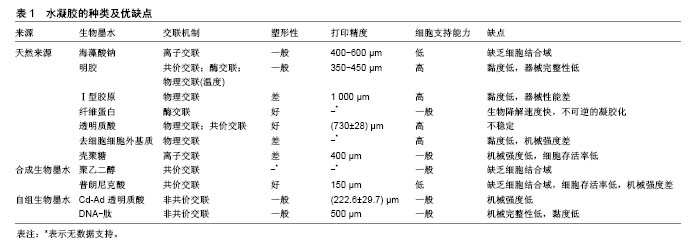
| [1] Langer R,Vacanti JP.Tissue engineering.Science.1993;260(5110):920-926.[2] Hutmacher DW.Scaffold design and fabrication technologies for engineering tissues--state of the art and future perspectives.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2001;12(1):107-124.[3] Hutmacher DW,Schantz T,Zein I,et al.Mechanical properties and cell cultural response of polycaprolactone scaffolds designed and fabricated via fused deposition modeling.J Biomed Mater Res.2001; 55(2):203-216.[4] Colacino JA.3D human tissue culture: modeling environmental effects on the stem cell epigenome.Epigenomics.2016;8(11):1453-1457.[5] Caiazzo M,Okawa Y,Ranga A,et al.Defined three-dimensional microenvironments boost induction of pluripotency.Nat Mater.2016; 15(3):344-352.[6] Nakamura M,Iwanaga S,Henmi C,et al.Biomatrices and biomaterials for future developments of bioprinting and biofabrication. Biofabrication. 2010;2(1):014110.[7] Fedorovich NE,Schuurman W,Wijnberg HM,et al.Biofabrication of osteochondral tissue equivalents by printing topologically defined, cell-laden hydrogel scaffolds.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2012;18(1): 33-44.[8] Derby B.Printing and prototyping of tissues and scaffolds.Science. 2012; 338(6109):921-926.[9] Nakamura M,Nishiyama Y,Henmi C,et al.Inkjet bioprinting as an effective tool for tissue fabrication[C].proceedings of the NIP & Digital Fabrication Conference, F,2006.[10] Kirchmajer DM,Iii RG,Panhuis MIH.An overview of the suitability of hydrogel-forming polymers for extrusion-based 3D-printing.J Mater Chem B.2015;3(20):4105-4117.[11] Kilpatrick JI,Revenko I,Rodriguez BJ.Nanomechanics of Cells and Biomaterials Studied by Atomic Force Microscopy.Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(16):2456-2474.[12] Zhao Y,Li Y,Mao S,et al.The influence of printing parameters on cell survival rate and printability in microextrusion-based 3D cell printing technology.Biofabrication.2015;7(4): 045002.[13] Poveda-Reyes S,Moulisova V,Sanmartin-Masia E,et al. Gelatin-Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels with Tuned Stiffness to Counterbalance Cellular Forces and Promote Cell Differentiation. Macromol Biosci.2016;16(9):1311-1324.[14] Slaughter BV,Khurshid SS,Fisher OZ,et al.Hydrogels in regenerative medicine. Adv Mater.2009; 21(32-33):3307-3329.[15] Jungst T,Smolan W,Schacht K,et al.Strategies and Molecular Design Criteria for 3D Printable Hydrogels.Chem Rev.2016;116(3):1496-1539.[16] Kang HW,Lee SJ,Ko IK,et al.A 3D bioprinting system to produce human-scale tissue constructs with structural integrity.Nat Biotechnol. 2016;34(3):312-319.[17] Pescosolido L,Vermonden T,Malda J,et al.In situ forming IPN hydrogels of calcium alginate and dextran-HEMA for biomedical applications.Acta Biomater.2011;7(4):1627-1633.[18] Seliktar D.Designing cell-compatible hydrogels for biomedical applications. Science.2012;336(6085):1124-1128.[19] Gasperini L,Mano JF,Reis RL.Natural polymers for the microencapsulation of cells.J R Soc Interface.2014;11(100): 20140817.[20] Wolf MT,Daly KA,Brennan-Pierce EP,et al.A hydrogel derived from decellularized dermal extracellular matrix.Biomaterials. 2012;33(29): 7028-7038.[21] Panwar A,Tan LP.Current Status of Bioinks for Micro-Extrusion-Based 3D Bioprinting. Molecules(Basel,Switzerland).2016;21(6).pii: E685.doi: 10.3390/molecules21060685.[22] Nichol JW,Koshy ST,Bae H,et al.Cell-laden microengineered gelatin methacrylate hydrogels.Biomaterials.2010;31(21):5536-5544.[23] Sakloetsakun D,Bernkop-Schnürch A.Thiolated chitosans.J Drug Deliv Sci Technol.2010;20(1):63-69.[24] Khetan S,Burdick JA.Patterning network structure to spatially control cellular remodeling and stem cell fate within 3-dimensional hydrogels. Biomaterials.2010;31(32):8228-8234.[25] Toh WS,Lim TC,Kurisawa M,et al.Modulation of mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis in a tunable hyaluronic acid hydrogel microenvironment.Biomaterials.2012;33(15):3835-3845.[26] Kang LH,Armstrong PA,Lee LJ,et al.Optimizing Photo-Encapsulation Viability of Heart Valve Cell Types in 3D Printable Composite Hydrogels. Ann Biomed Eng.2017;45(2):360-377.[27] Schuurman W,Levett PA,Pot MW,et al.Gelatin-methacrylamide hydrogels as potential biomaterials for fabrication of tissue-engineered cartilage constructs.Macromol Biosci.2013; 13(5):551-561.[28] Cheng E,Xing Y,Chen P,et al.A pH-triggered, fast-responding DNA hydrogel.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.2009;48(41):7660-7663.[29] Li C,Faulkner-Jones A,Dun AR,et al.Rapid formation of a supramolecular polypeptide-DNA hydrogel for in situ three-dimensional multilayer bioprinting.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015;54(13): 3957-3961.[30] Ozbolat IT,Hospodiuk M.Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting.Biomaterials.2016;76:321-343.[31] Blaeser A,Duarte Campos DF,Puster U,et al.Controlling Shear Stress in 3D Bioprinting is a Key Factor to Balance Printing Resolution and Stem Cell Integrity.Adv Healthc Mater.2016;5(3): 326-333.[32] Tabriz AG,Hermida MA,Leslie NR,et al.Three-dimensional bioprinting of complex cell laden alginate hydrogel structures.Biofabrication. 2015;7(4):045012.[33] Bertassoni LE,Cardoso JC,Manoharan V,et al.Direct-write bioprinting of cell-laden methacrylated gelatin hydrogels.Biofabrication. 2014;6(2): 024105.[34] Discher DE,Mooney DJ,Zandstra PW.Growth factors, matrices, and forces combine and control stem cells.Science. 2009;324(5935):1673-1677.[35] Engler AJ,Caragkrieger C,Johnson CP,et al.Embryonic cardiomyocytes beat best on a matrix with heart-like elasticity: scar-like rigidity inhibits beating.J Cell Sci.2008;121(22): 3794-3802.[36] Zimmermann WH,Schneiderbanger K,Schubert P,et al.Tissue Engineering of a Differentiated Cardiac Muscle Construct.Circ Res. 2002;90(2):223-230.[37] Pang Y,Wang X,Lee D,et al.Dynamic quantitative visualization of single cell alignment and migration and matrix remodeling in 3-D collagen hydrogels under mechanical force. Biomaterials. 2011;32(15): 3776-3783.[38] Diederich VE,Studer P,Kern A,et al.Bioactive polyacrylamide hydrogels with gradients in mechanical stiffness.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2013;110(5): 1508-1519.[39] Hockaday LA,Kang KH,Colangelo NW,et al.Rapid 3D printing of anatomically accurate and mechanically heterogeneous aortic valve hydrogel scaffolds.Biofabrication.2012;4(3):035005.[40] Patwari P,Lee RT.Mechanical Control of Tissue Morphogenesis.Circ Res.2008;103(3): 234-243.[41] Ulrich TA,De Juan Pardo EM,Kumar S.The mechanical rigidity of the extracellular matrix regulates the structure, motility, and proliferation of glioma cells.Cancer Res.2009;69(10):4167-4174.[42] Abraham S,Brahim S,Ishihara K,et al.Molecularly engineered p(HEMA)-based hydrogels for implant biochip biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2005;26(23):4767-4778.[43] Tse M,Uludag H,Sefton MV,et al.Secretion of recombinant proteins from hydroxyethyl methacrylate-methyl methacrylate capsules. Biotechnol Bioeng.996;51(3):271-280.[44] Jones TD,Kefi A,Sun S,et al.An Optimized Injectable Hydrogel Scaffold Supports Human Dental Pulp Stem Cell Viability and Spreading.Adv Med.2016;2016:7363579.[45] Cui X,Breitenkamp K,Lotz M,et al.Synergistic action of fibroblast growth factor-2 and transforming growth factor-beta1 enhances bioprinted human neocartilage formation. Biotechnol Bioeng.2012; 109(9):2357-2368.[46] Skardal A,Devarasetty M,Kang HW,et al.A hydrogel bioink toolkit for mimicking native tissue biochemical and mechanical properties in bioprinted tissue constructs.Acta Biomater.2015; 25:24-34. |
.jpg)
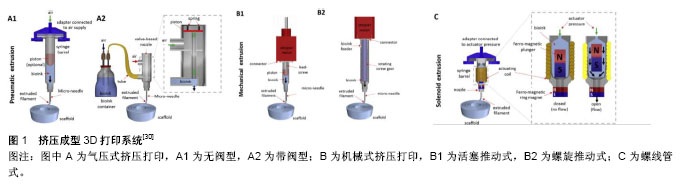
.jpg)