| [1] Maher B, Ryan E, Little M, et al. The management of colorectal liver metastases. Clin Radiol. 2017;72(8):617-625.[2] Aloia TA, Vauthey JN. Management of colorectal liver metastases: past, present, and future. Updates Surg. 2011;63(1):1-3.[3] Mantripragada K, Reagan JL, Quesenberry PJ, et al. Advances in cellular therapy for the treatment of leukemia. Discov Med. 2014; 17(91):15-24.[4] Davies JK, Taussig D, Oakervee H, et al. Long-term survival with low toxicity after allogeneic transplantation for acute myeloid leukaemia and myelodysplasia using non-myeloablative conditioning without T cell depletion. Br J Haematol. 2013;162(4):525-529.[5] van Bergen CA, Verdegaal EM, Honders MW, et al. Durable remission of renal cell carcinoma in conjuncture with graft versus host disease following allogeneic stem cell transplantation and donor lymphocyte infusion: rule or exception. PLoS One. 2014;9(1): e85198.[6] Hardy NM, Mossoba ME, Steinberg SM, et al. Phase I trial of adoptive cell transfer with mixed-profile type-I/type-II allogeneic T cells for metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(21): 6878-6887.[7] Aglietta M, Barkholt L, Schianca FC, et al. Reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in metastatic colorectal cancer as a novel adoptive cell therapy approach. The European group for blood and marrow transplantation experience. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009;15(3):326-335.[8] De Koning C, Nierkens S, Boelens JJ.Strategies before, during, and after hematopoietic cell transplantation to improve T-cell immune reconstitution. Blood. 2016;128(23):2607-2615.[9] 王理,文西年,高华,等. 结肠癌肝转移模型构建方法的优化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(36):5855-5860.[10] Shook DR, Triplett BM, Srinivasan A, et al. Successful allogeneic hematopoietic cell engraftment after a minimal conditioning regimen in children with relapsed or refractory solid tumors. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(2):291-297.[11] Mondino A, Vella G, Icardi L. Targeting the tumor and its associated stroma: One and one can make three in adoptive T cell therapy of solid tumors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017;36:57-65.[12] Heise D, Bayings W, Tuinhof A, et al. Long-term outcome and quality of life after initial and repeat resection of colorectal liver metastasis: A retrospective analysis. Int J Surg. 2017;48:281-285.[13] Ghosh N, Ye X, Tsai HL, et al. Allogeneic Blood or Marrow Transplantation with Post-Transplantation Cyclophosphamide as Graft-versus-Host Disease Prophylaxis in Multiple Myeloma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23(11):1903-1909.[14] Chang YJ, Huang XJ. Donor lymphocyte infusions for relapse after allogeneic transplantation: when, if and for whom. Blood Rev. 2013; 27(1):55-62.[15] Zhanna Y, Ester H, Lola W, et al. Multidonor bone marrow transplantation improves donor engraftment and increases the graft versus tumor effect while decreasing graft-versus-host disease. Transpl Int. 2011;24(2):194-200.[16] Delia M, Pastore D, Mestice A, et al. Outcome of allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation by donor graft CD3+/Tregs ratio: a single-center experience. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(3):495-499. |
.jpg)
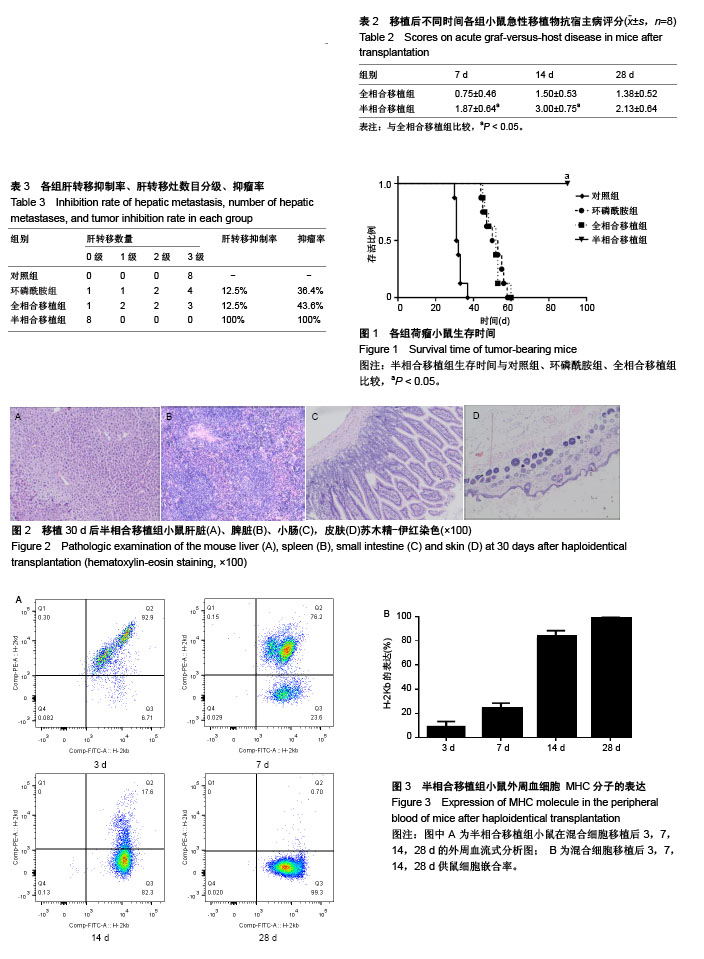
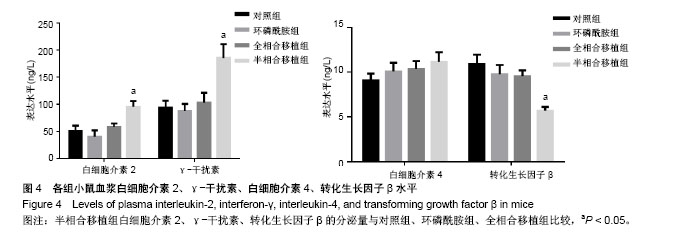
.jpg)
.jpg)