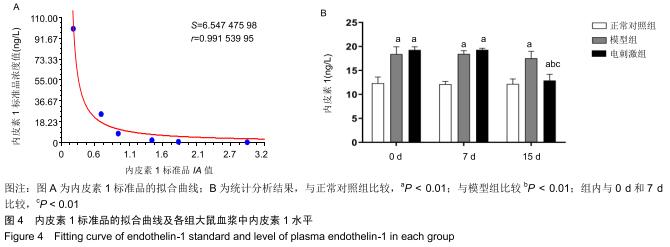
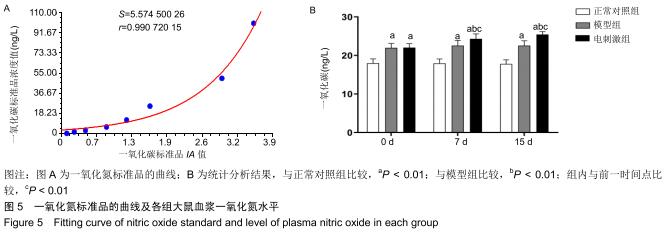
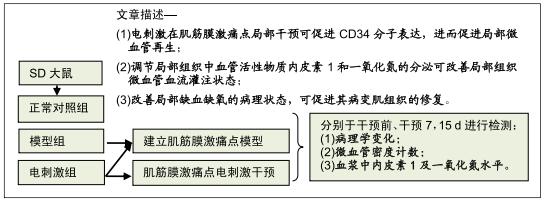
|
[1] MONEY S. Pathophysiology of Trigger Points in Myofascial Pain Syndrome.J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2017; 31(2):158-159.
[2] JUNBEOM K, HYOUNG SEOP K, WON HYUK C, et al. Characteristics of Myofascial pain syndro-me of the Infraspinatus Muscle.Ann Rehabil Med. 2017;41(4):573-581.
[3] GIAMBERARDINO MA, AFFAITATI G, FABRIZIO A, et al. Myofascial pain syndromes and their eval- uation. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011;25(2):185-198.
[4] CEREZO-TÉLLEZ E, TORRES-LACOMBA M, MAYORAL-DEL MORAL O, et al.Prevalence of Myofascial Pain Syndrome in Chronic Non-Specific Neck Pain: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study.Pain Med. 2016;17(12):2369-2377.
[5] GILHEANEY Ó, STASSEN LF, WALSHE M. Prevalence, Nature, and Management of Oral Stage Dysphagia in Adults With Temporomandibular Joint Disorders: Findings From an Irish Cohort.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018; S0278-2391(18) 30117-30124.
[6] NAZERI M, GHAHRECHAHI HR, POURZARE A, et al. Role of anxiety and depression in association with migraine and myofascial paintemporomandibular disorder.Indian J Dent Res.2018;29(5):583-587.
[7] LAVELLE ED, LAVELLE W, SMITH HS. Myofascial trigger points.Anesthesiol Clin.2007;25(4):841-851.
[8] SIMONS DG, TRAVELL JG. Myofascial trigger points,a possible explanation.Pain.1981;10(1):106-109.
[9] JEONG GJ, OH JY, KIM YJ, et al. Therapeutic Angiogenesis via Solar Cell-Facilitated Electric-al Stimulation.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2017;9(44):38344-38355.
[10] FRACCALVIERI M, SALOMONE M, DI SANTO C, et al. Quantum molecular resonance technology in hard-to-heal extremity wounds: histological and clinical results.Int Wound J.2017;14(6):1313-1322.
[11] SAHIN N, ALBAYRAK I, UGURLU H. Effect of Different Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation Modalities on Cervical Myofascial Pain Syndrome.J musculoskelet pain. 2011;19(1): 18-23.
[12] HUANG QM, LV JJ, RUANSHI QM, et al.Spontaneous electrical activities at myofascial trigger points at different stages of recovery from injury in a rat model.Acupunct Med. 2015;33(4):319-324.
[13] PAN B, ZHANG Z, CHAO D, et al. Dorsal Root Ganglion Field Stimulation Prevents Inflamma-tion and Joint Damage in a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Neuromodulation.2018; 21(3):247-253.
[14] PEREIRA T, DODAL S, TAMGADGE A, et al. Quantitative evaluation of microvessel density using CD34 in clinical variants of ameloblastoma: An immunohistochemical study.J Oral Maxil-lofac Pathol.2016;20(1):51-58.
[15] POWERS JENNIFER L, RIPPE KAREN DUDA, IMARHIA KELLY, et al. A Direct,Competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) as a Quantitative Technique for Small Molecules.Journal of Chemical Education.2012; 89(12):1587-1590.
[16] GERWIN RD.Myofascial Trigger Point Pain Syndromes. Seminars in Neurology.2016;36 (6): 469-473.
[17] 温干军,刘红,陈坚,等.温针对肌筋膜痛扳机点模型大鼠病理形态及致痛性炎性介质的影响[J].中国骨伤,2019,32(3):260-264.
[18] DOMMERHOLT J, FINNEGAN M, GRIEVE R, et al. A critical overview of the current myofascial pain literature-January 2016.J Bodyw Mov Ther.2016;20(1):156-167.
[19] SUZUKI S, CASTRILLON EE, ARIMA T, et al. Blood oxygenation of masseter muscle during sustai- ned elevated muscle activity in healthy participants.J Oral Rehabil.2016; 43(12):900-910.
[20] 景亚军,陈美雄,曹磊,等.温和灸对肌筋膜激痛点TGF-β1/Smad4表达的影响[J].中华中医药学刊, 2018,36(12): 3019-3022+ 3110-3112.
[21] BENGTSSON A, HENRIKSSON K, LARSSON J. Muscle biopsy in fibromyalgia:Light microscopical and histochemical findings.Scand J Rheumatol.1986;15:1-6.
[22] 杨初燕,王亮,冯珍,等.正中神经电刺激对脑外伤后昏迷患者促醒作用的临床及机制研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016,31(11): 1195-1199,1207.
[23] 李伟麒,郑磊,王前,等.脉冲电刺激对血管内皮细胞与其祖细胞黏附的影响[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2011,28(4):689-693+697.
[24] ASADI MR, TORKAMAN G, HEDAYATI M, et al. Angiogenic effects of low-intensity cathodal direct current on ischemic diabetic foot ulcers: A randomized controlled trial.Diabetes Res Clin Pract.2017;127:147-155.
[25] PAILLARD T. Muscle plasticity of aged subjects in response to electrical stimulation training and inversion and/or limitation of the sarcopenic process.Ageing Res Rev.2018;6(46):1-13.
[26] YARNITSKY D, VOLOKH L, IRONI A, et al. Nonpainful remote electrical stimulation alleviates episodic migraine pain. Neurology.2017;88(13):1250-1255.
[27] JOO MC, JANG CH, PARK JT, et al. Effect of electrical stimulation on neural regeneration via the p38-RhoA and ERK1/2-Bcl-2 pathways in spinal cord-injured rats.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(2):340-346.
[28] SEGATELLI V, DE OLIVEIRA EC, BOIN IF, et al. Evaluation and comparison of microvessel density using the markers CD34 and CD105 in regenerative nodules, dysplastic nodules and hepato-cellular carcinoma.Hepatol Int.2014;8(2):260-265.
[29] SIDNEY LE, BRANCH MJ, DUNPHY SE, et al. Concise Review: Evidence for CD34 as a Commo-n Marker for Diverse Progenitors.Stem cells.2014;32(6):1380-1389.
[30] 唐智,孙瑾,王继群,等.鼻腔鼻窦鳞状细胞癌中以CD34标记微血管密度的测定[J].广东医学,2013,34(22):3443-3445.
[31] BUJOR IS, CIOCA A, CEAUȘU RA, et al. Evaluation of Vascular Proliferation in Molecular Subt-ypes of Breast Cancer. In Vivo.2018;32(1):79-83.
[32] HOUDE M, DESBIENS L, D'ORLÉANS-JUSTE P. Endothelin: an endothelium-derived Endothelin-1: Biosynthesis, Signaling and Vasoreactivity.Adv Pharmacol.2016;77:143-175.
[33] 张向阳,加娜提,爱华.高同型半胱氨酸血症大鼠血浆一氧化氮和内皮素1水平的变化:血管内皮功能损伤验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(41):8242-8246.
[34] MUNDUGARU R, SIVANESAN S, POPA-WAGNER A, et al. Pluchea lanceolata protects hippocampal neurons from endothelin-1 induced ischemic injury to ameliorate cognitive deficits.J Chem Neuroanat. 2018;94(4):75-85.
[35] PALOMARES SM, CIPOLLA MJ. Myogenic tone as a therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2014;12(6):788-800.
[36] 陈芳,王丽,朱中玉,等.内皮素1及其受体在心血管疾病中作用的研究进展[J].中国全科医学.2013,16(32):3149-3151.
[37] DAI P, HUANG H, ZHANG L, et al. A pilot study on transient ischemic stroke induced with endothelin-1 in the rhesus monkeys. Sci Rep.2017;30(7):45097.
[38] ST RAMMOS K, KOULLIAS GJ, HATZIBOUGIAS JD, et al. Plasma endothelin-1 levels in adult patie-nts undergoing coronary revascularization.Cardiovasc Surg. 1996;4(6): 808-812.
[39] LEO CH, JELINIC M, NG HH, et al. Vascular actions of relaxin: nitric oxide and beyond.Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(10): 1002-1014.
[40] WATKINS DJ, BESNER GE. The role of the intestinal microcirculation in necrotizing enterocoli-tis.Semin Pediatr Surg.2013;22(2):83-87.
[41] 单剑萍,季刚.不同血液净化方式对慢性肾功能衰竭尿毒症患者血管活性物质的影响[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2015,29(5): 481-483.
[42] FARAHINI H, AJAMI M, MIRZAY RAZAZ J, et al. Nitric Oxide is Necessary for Diazoxide Protection Against Ischemic Injury in Skeletal Muscle. Iran J Pharm Res. 2012;11(1):375-381.
|