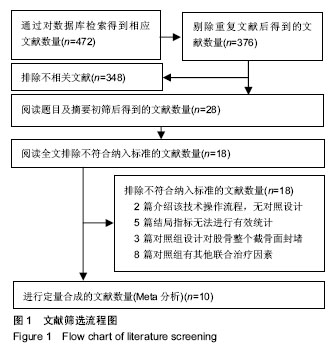
| [1] Yamaguchi S, Ohno G, Kitamura J. Evaluation of perioperative blood loss and transfusion in total knee arthroplasty. Masui. 2014; 63:1029-1033. [2] Ma J, Huang Z, Shen B, et al. Blood management of staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty in a single hospitalization period. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;9(1):116. [3] Spahn DR. Anemia and patient blood management in hip and knee surgery: a systematic review of the literature. Anesthesiology. 2010;113(2):482-495. [4] 董翠翠,贺付成.局部应用和静脉注射氨甲环酸对全膝关节置换术术后出血影响的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(22): 2070-2074.[5] 万伏银,郭万首,程立明,等.局部应用骨蜡和氨甲环酸在全膝关节置换术中止血作用的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24(3):193-197.[6] Eubanks JD. Antifibrinolytics in major orthopaedic surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(3):132-138. [7] Maniar RN, Kumar G, Singhi T, et al. Most effective regimen of tranexamic acid in knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled study in 240 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470(9):2605-2612. [8] Zhang H, Chen J, Chen F, et al. The effect of tranexamic acid on blood loss and use of blood products in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012; 20(9): 1742-1752. [9] Roy SP, Tanki UF, Dutta A, et al. Efficacy of intra-articular tranexamic acid in blood loss reduction following primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(12):2494-2501. [10] Thienpont E. Faster recovery after minimally invasive surgery in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10):2412-2417. [11] Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5. 1. 0. the cochrane collaboration. 2011; 17(4):535. [12] Li X, Qi XB, Han X, et al. Effects of sealing the intramedullary femoral canal in total knee arthroplasty: A randomized study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(29):e7388. [13] 陈先进,张道平,程后庆,等.股骨髓内定位孔填塞技术在全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(8):893.[14] 胡飞,尚希福,朱亚林,等.股骨髓内定位通道嵌压植骨减少全膝置换术后出血的前瞻性研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24(17): 1566-1569.[15] Batmaz AG, Kayaalp ME, Oto O, et al. Sealing of femoral tunnel with autologous bone graft decreases blood loss. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2016;83(5):348-350. [16] 宋志勇,王明礼,郭得辛,等.中老年患者膝关节表面置换术中股骨髓内定位孔封堵对术后失血量的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2015,35(17): 4997-4998.[17] 接健,陈福扬,徐国浩,等.髓内定位孔骨塞对全膝关节置换术中出血综合控制作用的对照研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015,30(10): 1049-1051.[18] Torres-Claramunt R, Hinarejos P, Pérez-Prieto D, et al. Sealing of the intramedullar femoral canal in a TKA does not reduce postoperative blood loss: a randomized prospective study. Knee. 2014;21(4):853-857. [19] Protzman NM,Buck NJ,Weiss CB. Autologous bone plugs in unilateral total knee arthroplasty. Indian J Orthop. 2013;47(2):182-187. [20] Ko PS, Tio MK, Tang YK, et al. Sealing the intramedullary femoral canal with autologous bone plug in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(1):6-9. [21] Kumar N, Saleh J, Gardiner E, et al. Plugging the intramedullary canal of the femur in total knee arthroplasty: reduction in postoperative blood loss. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(7):947-949. [22] Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86(4):561-565. [23] Teter KE, Bregman D, Colwell CW Jr. The efficacy of intramedullary femoral alignment in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;321:117-121. [24] 边焱焱,翁习生,林进,等.人工膝关节表面置换术中胫骨髓内与髓外定位的临床效果比较[J].中国医学科学院学报, 2015,37(4):373-377.[25] Klein MP, Rahn BA, Frigg R, et al. Reaming versus non-reaming in medullary nailing: interference with cortical circulation of the canine tibia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1990;109(6):314-316. [26] Moo IH, Chen JYQ, Pagkaliwaga EH, et al. Bone wax is effective in reducing blood loss after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(5):1483-1487[27] Vulcano E, Regazzola GM, Murena L, et al. Femoral bone plug in total knee replacement. Orthopedics. 2015;38(10):617-618. [28] K?ska R, Paradowski TP, Witoński D. Outcome in primary cemented total knee arthroplasty with or without drain: A prospective comparative study. Indian J Orthop. 2014;48(4): 404-409. [29] Cao L, Ablimit N, Mamtimin A, et al. Comparison of no drain or with a drain after unilateral total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009;18(47): 1390-1393. [30] Gross JB. Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology. 1983;58(3):277-280. [31] Thienpont E. Faster recovery after minimally invasive surgery in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10):2412-2417. [32] Roy SP, Tanki UF, Dutta A, et al. Efficacy of intra-articular tranexamic acid in blood loss reduction following primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(12):2494-2501. [33] Maniar RN, Kumar G, Singhi T, et al. Most effective regimen of tranexamic acid in knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled study in 240 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470(9):2605-2612. [34] Sarkanovi? ML, Gvozdenovi? L, Savi? D, et al. Autologous blood transfusion in total knee replacement surgery. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2013;70(3):274-278. [35] Thomassen BJ, den Hollander PH, Kaptijn HH, et al. Autologous wound drains have no effect on allogeneic blood transfusions in primary total hip and knee replacement: a three-arm randomised trial. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(6):765-771. [36] 余存泰,覃健,侯之启,等.全膝关节置换术隐性失血的初步研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2006,21(10):784-786. |
.jpg)
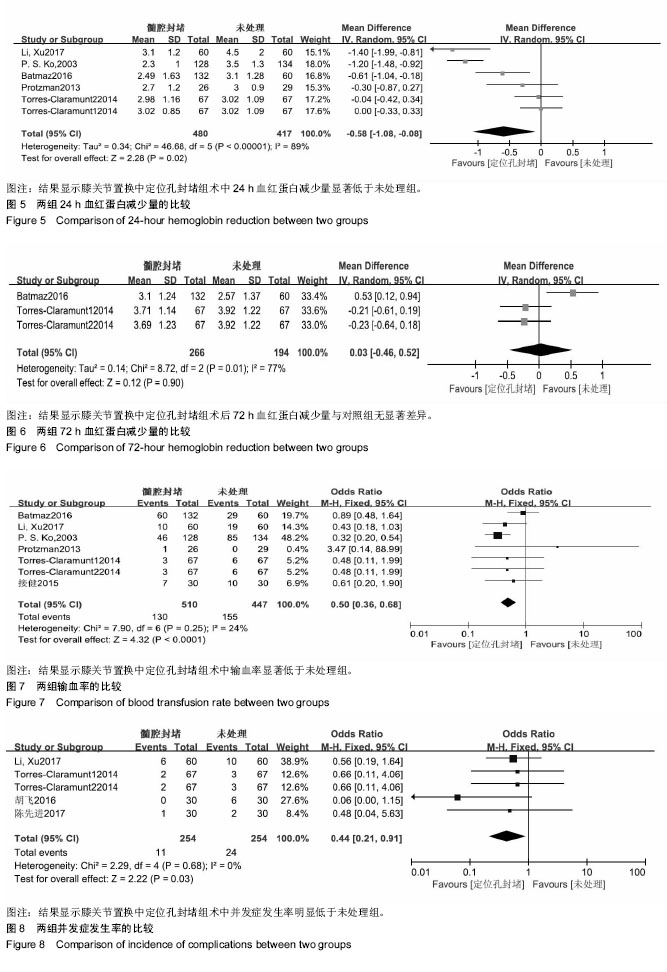
.jpg)