| [1] Yoshino K,Nishibori M,Fujiseki M,et al.Loss of teeth in positions mesially adjacent to implant-supported fixed dentures: a retrospective clinical survey.Int J Prosthodont. 2015;28(2):158-160. [2] Campos CH,Gonçalves TM,Garcia RC.Implant-Supported Removable Partial Denture Improves the Quality of Life of Patients with Extreme Tooth Loss.Braz Dent J. 2015;26(5): 463-467.[3] 何女,钱江,赵佳佳,等.数字化导板用于牙种植的三维精度分析[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2015,25(2):117-120.[4] Schepers RH,Raghoebar GM,Vissink A,et al.Accuracy of fibula reconstruction using patient-specific CAD/CAM reconstruction plates and dental implants: A new modality for functional reconstruction of mandibular defects.J Craniomaxillofac Surg.2015;43(5):649-657. [5] 蔡洁明,褚烛天,舒传继,等.种植牙技术对老年牙列游离端缺失修复的疗效分析[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(13):2509-2511.[6] 汤雨龙,惠瑞宗,曹志强,等.3D打印技术在口腔种植导板制作中的应用[J].解放军医药杂志,2015,27(11):32-35.[7] 何女,钱江,赵佳佳,等.数字化导板用于牙种植的三维精度分析[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2015,25(2):117-120.[8] Jin T,Hou X,Li P,et al.A Novel Method of Automatic Plant Species Identification Using Sparse Representation of Leaf Tooth Features.PloS One.2015;10(10):139482.[9] 向梅,张宇.种植导板的设计制作及临床应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(3):488-492.[10] Schneider D,Schober F,Grohmann P,et al.In-vitro evaluation of the tolerance of surgical instruments in templates for computer-assisted guided implantology produced by 3-D printing.Clin Oral Implants Res.2015;26(3):320-325.[11] 范园园,宋岩,高宇飞,等.前牙美学区牙槽骨宽度不足牙种植的临床观察[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2017,33(2):101-104.[12] 宫苹.牙种植修复中的咬合重建[J].口腔颌面外科杂志, 2016, 26(6):381-384.[13] 何女,钱江,赵佳佳,等.数字化导板用于牙种植的三维精度分析[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2015,2(1):117-120.[14] 马竞.上颌后牙区口腔3D导板种植精确性研究[J].中国医学工程, 2015,23(5):88,90.[15] Wilde F,Hanken H,Probst F,et al.Multicenter study on the use of patient-specific CAD/CAM reconstruction plates for mandibular reconstruction.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg, 2015,10(12):2035-2051[16] 周小义,刘尧,叶斌,等.3D打印导板辅助髁突骨软骨瘤及继发复杂牙颌面畸形的手术治疗[J].口腔医学研究, 2017,33(2): 166-169.[17] Anssari Moin D,Derksen W,Verweij JP,et al.A Novel Approach for Computer-Assisted Template-Guided Autotransplantation of Teeth With Custom 3D Designed/Printed Surgical Tooling.An Ex Vivo Proof of Concept.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;74(5):895-902.[18] 张悦,徐连来.计算机导航在口腔种植牙领域的应用[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2015,31(10):603-606.[19] 李志刚,刘宁,郝智莉,等.牙种植全程导航技术的临床应用[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2015,50(1):47-49.[20] 王佐林,王方.牙种植修复中的咬合重建、数字化技术、无牙颌种植修复方法--“争鸣与共识”种植论坛(第二季)学术共识[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2016,26(3):153-155.[21] 徐普,李晓妮,徐邢环宇,等.牙槽骨黏骨膜骨瓣新技术在牙种植手术中的应用[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2016,51(11):688-690.[22] Khalil W,EzEldeen M,Van De Casteele E,et al.Validation of cone beam computed tomography-based tooth printing using different three-dimensional printing technologies.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol.2016;121(3):307-315.[23] 汤雨龙,惠瑞宗,曹志强,等.3D打印技术在口腔种植导板制作中的应用[J].解放军医药杂志,2015,27(11):32-35.[24] Nickenig HJ,Wichmann M,Terheyden H,et al.Oral health-related quality of life and implant therapy: A prospective multicenter study of preoperative, intermediate, and posttreatment assessment.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016;44(6):753-757. [25] Bilhan H,Bilmenoglu C,Urgun AC,et al.Comparison of the Primary Stability of Two Implant Designs in Two Different Bone Types: An In Vitro Study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2015;30(5):1036-1040.[26] Mo H,Mo T,Zhuang X,et al.Clinical application of the new type Metal Pierced Surgical Template based on 3D printing technology: a 1-year prospective study.Clin Oral Impl Res. 2014;4(8):128-133.[27] Cornelius CP,Smolka W,Giessler GA,et al.Patient-specific reconstruction plates are the missing link in computer-assisted mandibular reconstruction: A showcase for technical description.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015;43(5): 624-649. [28] 魏宁.不同种植系统口腔种植临床病例的临床疗效分析[J].中外医疗,2017,36(1):61-62,68.[29] 张宏伟,李春茹.即刻种植和常规种植在牙齿缺失修复中的临床价值对比[J].黑龙江医药科学,2017,40(1):115-116.[30] 石磊,黄盛兴,刘慧凤,等.前牙区数字化即刻种植即刻修复病例报道及文献回顾[J].口腔疾病防治,2017,25(2):119-122.[31] Zheng P, Yao Q, Xu P,et al.Application of computer-aided design and 3D-printed navigation template in Locking Compression Pediatric Hip Plate[Formula: see text] placement for pediatric hip disease.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2017;12(5):865-871. |
.jpg)
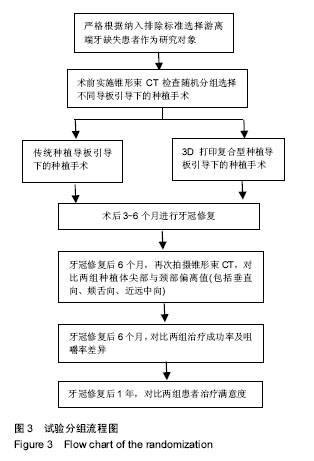
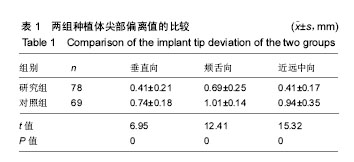
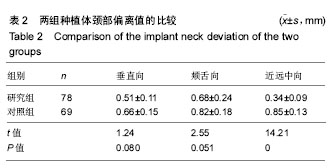
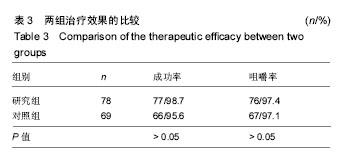
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)