中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (16): 2989-2993.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.16.020
• 材料力学及表面改性 material mechanics and surface modification • 上一篇 下一篇
纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及改性
庞桂花1,3,程志强2,3,李俊锋3
- 1东岳集团研究院,山东省淄博市 256400
2吉林农业大学资源与环境学院,吉林省长春市 130118
3吉林大学化学学院,吉林省长春市 130012
Preparation and modification of nano-hydroxyapatite
Pang Gui-hua 1,3, Cheng Zhi-qiang 2,3, Li Jun-feng3
- 1 Dongyue Group Institute, Zibo 256400, Shandong Province, China
2 College of Resources and Environment, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun 130118, Jilin Province, China
3 Chemistry College, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, Jilin Province, China
摘要:
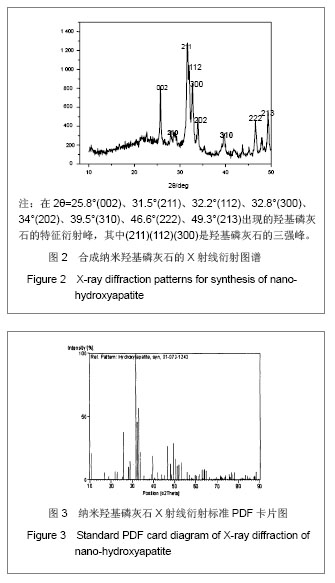
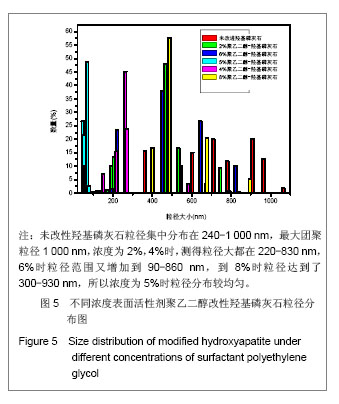
背景:人工制得的羟基磷灰石具有较强的比表面,极易发生团聚。 目的:解决羟基磷灰石团聚问题,使其分散性更好。 方法:以硝酸钙和磷酸二氢氨为原料,采用溶液共沉淀法制备纳米羟基磷灰石,分别应用聚乙二醇(2%,4%,5%,6%,8%)、聚乙烯醇(2%,4%,5%,6%,8%)、硬脂酸(2%,4%,5%,6%,8%)对其进行改性。 结果与结论:X射线衍射分析显示获得了纯度较高的纳米羟基磷灰石。在表面包覆改性纳米羟基磷灰石时,表面改性剂种类、活性剂浓度等都对其粒径大小产生影响。综合考察羟基磷灰石合成及改性过程中的影响因素主要得出以下结论:通过对羟基磷灰石改性,羟基磷灰石对聚乙二醇、聚乙烯醇、硬脂酸具有一定的选择性,聚乙二醇对羟基磷灰石改性最好,且浓度为5%时羟基磷灰石分散性最好。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)