中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (28): 4434-4439.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0840
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
白细胞介素23受体基因多态性与广西壮族人群骨关节结核的易感性
吴昭元1,谢克恭2,陆 潞2,卢贤哲2,黄 可2,廖林波1,唐毓金2
- 1右江民族医学院研究生学院,广西壮族自治区百色市 533000; 2右江民族医学院附属医院脊柱骨病外科,广西壮族自治区百色市 533000
Polymorphisms of interleukin-23 receptor gene and susceptibility of bone and joint tuberculosis in Guangxi Zhuang populations
Wu Zhao-yuan1, Xie Ke-gong2, Lu Lu2, Lu Xian-zhe2, Huang Ke2, Liao Lin-bo1, Tang Yu-jin2
- 1Graduate School of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
基因多态性:多态性是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在2种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型或等位基因,亦称遗传多态性或基因多态性。从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域。对于一个体而言,基因多态性碱基顺序终生不变,并按孟德尔规律世代相传。
易感性:是指人和动物对某种人畜共患病病原体感染受性的大小,是指由遗传基础所决定的个体患病的风险。也可以理解为在相同环境下,不同个体患病的风险。易感性完全由基因决定,在环境致病因子作用下的基因表达往往起着更重要的作用。因为即使基因型一致,基因表达还会受到甲基化、体细胞突变、X染色体的随机失活等影响。
文题释义:
基因多态性:多态性是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在2种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型或等位基因,亦称遗传多态性或基因多态性。从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域。对于一个体而言,基因多态性碱基顺序终生不变,并按孟德尔规律世代相传。
易感性:是指人和动物对某种人畜共患病病原体感染受性的大小,是指由遗传基础所决定的个体患病的风险。也可以理解为在相同环境下,不同个体患病的风险。易感性完全由基因决定,在环境致病因子作用下的基因表达往往起着更重要的作用。因为即使基因型一致,基因表达还会受到甲基化、体细胞突变、X染色体的随机失活等影响。
.jpg) 文题释义:
基因多态性:多态性是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在2种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型或等位基因,亦称遗传多态性或基因多态性。从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域。对于一个体而言,基因多态性碱基顺序终生不变,并按孟德尔规律世代相传。
易感性:是指人和动物对某种人畜共患病病原体感染受性的大小,是指由遗传基础所决定的个体患病的风险。也可以理解为在相同环境下,不同个体患病的风险。易感性完全由基因决定,在环境致病因子作用下的基因表达往往起着更重要的作用。因为即使基因型一致,基因表达还会受到甲基化、体细胞突变、X染色体的随机失活等影响。
文题释义:
基因多态性:多态性是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在2种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型或等位基因,亦称遗传多态性或基因多态性。从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域。对于一个体而言,基因多态性碱基顺序终生不变,并按孟德尔规律世代相传。
易感性:是指人和动物对某种人畜共患病病原体感染受性的大小,是指由遗传基础所决定的个体患病的风险。也可以理解为在相同环境下,不同个体患病的风险。易感性完全由基因决定,在环境致病因子作用下的基因表达往往起着更重要的作用。因为即使基因型一致,基因表达还会受到甲基化、体细胞突变、X染色体的随机失活等影响。摘要
背景:广西壮族自治区是结核病的高发地域,大量研究证实结核病存在易感基因。
目的:分析白细胞介素23受体基因多态性及其与广西壮族人群骨关节结核易感性之间的关系。
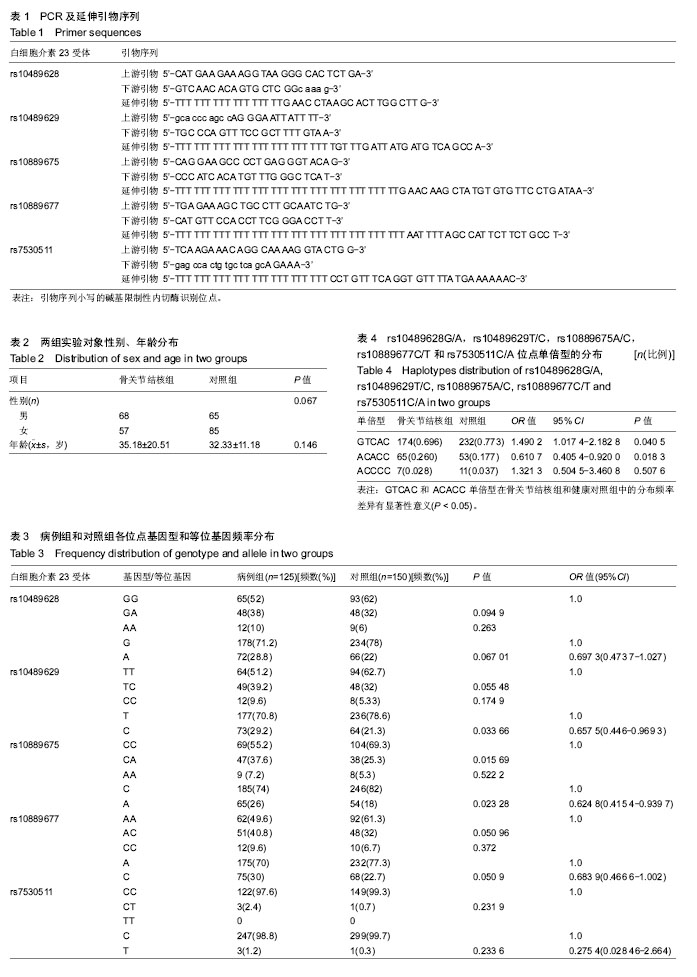
方法:选取2014年7月到2017年3月右江民族医学院附属医院住院的125例骨关节结核患者及150例健康体检者作为研究对象,利用PCR扩增技术和 DNA 测序方法分别对骨关节结核患者及健康体检者白细胞介素23受体rs10489628G/A、rs10489629T/C、rs10889675A/C、rs10889677C/T、rs7530511C/A位点进行多态性检测,比较2组基因型以及等位基因的频率分布差异,探讨各基因型与骨关节结核易感性的关系。
结果与结论:白细胞介素23受体基因rs10489629 T/C位点骨关节结核组C等位基因频率29.2%,高于对照组(21.3%);rs10889675 C/A位点骨关节结核组A等位基因频率26.0%,高于对照组(18.0%),骨关节结核组CA频率37.6%高于对照组(25.3%);差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。骨关节结核组单倍型GTCAC频率69.6%低于对照组(77.3%)、ACACC频率26.0%高于对照组(17.7%)。提示白细胞介素23受体 rs10489629T/C、rs10889675C/A位点多态性可能与广西壮族人群骨关节结核易感性有关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4522-6260(吴昭元)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
基因多态性:多态性是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在2种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型或等位基因,亦称遗传多态性或基因多态性。从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域。对于一个体而言,基因多态性碱基顺序终生不变,并按孟德尔规律世代相传。
易感性:是指人和动物对某种人畜共患病病原体感染受性的大小,是指由遗传基础所决定的个体患病的风险。也可以理解为在相同环境下,不同个体患病的风险。易感性完全由基因决定,在环境致病因子作用下的基因表达往往起着更重要的作用。因为即使基因型一致,基因表达还会受到甲基化、体细胞突变、X染色体的随机失活等影响。
文题释义:
基因多态性:多态性是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在2种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型或等位基因,亦称遗传多态性或基因多态性。从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域。对于一个体而言,基因多态性碱基顺序终生不变,并按孟德尔规律世代相传。
易感性:是指人和动物对某种人畜共患病病原体感染受性的大小,是指由遗传基础所决定的个体患病的风险。也可以理解为在相同环境下,不同个体患病的风险。易感性完全由基因决定,在环境致病因子作用下的基因表达往往起着更重要的作用。因为即使基因型一致,基因表达还会受到甲基化、体细胞突变、X染色体的随机失活等影响。