[1]吕一帆.同步电刺激与交替电刺激训练对力量的影响[D].北京:北京体育大学,2019.
[2]MILLER C, THÉPAUT-MATHIEU C. Strength training by electrostimulation conditions for efficacy. Int J Sports Med. 1993;14(1):20-28.
[3]VITENZON AS, BUROVOĬ AM. Method and construction of programmed electric muscle stimulation in gait disorders.Med Tekh. 2002;(1):14-19.
[4]王保成,杨汉雄.竞技体育力量训练指导[M].人民体育出版社, 2001:1-300.
[5]宋德海,巢晓春.力量训练方式发展研究[J].山东体育科技,2011, 33(4):8-12.
[6]周欣星. SEMG和NMES仪的设计及对肌肉的强化效果研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2014.
[7]FUKASAWA Y, OHNO N, SAITOH Y, et al. Immunohistochemical and morphofunctional studies of skeletal muscle tissues with electric nerve stimulation by in vivo cryotechnique.Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2015;48(2): 27-36.
[8]黄志刚,周里,王煜,等.电刺激训练前后肌肉力量交叉迁移效果的实验观察[J].中国运动医学杂志,2002,21(2):203-205.
[9]王丽,梁潇.电刺激影响力量增长与退化的轨迹[J].武汉体育学院学报,2013,47(10):59-62.
[10]杨斌.不同强度电刺激对足球运动员专项力量的影响[J].唐山师范学院学报,2017,39(5): 89-92.
[11]张海潮,潘浩.电刺激对肌肉力量作用的研究分析[J].北京体育大学学报,2001,24(2):189-190+196.
[12]唐涌,曹云.电刺激训练对散打运动员下肢力量及鞭腿影响的实验研究[J].武汉体育学院学报,2015,49(2):90-94.
[13]周思红,张海潮.电刺激方法对武术运动员反应速度和肌肉力量的实验研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2004,27(12):1647-1648+ 1683.
[14]杨华元,刘堂义,蒯乐,等.穴位电刺激增强运动员快速力量的作用观察[J].中国针灸,2006,26(5):313-315.
[15]PANTOVIĆ M, POPOVIĆ B, MADIĆ D, et al. Effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation and resistance training on knee extensor/flexor muscles.Coll Antropol. 2015;39 Suppl 1:153-157.
[16]MARTÍNEZ-LÓPEZ EJ, BENITO-MARTÍNEZ E, HITA-CONTRERAS F, et al. Effects of electrostimulation and plyometric training program combination on jump height in teenage athletes.J Sports Sci Med. 2012;11(4):727-735.
[17]DELEY G, COMETTI C, FATNASSI A, et al. Effects of combined electromyostimulation and gymnastics training in prepubertal girls.J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(2):520-526.
[18]BILLOT M, MARTIN A, PAIZIS C, et al. Effects of an electrostimulation training program on strength, jumping, and kicking capacities in soccer players.J Strength Cond Res. 2010;24(5):1407-1413.
[19]OLIVEIRA P, MODESTO KAG, BOTTARO M, et al. Training Effects of Alternated and Pulsed Currents on the Quadriceps Muscles of Athletes.Int J Sports Med. 2018;39(7):535-540.
[20]HERRERO JA, IZQUIERDO M, MAFFIULETTI NA, et al. Electromyostimulation and plyometric training effects on jumping and sprint time.Int J Sports Med. 2006;27(7): 533-539.
[21]GIROLD S, JALAB C, BERNARD O, et al. Dry-land strength training vs. electrical stimulation in sprint swimming performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26(2):497-505.
[22]PAILLARD T, NOE F, BERNARD N, et al. Effects of two types of neuromuscular electrical stimulation training on vertical jump performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2008;22(4): 1273-1278.
[23]GONDIN J, GUETTE M, BALLAY Y, et al. Neural and muscular changes to detraining after electrostimulation training.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006;97(2):165-173.
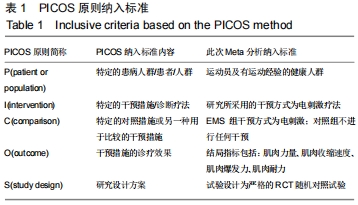
[24]李雪迎.Meta分析研究设计中的PICOS原则[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2016,24(11):611.
[25]HIGGINS JPT,GREEN S.Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 5.2.0. http://www.cochrane.org/resources/handbook/hbook.htm (accessed June 2017).
[26]刘关键,吴泰相.Meta-分析的森林图及临床意义[J].中国循证医学杂志,2004(03):198-201.
[27]SILVA AB, SOUSA N, AZEVEDO LF, et al. Physical activity and exercise for erectile dysfunction: systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Sports Med.2017;51(19): 1419-1424.
[28]THOMPSON SG, SHARP SJ. Explaining heterogeneity in meta-analysis: a comparison of methods.Stat Med. 1999; 18(20):2693-2708.
[29]王丹,牟振云,翟俊霞,等.Stata软件在Meta-分析发表性偏倚识别中的探讨[J].现代预防医学,2008,35(15):2819-2822.
[30]杜承润,史衍.肌肉电刺激训练研究综述[J].运动,2018(1): 26-27+46.
[31]鲁建清,常永玲,黎冬.电刺激增强肌肉力量的机制及应用[J].湘南学院学报,2011,32(2):116-119.
[32]OVERDUIN SA, D’AVELLA A, CARMENA JM, et al. Microstimulation activates a handful of muscle synergies. Neuron.2012;76(6):1071-1077.
[33]HEIDLAND A, FAZELI G, KLASSEN A, et al.Neuromuscular electrostimulation techniques: historical aspects and current possibilities in treatment of pain and muscle waisting. Clin Nephrol.2013; 79(Suppl 1): S12-S23.
[34]OGASAWARA R, KOBAYASHI K, TSUTAKI A, et al. mTOR signaling response to resistance exercise is altered by chronic resistance training and detraining in skeletal muscle.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013;114(7):934-940.
[35]FUKAZAWA T, MATSUMOTO M, IMURA T, et al. Electrical stimulation accelerates neuromuscular junction formation through ADAM19/neuregulin/ErbB signaling in vitro.Neurosci lett.2013;545: 29-34.
[36]曾宪涛,李胜,马钻,等.Meta分析系列之八:Meta分析的报告规范[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(6):500-503.
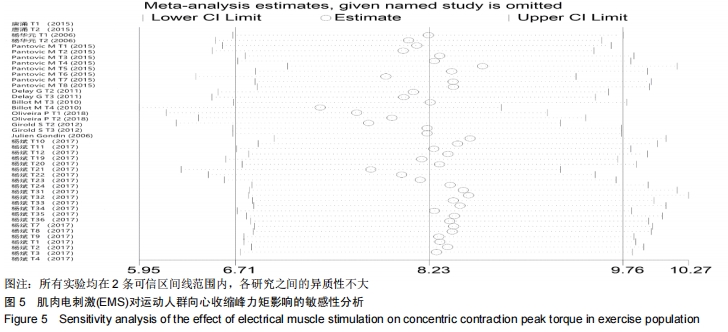
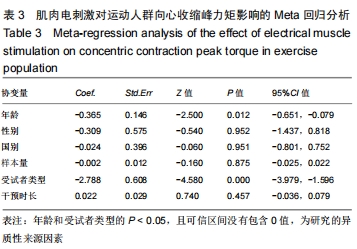
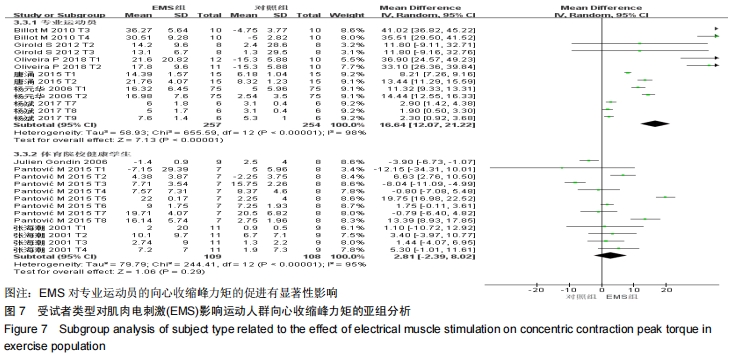
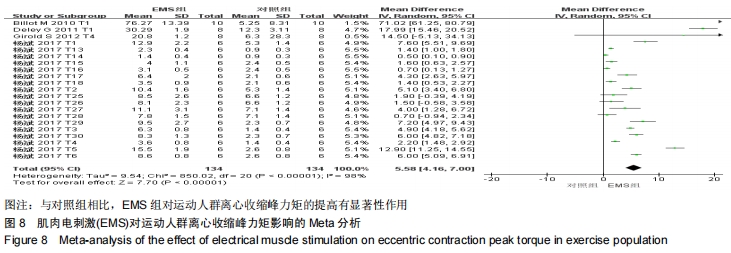
|