| [1]Takamatsu Y,Sunami K,Muta T,et al.Kyushu Hematology Organization for Treatment Study Group(K-HOT). Bortezomib, doxorubicin and intermediate-dose dexamethasone (iPAD) therapy for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: a multicenter phase 2 study.Int J Hematol. 2013;98(2):179-185.
[2]Shahil KM,Alexander A.Thermal properties of graphene and multilayer graphene: Applications in thermal interface materials.Solid State Commun. 2012; 152(15): 1331-1340.
[3]Lian P,Zhu X,Liang S,et al.High reversible capacity of SnOi/graphene nanocomposite as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries.Electrochim Acta.2011;56: 4532-4539.
[4]Gao Y,Li Y,Zhang L,et al.Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2012;368(1):540-546.
[5]Kwak YH,Choi DS,Kim YN,et al.Flexible glucose sensor using CVD-grown graphene-based field effect transistor.Biosens Bioelectron.2012;37(1):82-87.
[6]Premkumar T,Geckeler KE.Graphene-DNA hybrid materials:Assembly, applications,and prospects. Prog Polym Sci.2012;37(4):515-529.
[7]Li Y,Liu Y,Fu Y,et al.The triggering of apoptosis in macrophages by pristine graphene through the MAPK and TGF-beta signaling pathways.Biomaterials. 2012; 33(2):402-411.
[8]Zhou H,Zhao K,Li W,et al.The interactions between pristine graphene and macrophages and the production of cytokines/chemokines via TLR- and NF-KB-related signaling pathways.Biomaterials. 2012; 33(29):6933-6942.
[9]Akhavan O,Ghaderi E,Akhavan A.Size-dependent genotoxicity of graphene nanoplatelets in human stem cells.Biomaterials.2012;33(32):8017-8025.
[10]Chang Y,Yang ST,Liu JH,et al.In vitro toxicity evaluation of graphene oxide on A549 cells.Toxicol Lett.2011;200(3):201-210.
[11]Cavo M,Tacchetti P,Patriarca F,et al.Bortezomib with thalidomide plus dexamethasone compared with thalidomide plus dexamthasone as induction therapy before, and consolidation therapy after, double autologous stem-cell transplantation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma:a randomised phase 3 study.Lancet.2010;376(9758): 2075-2085.
[12]Harousseau JL,Attal M,Avet-Loiseau H,et al. Bortezomib plus dexamethasone is superior to vincristine plus doxorubicin plus dexamethasone as induction treatment prior to autologous stem-cell transplantation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: results of the IFM 2005-01 phase III trial.J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(30):4621-9462.
[13]Sonneveld P,Schmidt-Wolf IG,van der Holt B,et al. Bortezomib induction and maintenance treatment in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: results of the randomized phase Ⅲ HOVON-65 / GMMG-HD4 trial.J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(24): 2946-2955.
[14]Sellner L,Heiss C,Benner A,et al.Autologous retransplantation for patients with recurrent multiple myeloma: a single-center experience with 200 patients. Cancer.2013;119(13):2438-2446.
[15]陈燚,杨泽松,陈建斌.造血干细胞移植治疗难治性多发性骨髓瘤[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(1):131-136.
[16]李燕郴,耿传营.多发性骨髓瘤治疗中的造血干细胞移植[J].临床药物治疗杂志,2013,14(6):38-42.
[17]侯慧明,刘林.自体造血干细胞移植治疗多发性骨髓瘤的疗效分析[J].临床血液学杂志,2014,27(2):230-233.
[18]Koehne G,Giralt S.Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma: curative but not the standard of care.Curr Opin Oncol.2012;24(6): 720-726.
[19]杨励,蔡真.多发性骨髓瘤的维持治疗[J].中华血液学杂志, 2013,34(4):295-297.
[20]Moreau P,Avet-Loiseau H,Harousseau JL,et al.Current trends in autologous stem-cell transplantation for myeloma in the era of novel therapies. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(14):1898-1906.
[21]冯俊,周道斌.多发性骨髓瘤与第二肿瘤[J].中华血液学杂志,2013,34(4):294-295.
[22]Knepper SE,van der Holt B,Kersten MJ,et al. Lenalidomide maintenance following non-myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma is not feasible : results of the HOVON 76 trial.Blood.2011;118(9):2413-2419.
[23]Richardson PG,Jagannath S,Jakubowiak AJ,et al. Phase II Trial of lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone in patients (pts) with relapsed and relapsed /refractory multiple myeloma(MM) : updated efficacy and safety data after > 2 years of follow-up. Blood.2010;116(5):3049.
[24]Hjorth M,Hjertner Ø,Knudsen LM,et al.Thalidomide and dexamethasone vs. bortezomib and dexamethasone for melphalan refractory myeloma: a randomized study.Eur J Haematol. 2012;88(6): 485-496.
[25]Mosieniak G,Sliwinska MA,Alster O,et al.Polyploidy Formation in Doxorubicin-Treated Cancer Cells Can Favor Escape from Senescence.Neoplasia. 2015; 17(12):882-893.
[26]Wang LF,Su SW,Wang L.Tert-butylhydroquinone ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by activating Nrf2 and inducing the expression of its target genes.Am J Transl Res.2015;7(10):1724-1735.
[27]Ge W,Yuan M,Ceylan AF,et al.Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase protects against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity through a transient receptor potential channel vanilloid 1-mediated mechanism.Biochim Biophys Acta.2015.pii:S0925-4439(15)00368-3.
[28]Vyas D,Lopez-Hisijos N,Gandhi S,et al. Doxorubicin-Hyaluronan Conjugated Super-Paramagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (DOX-HA-SPION) Enhanced Cytoplasmic Uptake of Doxorubicin and Modulated Apoptosis, IL-6 Release and NF-kappaB Activity in Human MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015; 15(9): 6413-6422.
[29]朱晓峰,汪安友,蔡晓燕.脂质体多柔比星对初治多发性骨髓瘤疗效及安全性评估[J].安徽医药, 2015,19(2): 371-373.
[30]高慧萍.多柔比星脂质体联合低剂量沙利度胺治疗多发性骨髓瘤的临床分析[J].临床药物治疗杂志, 2015,13(5): 41-43.
[31]梁锦湄,朱旻,任浩洋.多柔比星脂质体制剂与非脂质体制剂的不良反应/事件评价[J].中国新药杂志, 2013,22(9): 1100-1104.
[32]Biju V,Itoh T,Ishikawa M,et al.Delivering quantum dots to cells: bioconjugated quantum dots for targeted and nonspecific extracellular and intracellular imaging. Chem Soc Rev.2010;39(8):3031-3056.
[33]Park S,Mohanty N,Suk JW,et al. Biocompatible, robust free-standing paper composed of a TWEEN/graphene composite.Adv Mater.2010;22(15):1736-1740.
[34]Zhang L,Xia J,Zhao Q,et al.Functional graphene oxide as a nanocarrier for controlled loading and targeted delivery of mixed anticancer drugs.Small.2010;6(4): 537-544.
[35]Zhang L,Lu Z,Zhao Q,et al.Enhanced chemotherapy efficacy by sequential delivery of siRNA and anticancer drugs using PEI-grafted graphene oxide. Small. 2011; 7(4): 460-464.
[36]Yang K,Zhang S,Zhang G,et al.Graphene in mice: ultrahigh in vivo tumor uptake and efficient photothermal therapy.Nano Lett. 2010;10(9): 3318-3323.
[37]Bao H,Pan Y,Ping Y,et al.Chitosan-functionalized grapheme oxide as a nanocarrier for drug and gene delivery.Small.2011;7(11):1569-1578.
[38]Wang K,Ruan J,Song H,et al.Biocompatibility of graphene oxide.Nanoscale Res Lett.2011;6(1): 8.
[39]Liao KH,Lin YS,Macosko CW,et al.Cytotoxicity of graphene oxide and graphene in human erythrocytes and skin fibroblasts.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2011; 3(7): 2607-2615. |
.jpg)
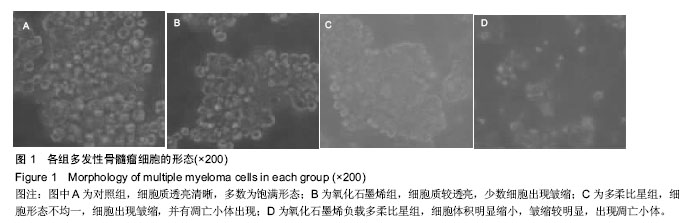
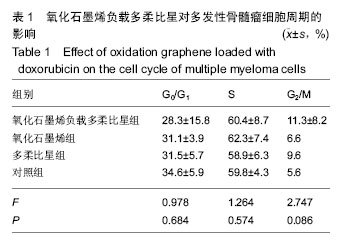
.jpg)
.jpg)