| [1] Doetsch F, Caillé I, Lim DA, et al. Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell. 1999;97(6):703-716. [2] Suh H, Deng W, Gage FH. Signaling in adult neurogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2009;25:253-275. [3] Trounson A, McDonald C. Stem Cell Therapies in Clinical Trials: Progress and Challenges. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17(1): 11-22. [4] Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(3):203-222. [5] Morgado AL, Xavier JM, Dionísio PA, et al. MicroRNA-34a Modulates Neural Stem Cell Differentiation by Regulating Expression of Synaptic and Autophagic Proteins. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;51(3):1168-1183. [6] Gioia U, Di Carlo V, Caramanica P, et al. Mir-23a and mir-125b regulate neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation by targeting Musashi1. RNA Biol. 2014;11(9):1105-1112. [7] Liu Z, Zhao R.Small regulators making big impacts: regulation of neural stem cells by small non-coding RNAs.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(3):397-398.[8] Ponomarev ED, Veremeyko T, Barteneva N, et al. MicroRNA- 124 promotes microglia quiescence and suppresses EAE by deactivating macrophages via the C/EBP-α-PU. 1 pathway. Nat Med. 2011;17(1):64-70. [9] Smirnova L, Gräfe A, Seiler A, et al. Regulation of miRNA expression during neural cell specification. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21(6):1469-1477. [10] Luo WW, Han Z, Ren DD,et al.Notch pathway inhibitor DAPT enhances Atoh1 activity to generate new hair cells in situ in rat cochleae.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(12):2092-2099.[11] Siebel C, Lendahl U. Notch Signaling in Development, Tissue Homeostasis, and Disease. Physiol Rev. 2017;97(4): 1235-1294. [12] Yoon K, Gaiano N. Notch signaling in the mammalian central nervous system: insights from mouse mutants. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(6):709-715. [13] Ge D, Song K, Guan S, et al. Culture and differentiation of rat neural stem/progenitor cells in a three-dimensional collagen scaffold. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2013;170(2):406-419. [14] Chen L, Qiu R, Li L, et al. The role of exogenous neural stem cells transplantation in cerebral ischemic stroke. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10(11):3219-3230. [15] Moon SU, Kim J, Bokara KK, et al. Carbon nanotubes impregnated with subventricular zone neural progenitor cells promotes recovery from stroke. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7: 2751-2765. [16] Ryu S, Lee SH, Kim SU,et al.Human neural stem cells promote proliferation of endogenous neural stem cells and enhance angiogenesis in ischemic rat brain.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(2):298-304.[17] Morgado AL, Rodrigues CM, Solá S. MicroRNA-145 Regulates Neural Stem Cell Differentiation Through the Sox2-Lin28/let-7 Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells. 2016;34(5): 1386-1395. [18] Shen Q, Jin H, Wang X. Epidermal stem cells and their epigenetic regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(9):17861-17880. [19] Zheng J, Yi D, Shi X, et al. miR-1297 regulates neural stem cell differentiation and viability through controlling Hes1 expression. Cell Prolif. 2017;50(4):e12347. [20] Shi X, Yan C, Liu B, et al. miR-381 Regulates Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation via Regulating Hes1 Expression. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0138973. [21] Jiao S, Liu Y, Yao Y, et al. miR-124 promotes proliferation and differentiation of neuronal stem cells through inactivating Notch pathway. Cell Biosci. 2017;7:68. [22] Louvi A, Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Notch signalling in vertebrate neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(2):93-102. [23] Ross SE, Greenberg ME, Stiles CD. Basic helix-loop-helix factors in cortical development. Neuron. 2003;39(1):13-25. [24] Kageyama R, Ohtsuka T, Shimojo H, et al. Dynamic Notch signaling in neural progenitor cells and a revised view of lateral inhibition. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11(11):1247-1251.[25] Geng X, Sun T, Li JH, et al.Electroacupuncture in the repair of spinal cord injury: inhibiting the Notch signaling pathway and promoting neural stem cell proliferation.Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(3):394-403. |
.jpg)
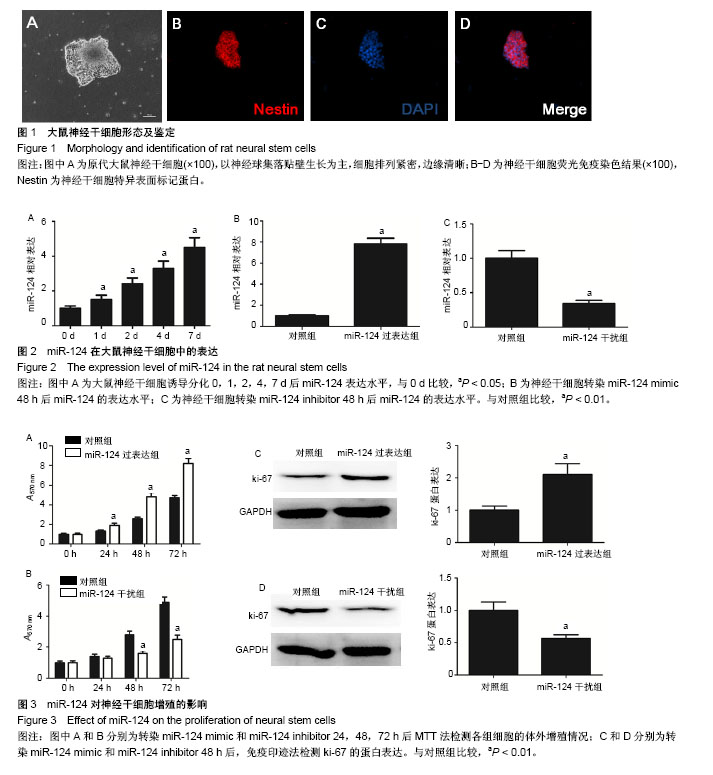
.jpg)
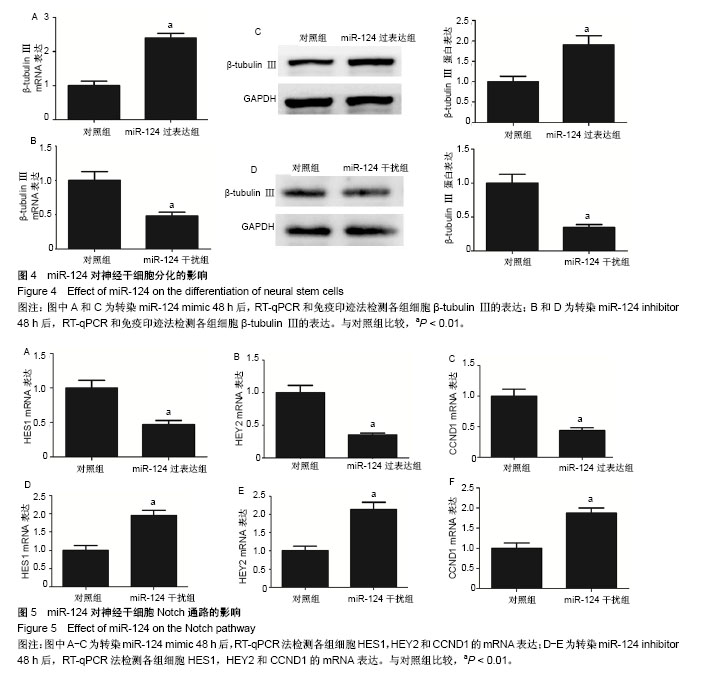
.jpg)