中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (26): 4169-4175.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2764
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
电针刺激脊髓损伤大鼠足阳明胃经脊髓受损节段Bax、Bcl-2的mRNA和蛋白的表达
吴 凡1,许 权1,周宾宾2,魏卫兵3,王 珠1,严潮浪1
1江西中医药大学附属医院,江西省南昌市 330000;2广西中医药大学第一附属医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530000;3柳州市中医医院,广西壮族自治区柳州市 545000
Electroacupuncture stimulation of Foot-Yangming Stomach Meridian regulates mRNA and protein expression of Bax and Bcl-2 in spinal cord injury rats
Wu Fan1, Xu Quan1, Zhou Binbin2, Wei Weibing3, Wang Zhu1, Yan Chaolang1
1Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330000, Jiangxi Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Liuzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Liuzhou 545000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
脊髓损伤大鼠模型:用于研究脊髓损伤而制作的大鼠模型,良好的动物模型是实验成功的重要基础,经过不断的研究发展,其造模方法也多种多样,包括钳夹法、打击法、半横切法、完全横切法等,各种方法在稳定性及死亡率方面各有优劣,研究者应当根据自身需求选择合适的造模方式。
细胞凋亡:是细胞的一种基本生物学现象,在多细胞生物去除不需要的或异常的细胞中起着必要的作用。凋亡是多基因严格控制的过程,当脊髓损伤发生时,Bcl-2家族、caspase家族等开始发生调控作用。
背景:中医自《内经》开始就提出了“治痿独取阳明”之理论,但是有关电针干预足阳明胃经治疗脊髓损伤的报道相对较少,该课题研究从细胞凋亡因子Bax、Bcl-2的角度出发,初步探讨电针干预足阳明胃经对脊髓损伤神经修复的相关机制。
目的:探讨电针刺激足阳明胃经对脊髓损伤大鼠受损节段Bax、Bcl-2表达的影响。
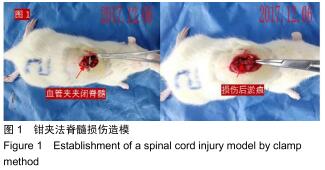
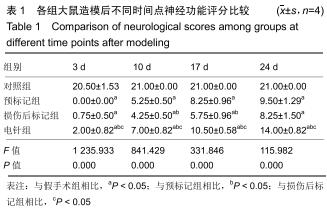
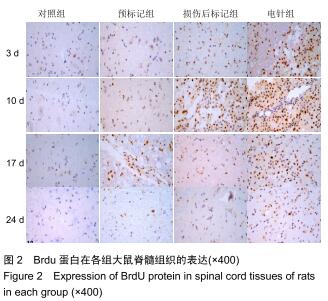
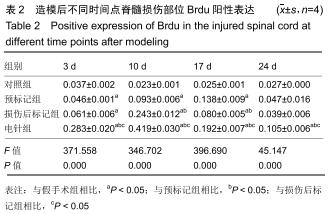
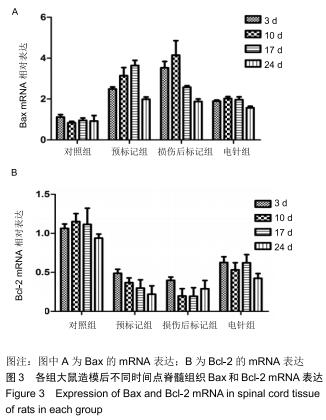
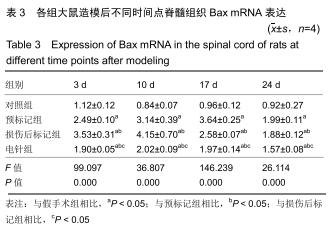
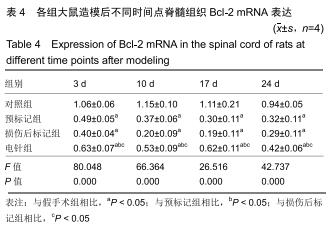
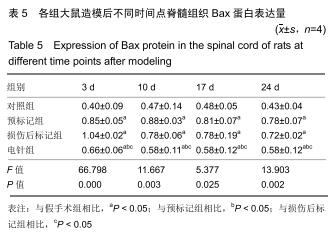
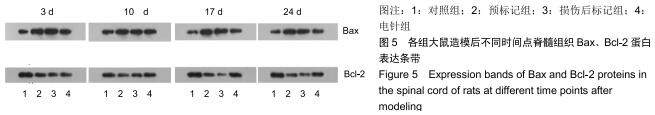
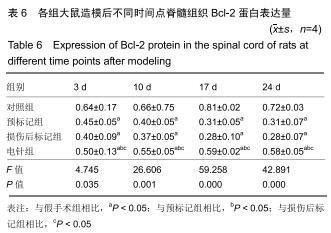
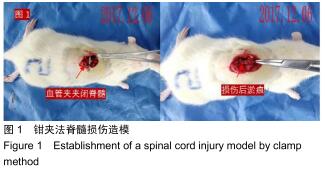
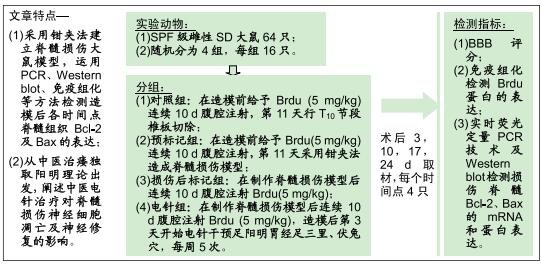
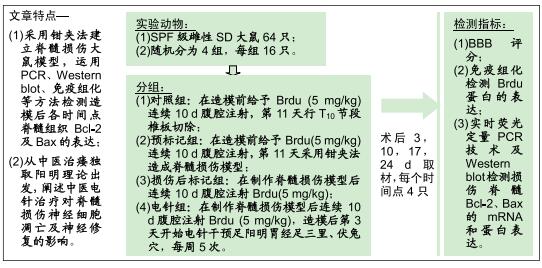
方法:将64只SPF级SD雌性大鼠随机分为4组:对照组、预标记组、损伤后标记组和电针组,每组16只。对照组及预标记组在操作前给予Brdu(5 mg/kg)连续10 d腹腔注射,以标记脊髓内保持分化活力的细胞,对照组于第11天行T10节段椎板切除,预标记组于第11天采用钳夹法造成脊髓损伤缺血模型;损伤后标记组、电针组在制作脊髓损伤模型后连续10 d腹腔注射Brdu(5 mg/kg)标记损伤后活化增殖的细胞,电针组于造模后第3天开始电针干预足阳明胃经足三里、伏兔穴,每周5次。造模后3,10,17,24 d(电针0,7,14,21 d),每个时间点取4只大鼠,采用BBB评分评估运动功能恢复情况,qRT-PCR和Western blot检测脊髓组织Bax、Bcl-2 mRNA及蛋白的表达。
结果与结论:①术后3-24 d时,预标记组、损伤后标记组、电针组大鼠神经功能评分低于对照组,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),电针组神经功能评分高于预标记组、损伤后标记组,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②随着脊髓损伤时间的延长,Bax mRNA及蛋白表达先升高后降低,Bcl-2 mRNA及蛋白表达先降低后升高,Bax/Bcl-2比值随着电针干预时间的推移逐渐减少;③结果表明,电针刺激足阳明胃经可以通过调节Bcl-2、Bax的表达减少神经细胞凋亡,促进脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能的恢复。
ORCID: 0000-0001-6069-4997(魏卫兵)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: