| [1] Romanov YA, Svintsitskaya VA, Smirnov VN. Searching for alternative sources of postnatal human mesenchymal stem cells: candidate MSC-like cells from umbilical cord. Stem Cells. 2003;21(1):105-110.
[2] Zhang K, Liu R, Yin G, et al. Differential cytokine secretion of cultured bone marrow stromal cells from patients with psoriasis and healthy volunteers. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20(1):49-53.
[3] 刘瑞风,尹国华,张静,等.寻常型银屑病患者骨髓间充质干细胞生物学特性研究[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志, 2010,30(3): 238.
[4] Reich K. The concept of psoriasis as a systemic inflammation: implications for disease management. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26 Suppl 2:3-11.
[5] 张建中.银屑病的流行病学与危险因素[J].实用医院临床杂志,2013,10(1):4-6.
[6] 郑敏.银屑病治疗进展[J].继续医学教育,2006,20(23): 40-43.
[7] 周密妹,姚伟星.银屑病发病机理及药物治疗进展[J].抗感染药学,2006,3(3):97-101.
[8] 张禁,范平.银屑病的治疗进展[J].中国误诊学杂志,2008, 8(25): 6059-6060.
[9] 杨宝琦,赵娜,张福仁.银屑病光疗和光化学疗法的研究进展[J].中华皮肤科杂志,2005,38(3):195-197.
[10] 黄国坚.银屑病的中西医治疗进展[J].山西中医,2008, 24(4):54-56.
[11] 孙建方.银屑病治疗进展[J].中国麻风皮肤病杂志,2003, 19(6):601-603.
[12] 刘新国,郑义宏.雷公藤多甙与阿维A联合治疗重型银屑病临床疗效观察[J].中国麻风皮肤病杂志,2005,21(10): 824-825.
[13] Gustafson CJ, Watkins C, Hix E, et al. Combination therapy in psoriasis: an evidence-based review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013;14(1):9-25.
[14] Devaux S, Castela A, Archier E, et al. Topical vitamin D analogues alone or in association with topical steroids for psoriasis: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26 Suppl 3:52-60.
[15] 顾有守.中、重度银屑病的联合疗法[J].临床皮肤科杂志, 2005,34(3):196-198.
[16] 赵辨.临床皮肤病学[M].3版.南京:江苏科技出版社,2011: 813.
[17] Kim CH. Migration and function of Th17 cells. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2009;8(3):221-228..
[18] Littman DR, Rudensky AY. Th17 and regulatory T cells in mediating and restraining inflammation. Cell. 2010; 140(6):845-858.
[19] Beriou G, Costantino CM, Ashley CW, et al. IL-17- producing human peripheral regulatory T cells retain suppressive function. Blood. 2009;113(18): 4240-4249.
[20] Kimura A, Kishimoto T. IL-6: regulator of Treg/Th17 balance. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40(7):1830-1835.
[21] Wing K, Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells exert checks and balances on self tolerance and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(1):7-13.
[22] Yawalkar N, Tscharner GG, Hunger RE, et al. Increased expression of IL-12p70 and IL-23 by multiple dendritic cell and macrophage subsets in plaque psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci. 2009;54(2):99-105.
[23] Thakker P, Leach MW, Kuang W, et al. IL-23 is critical in the induction but not in the effector phase of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2007;178(4):2589-2598.
[24] Nakajima K. Critical role of the interleukin-23/T-helper 17 cell axis in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. J Dermatol. 2012;39(3):219-224.
[25] Sugiyama H, Gyulai R, Toichi E, et al. Dysfunctional blood and target tissue CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells in psoriasis: mechanism underlying unrestrained pathogenic effector T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 2005;174(1):164-173.
[26] Kagen MH, McCormick TS, Cooper KD. Regulatory T cells in psoriasis. Ernst Schering Res Found Workshop. 2006;(56):193-209.
[27] 刘瓦利,何伟.银屑病的病因与发病机制[J].中国临床医生,2009,37(8):7-8.
[28] Skov L, Baadsgaard O. Bacterial superantigens and inflammatory skin diseases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000; 25(1):57-61.
[29] 田中华, 赵天恩.肥大细胞参与免疫反应及其在银屑病发病机制中的作用[J].中国麻风皮肤病杂志,2003,19(1): 45-47.
[30] Zhang X, Wang H, Te-Shao H, et al. Frequent use of tobacco and alcohol in Chinese psoriasis patients. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41(10):659-662.
[31] 杨洪浦,冯志合.156 例银屑病患者外周血T 淋巴细胞亚群的表现[J].皮肤病与性病,2012,24(3):1-2.
[32] Alli N, Güngör E, Karakayali G, et al. The use of cyclosporin in a child with generalized pustular psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1998;139(4):754-755.
[33] Ortonne JP, van de Kerkhof PC, Prinz JC, et al. 0.3% Tacrolimus gel and 0.5% Tacrolimus cream show efficacy in mild to moderate plaque psoriasis: Results of a randomized, open-label, observer-blinded study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2006;86(1):29-33.
[34] Wohlrab J. Calcineurin inhibitors for topical therapy in psoriasis. Hautarzt. 2006;57(8):685-689.
[35] Jain VK, Aggarwal K, Jain K, et al. Narrow-band UV-B phototherapy in childhood psoriasis. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46(3):320-322.
[36] Tarcic G, Avraham R, Pines G, et al. EGR1 and the ERK-ERF axis drive mammary cell migration in response to EGF. FASEB J. 2012;26(4):1582-1592.
[37] Barreiros AP, Sprinzl M, Rosset S, et al. EGF and HGF levels are increased during active HBV infection and enhance survival signaling through extracellular matrix interactions in primary human hepatocytes. Int J Cancer. 2009;124(1):120-129.
[38] Varani J, Kang S, Stoll S, et al. Human psoriatic skin in organ culture: comparison with normal skin exposed to exogenous growth factors and effects of an antibody to the EGF receptor. Pathobiology. 1998;66(6):253-259.
[39] Tran QT, Kennedy LH, Leon Carrion S, et al. EGFR regulation of epidermal barrier function. Physiol Genomics. 2012;44(8):455-469.
[40] Sutherland J, Denyer M, Britland S. Motogenic substrata and chemokinetic growth factors for human skin cells. J Anat. 2005;207(1):67-78.
[41] Toraldo G, Bhasin S, Bakhit M, et al. Topical androgen antagonism promotes cutaneous wound healing without systemic androgen deprivation by blocking β-catenin nuclear translocation and cross-talk with TGF-β signaling in keratinocytes.Wound Repair Regen. 2012;20(1):61-73.
[42] Badiavas EV, Zhou L, Falanga V. Growth inhibition of primary keratinocytes following transduction with a novel TGFbeta-1 containing retrovirus. J Dermatol Sci. 2001;27(1):1-6. |
.jpg)
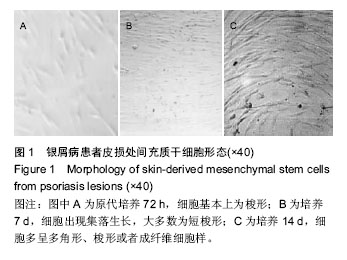
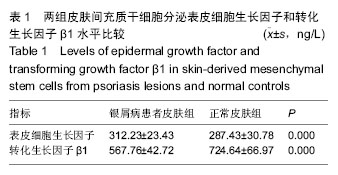
.jpg)
.jpg)