| [1] Morrison CA.The prehospital treatment of the bleeding patient--dare to dream.J Surg Res.2013;180 (2):246-147.[2] Sambasivan CN,Cho SD,Zink KA,et al.A highly porous silica and chitosan-based hemostatic dressing is superior in controlling hemorrhage in a severe groin injury model in swine.Am J Surg. 2009; 197(5): 576-580.[3] Khoshmohabat H,Paydar S,Kazemi HM,et al.Overview of agents used for emergency hemostasis.Trauma Mon.2016;21(1):e26023.[4] Lier H,Krep H,Schroeder S,et al.Prospective randomized multicenter trial of fibrin sealant versus thrombin-soaked gelatin sponge for suture- or needle-hole bleeding from polytetrafluoroethylene femoral artery grafts.J Vasc Surg.2003;38(4):766-771.[5] Taylor LM Jr,Mueller-Velten G,Koslow A,et al.Prospective randomized multicenter trial of fibrin sealant versus thrombin-soaked gelatin sponge for suture-or needle-hole bleeding from polytetrafluoroethylene femoral artery grafts.J Vas Surg.2003;38(4):766-771.[6] Dai C,Liu C,Wei J,et al.Molecular imprinted macroporous chitosan coated mesoporous silica xerogels for hemorrhage control. Biomaterials. 2010;31(30):7620-7630.[7] Rothwell SW,Fudge JM,Chen WK,et al.Addition of a propyl gallate-based procoagulant to a fibrin bandage improves hemostatic performance in a swine arterial bleeding model.Thromb Res. 2002;108 (5-6):335-340.[8] Gruen RL,Brohi K,Schreiber M,et al. Haemorrhage control in severely injured patients.Lancet. 2012;380(9847):1099-1108.[9] Bilgili H,Kosar A,Kurt M,et al.Hemostatic efficacy of ankaferd blood stopper in a swine bleeding model.Med Princ Pract. 2009;18(3): 165-169.[10] Mannucci PM.Hemostatic drugs.N Engl J Med. 1998;339(4):245-253.[11] Rossaint R,Cerny V,Coats TJ,et al.Key issues in advanced bleeding care in trauma.Shock.2006;26 (4):322-331.[12] Kelly JF,Ritenour AE,McLaughlin DF,et al.Injury severity and causes of death from operation iraqi freedom and operation enduring freedom: 2003-2004 versus 2006.J Trauma. 2008;64(2 Suppl):S21-26.[13] Granville-Chapman J,Jacobs N,Midwinter MJ.Pre-hospital haemostatic dressings: A systematic review. Injury. 2011;42(5):447-459.[14] Vournakis JN,Demcheva M,Whitson AB,et al.The rdh bandage: Hemostasis and survival in a lethal aortotomy hemorrhage model.J Surg Res.2003;113(1):1-5.[15] Smith AH,Laird C,Porter K,et al.Haemostatic dressings in prehospital care.Emerg Med J.2013;30(10):784-789.[16] Mabry RL,Holcomb JB,Baker AM,et al.United states army rangers in somalia: An analysis of combat casualties on an urban battlefield.J Trauma.2000;49(3): 515-528.[17] Navein J,Coupland R,Dunn R.The tourniquet controversy.J Trauma. 2003;54(5 Suppl):S219-220.[18] Pozza M,Millner RW.Celox (chitosan) for haemostasis in massive traumatic bleeding: Experience in afghanistan.Eur J Emerg Med. 2011;18(1):31-33.[19] Carraway JW,Kent D,Young K,et al.Comparison of a new mineral based hemostatic agent to a commercially available granular zeolite agent for hemostasis in a swine model of lethal extremity arterial hemorrhage.Resuscitation. 2008;78(2):230-235.[20] Ward KR,Tiba MH,Holbert WH,et al.Comparison of a new hemostatic agent to current combat hemostatic agents in a swine model of lethal extremity arterial hemorrhage.J Trauma.2007;63(2):276-283.[21] Yucel N,Lefering R,Maegele M,et al.Polytrauma Study Group of the German Trauma Society. Trauma associated severe hemorrhage (tash)-score: Probability of mass transfusion as surrogate for life threatening hemorrhage after multiple trauma.J Trauma. 2006; 60(6):1228-1236.[22] Brohi K,Singh J,Heron M,et al.Acute traumatic coagulopathy.J Trauma.2003;54(6):1127-1130.[23] Davenport R,Manson J,De'Ath H,et al.Functional definition and characterization of acute traumatic coagulopathy.Crit Care Med.2011; 39(12):2652-2658.[24] Pusateri AE,McCarthy SJ,Gregory KW,et al.Effect of a chitosan-based hemostatic dressing on blood loss and survival in a model of severe venous hemorrhage and hepatic injury in swine.J Trauma. 2003;54(1): 177-182.[25] Clay JG,Zierold D,Grayson K,et al.Dextran polymer hemostatic dressing improves survival in liver injury model.J Surg Res. 2009; 155(1):89-93.[26] Kilbourne M,Keledjian K,Hess JR,et al.Hemostatic efficacy of modified amylopectin powder in a lethal porcine model of extremity arterial injury.Ann Emerg Med.2009;53(6):804-810.[27] Pusateri AE,Holcomb JB,Kheirabadi BS,et al.Making sense of the preclinical literature on advanced hemostatic products.J Trauma. 2006; 60(3):674-682.[28] Robinson K.Controlling bleeding in the field: Hemostatic powders and dressings debut in the prehospital setting.J Emerg Nurs. 2004;30(2): 160-161.[29] Lawton G,Granville-Chapman J,Parker PJ.Novel haemostatic dressings.J R Army Med Corps., 2009;155(4):309-314.[30] Bennett BL,Littlejohn L.Review of new topical hemostatic dressings for combat casualty care.Mil Med. 2014;179(5):497-514.[31] Kratz A,Danon A.Controlling bleeding from superficial wounds by the use of topical alpha adrenoreceptor agonists spray. A randomized, masked, controlled study.Injury. 2004;35(11):1096-1101.[32] Littlejohn L,Bennett BL,Drew B.Application of current hemorrhage control techniques for backcountry care: Part two, hemostatic dressings and other adjuncts.Wilderness Environ Med.2015;26 (2):246-254.[33] Devlin JJ,Kircher S,Kozen BG,et al.Comparison of chitoflex(r), celox, and quikclot(r) in control of hemorrhage.J Emerg Med. 2011;41(3): 237-245.[34] Clay JG,Grayson JK,Zierold D.Comparative testing of new hemostatic agents in a swine model of extremity arterial and venous hemorrhage. Mil Med.2010;175(4):280-284.[35] Valeri CR,Vournakis JN.Mrdh bandage for surgery and trauma: Data summary and comparative review, J Trauma. 2011;71(2 Suppl 1): S162-166.[36] Rhee P,Brown C,Martin M,et al.Quikclot use in trauma for hemorrhage control: Case series of 103 documented uses.J Trauma. 2008;64(4): 1093-1099.[37] Arnaud F,Tomori T,Carr W,et al.Exothermic reaction in zeolite hemostatic dressings: Quikclot acs and acs+.Ann Biomed Eng. 2008;36(10):1708-1713.[38] Wright JK,Kalns J,Wolf EA,et al.Thermal injury resulting from application of a granular mineral hemostatic agent.J Trauma. 2004; 57(2):224-230.[39] Velmahos GC,Tabbara M,Spaniolas K,et al.Self-expanding hemostatic polymer for control of exsanguinating extremity bleeding.J Trauma. 2009;66(4):984-988.[40] Sambasivan CN,Schreiber MA.Emerging therapies in traumatic hemorrhage control.Curr Opin Crit Care. 2009;15(6):560-568.[41] 史跃,杜宝堂,何远清,等.多微孔多聚糖止血粉应用于软组织创伤性出血[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(3): 406-411.[42] Gegel B,Burgert J,Cooley B,et al.The effects of bleedarrest, celox, and traumadex on hemorrhage control in a porcine model.J Surg Res. 2010;164(1):e125-129.[43] Malmquist JP,Clemens SC,Oien HJ,et al.Hemostasis of oral surgery wounds with the hemcon dental dressing.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;66(6):1177-1183.[44] Millner RW,Lockhart AS,Bird H,et al.A new hemostatic agent: Initial life-saving experience with celox (chitosan) in cardiothoracic surgery. Ann Thorac Surg.2009;87(2):e13-14.[45] Waibel KH,Haney B,Moore M,et al.Safety of chitosan bandages in shellfish allergic patients.Mil Med. 2011;176(10):1153-1156.[46] Arnaud F,Teranishi K,Okada T,et al.Comparison of combat gauze and traumastat in two severe groin injury models.J Surg Res. 2011;169(1): 92-98.[47] Gerlach T,Grayson JK,Pichakron KO,et al.Preliminary study of the effects of smectite granules (woundstat) on vascular repair and wound healing in a swine survival model.J Trauma. 2010;69(5):1203-1209.[48] Kheirabadi BS,Mace JE,Terrazas IB,et al.Safety evaluation of new hemostatic agents, smectite granules, and kaolin-coated gauze in a vascular injury wound model in swine.J Trauma. 2010;68(2): 269-278.[49] Kheirabadi BS,Scherer MR,Estep JS,et al.Determination of efficacy of new hemostatic dressings in a model of extremity arterial hemorrhage in swine.J Trauma.2009;67(3):450-459.[50] King DR,Schreiber MA.The mrdh bandage provides effective hemostasis in trauma and surgical hemorrhage.J Trauma. 2011;71 (2Suppl 1):S167-170.[51] 张平,肖南,张治纲,等.战创伤止血敷料的现状及展望[J].创伤外科杂志, 2009,(4):378-380.[52] Ong SY,Wu J, Moochhala SM,et al.Development of a chitosan-based wound dressing with improved hemostatic and antimicrobial properties. Biomaterials. 2008;29(32):4323-4332.[53] Gaharwar AK,Avery RK,Assmann A,et al.Shear-thinning nanocomposite hydrogels for the treatment of hemorrhage. Acs Nano. 2014;8(10):9833-9842.[54] Hsu BB,Conway W,Tschabrunn CM,et al.Clotting mimicry from robust hemostatic bandages based on self-assembling peptides.Acs Nano. 2015;9(9):9394-9406.[55] 李佳楠,钟小忠,王婷.短肽rada16-1自组装纤维长度与止血关系研究[J].江汉大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(5):76-80.[56] 甘慧,孟志云,吴卓娜,等.自组装肽的止血应用[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2015,23(3):903-909.[57] 陈向标.水凝胶医用敷料的研究概况[J].轻纺工业与技术, 2011,40(1):66-68.[58] Du L,Tong L,Jin Y,et al.A multifunctional in situ-forming hydrogel for wound healing.Wound Repair Regen. 2012;20(6):904-910.[59] Komatsu S,Nagai Y,Naruse K,et al.The neutral self-assembling peptide hydrogel spg-178 as a topical hemostatic agent.PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102778.[60] Bu Y,Zhang L,Liu J,et al.Synthesis and properties of hemostatic and bacteria-responsive in situ hydrogels for emergency treatment in critical situations.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016;8(20): 12674-23683.[61] Zhang YJ,Gao B,Liu XW.Topical and effective hemostatic medicines in the battlefield. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(1):10-19. |
.jpg)
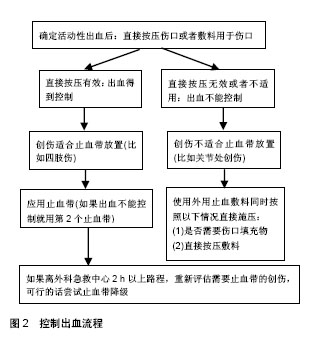
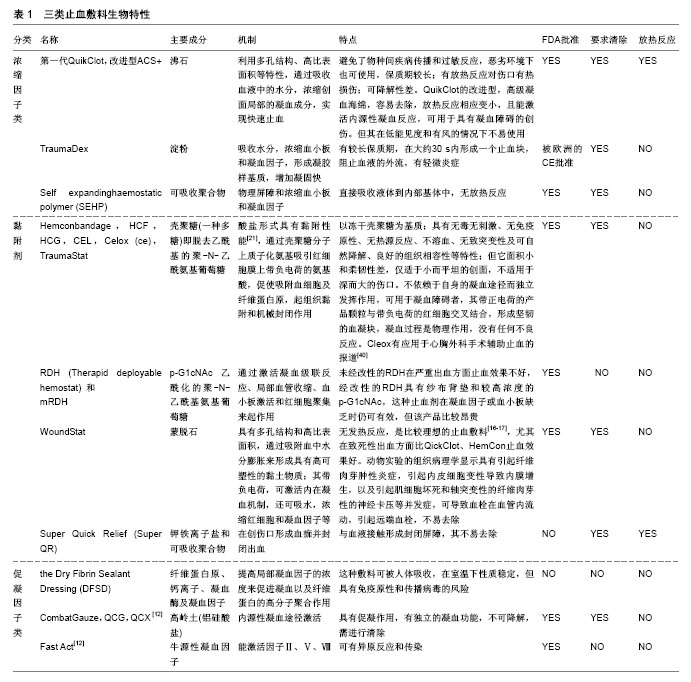
.jpg)
.jpg)