中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 1585-1591.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3033
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
胰岛移植物封装水凝胶材料研究的重点和应用优势
柏 雪,王 彬,何斯荣
- 重庆医科大学基础医学院免疫学教研室,重庆市 400016
-
收稿日期:2020-04-09修回日期:2020-04-15接受日期:2020-06-12出版日期:2021-04-08发布日期:2020-12-18 -
通讯作者:何斯荣,重庆医科大学基础医学院免疫学教研室,重庆市 40001 -
作者简介:柏雪,女,1994年生,重庆市人,汉族,重庆医科大学医学在读硕士,主要从事自身免疫性疾病研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(81500590);重庆市自然科学基金项目(cstc2017jcyjAX0267);重庆市教委科学技术研究项目(KJQN201800418)
Research focus and application advantages in encapsulating biomaterial for islet transplantation
Bai Xue, Wang Bin, He Sirong
- Department of Immunology, College of Basic Medicine, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China
-
Received:2020-04-09Revised:2020-04-15Accepted:2020-06-12Online:2021-04-08Published:2020-12-18 -
Contact:He Sirong, Department of Immunology, College of Basic Medicine, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China -
About author:Bai Xue, Master candidate, Department of Immunology, College of Basic Medicine, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81500590; the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, No. cstc2017jcyjAX0267; the Scientific and Technological Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission, No. KJQN201800418
摘要:
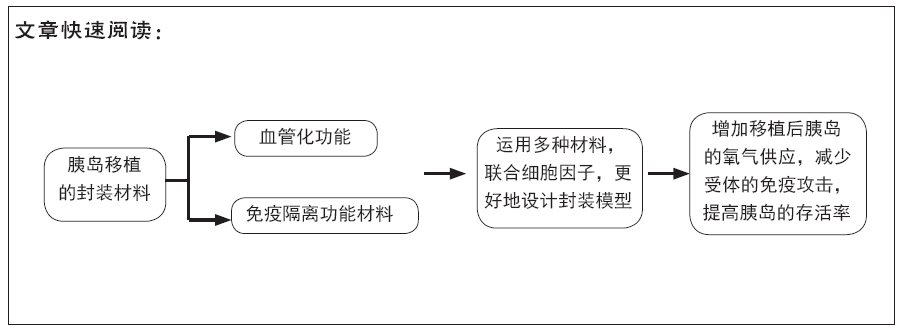
文题释义:
胰岛移植:是指将从供者胰腺中分离出来的胰岛移植到受者体内,从而重建受者的胰岛素分泌功能,使其脱离使用胰岛素的一种治疗方法。
胰岛移植封装材料:指可用于胰岛封装的天然高分子或合成高分子等生物材料,具有在胰岛表面营造免疫隔离的微环境、促进移植后局部血管的生成和增加移植后的黏附性等功能。
背景:近年研究表明,用天然或合成材料将胰岛移植物封装起来在移植物表面形成一个具有免疫隔离功能的屏障,不仅能在一定程度上减少免疫抑制剂的全身使用,而且能让异种来源的胰岛成为临床移植供源。
目的:介绍胰岛移植封装材料的研究进展,描述几种胰岛封装模型,并讨论当前的研究重点和未来的发展趋势。
方法:由第一作者以“islet encapsulation,islet transplantation biomaterials,islet transplantation hydrogel”为关键词,检索PubMed、Web of Science数据库中相关文献。初检测文章447篇,筛选后纳入89篇。
结果与结论:用水凝胶包裹胰岛进行胰岛移植主要有2方面不足:一是受体免疫排斥反应的攻击,二是内部氧供和营养运输的不足。单独使用合成或天然生物材料封装胰岛并不能很好地解决这2个问题,所以必须对生物材料进行修饰。目前的胰岛水凝胶模型都倾向于将合成生物材料和天然生物材料联合起来,充分发挥它们的优势。除此之外,一些免疫调节药物、促血管生成因子或促胰岛生长相关因子等也可以加入到生物材料中,并且可以联合其他细胞共移植。如何巧妙地运用多种策略来解决上述问题是未来研究的关键。
中图分类号:
引用本文
柏 雪, 王 彬, 何斯荣. 胰岛移植物封装水凝胶材料研究的重点和应用优势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(10): 1585-1591.
Bai Xue, Wang Bin, He Sirong. Research focus and application advantages in encapsulating biomaterial for islet transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1585-1591.
2.2 胰岛封装材料概述 水凝胶是一种具有良好性能的材料,在组织工程和药物传递等领域有着广泛的应用。根据其来源和聚合性质,水凝胶可分为天然水凝胶和合成水凝胶。天然水凝胶包括纤维蛋白、纤连蛋白、胶原、海藻酸盐、琼脂糖、壳聚糖、透明质酸、蚕丝蛋白等;合成水凝胶包括聚乙二醇、聚乙二醇-聚乳酸、二丙烯酸酯、聚乙烯醇、羟乙酯水凝胶等[15]。在天然材料中,海藻酸钠是一种起源于褐藻的多聚糖,其具有良好的生物相容性,并且能在温和条件下与两性阳离子络合,被广泛用作胰岛移植的封装材料。海藻酸钠在成胶的状态下形成的筛孔是纳米级的[16],能够允许胰岛素和小分子物质扩散,阻止大分子物质的转运。但是由于海藻酸盐是来自于自然资源,多聚物的性质并不一致,并且可能含有残留的内毒素。FENORADOSOA等[17]的研究也表明,海藻酸盐自身也能触发一定程度的纤维化,所以目前对海藻酸钠的使用还存在一些顾虑。由于合成水凝胶的孔隙率、稳定性、机械强度和生物相容性等性能都可以调节,所以合成水凝胶在组织工程中比天然聚合物水凝胶更具有优势[18]。在众多水凝胶中,聚乙二醇作为细胞封装的材料有许多优点,比如成胶条件温和、可模拟基质、可隐藏表面抗原、可被生物制剂修饰、亲水性好、污染性低等,所以目前认为聚乙二醇是较好的一种移植物表面材料[12]。天然水凝胶与合成水凝胶各有优缺点,在设计胰岛移植物封装水凝胶模型时充分考虑天然水凝胶的优缺点,结合二者的优势是不错的策略。
2.3 聚乙二醇与胰岛细胞表面结合的方法 聚乙二醇这种水凝胶材料结合胰岛细胞的常用方法有:光交联结合法、共价交联结合法及疏水键结合法。①光交联:聚乙二醇可通过紫外线交联成水凝胶。将胰岛置于含有光引发剂(如伊红Y、三乙醇胺)的溶液中光引发剂会吸附于胰岛细胞膜上,再将胰岛置于聚乙二醇前体溶液中,在紫外线的照射下聚乙二醇会在胰岛表面交联成网状。用这种方法将聚乙二醇固定到胰岛表面,形成交联网的效率、厚度和筛孔大小可以根据引发剂的种类和浓度、紫外光照射的时间和强度、聚乙二醇的单分子质量来进行调节[19]。而且运用这种方法交联胰岛细胞的活性可以达到90%以上,不影响后续的胰岛移植。②共价交联:末端带有活性酯基(如N-羟基丁二酰亚胺)的聚乙二醇可以实现共价交联。聚乙二醇末端酯基能够和细胞表面蛋白的游离氨基形成酰胺键[12],从而使聚乙二醇结合到胰岛细胞膜上。运用这种共价交联将聚乙二醇与胰岛结合起来的方式比物理结合方式更加稳定,虽然以共价键的方式交联聚乙二醇能够较好地保持胰岛的活性和胰岛素的分泌能力,但这种交联方式有可能会损伤胰岛细胞膜表面的结构[20-21]。另外,胰岛细胞膜蛋白可以自由翻转,不能为聚乙二醇共价交联提供长期的膜表面结构支持[12]。③疏水键结合法:将脂质与聚乙二醇结合起来可以形成脂质-聚乙二醇链,该链能够通过疏水的烷基尾自发地结合到细胞的磷脂双分子层上,从而达到封装胰岛的效果。TERAMURA与IWATA等[22-25]研究团队基于这种方法开发了一个多功能的胰岛封装平台,这种封装方法不会影响胰岛的活性。而且他们还通过添加了其他的多聚物(比如聚乙烯醇、海藻酸盐或其他的聚乙二醇衍生物)进一步优化了这种封装结构,但是这种疏水结合会逐渐从胰岛细胞表面脱离下来,也达不到长期封装胰岛的效果[12]。
有研究表明,胰岛能够通过天然生物材料中的整合素α1、α3和β1来接受信号[26-27],而合成多聚材料不能完全模拟复杂的天然组织,所以需要使用细胞外基质蛋白(如胶原)或短肽来提高合成材料与胰岛细胞的黏附效率[28-30]。为了使合成多聚体能模拟天然多聚体的功能,合成多聚体经过化学修饰后可以跟胰岛细胞共价交联在一起[31]。
2.4 水凝胶支架的分类 根据支架分类标准的不同,胰岛移植物封装的水凝胶支架有不同的分类方法。按照胰岛的封装量来分类可以分为大量封装、微量封装和纳米封装。大量封装是将足够当量的胰岛封装在一个较大的移植材料中,但是由于大量封装的表面积与体积之比较低,不利于营养物质和氧气的扩散,而且血糖和胰岛素的交换也将受到影响。大量封装最大的优点是移植后能够将胰岛固定在移植装置中,胰岛不会在移植部位游离,而且移植后也可以取出[32]。微量封装是指每个封装结构直径均低于1 mm,在半透膜里面只能包裹上一两个胰岛细胞团[33-36]。微量封装克服了大量封装的缺点,所以微量封装移植后的成功率较高。纳米封装指的是在胰岛细胞表面进行层层组装,形成厚度为纳米级别的[37]、具有特定功能的薄膜,从而封装胰岛。纳米封装的优点是纳米薄膜一般对胰岛的存活率不造成影响[38]。另外,根据水凝胶支架是否具有免疫屏障作用也可分为胰岛移植免疫隔离系统和胰岛移植免疫开放系统。免疫隔离系统是指在胰岛表面形成一层免疫隔离屏障或者移植到免疫豁免部位[32],最终可以减弱免疫排斥反应,移植受体可以免于免疫抑制剂的使用。目前研究发现,在小动物身上进行同种胰岛免疫隔离系统移植时可以不使用免疫抑制剂[39],但在大型动物或者患者中进行时仍然必须使用免疫抑制剂[14]。胰岛移植免疫开放系统虽然不能建立起免疫隔离的屏障,但是移植物能与机体进行更好的营养物质交换,移植物的新生血管更容易长入,可以很好地保证胰岛移植物的供氧和功能[12]。
2.5 水凝胶封装胰岛的优化策略 用水凝胶包裹胰岛进行胰岛移植目前主要有2方面不足,一是受体免疫排斥反应的攻击,二是内部氧供和营养运输的不足。胰岛素是直径为2 nm的单体或者直径为3.5 nm的六聚体[40-41],而普通细胞的直径一般为微米级,如果要实现生物材料的免疫隔离功能,那么免疫隔离屏障的筛孔必须在两者之间,这样才具有合适的选择透过性[12]。聚乙二醇可以通过光引发剂交联在胰岛细胞的表面,并且通过改变一系列的参数来调整交联的厚度和筛孔的大小,从而只允许葡萄糖、溶解的气体分子、胰岛素和小分子代谢物通过[19],将IgG、IgM和C1q等免疫分子隔离在移植物之外。在胰岛移植物血管生成能力的研究中发现,直径为20 nm筛孔的促血管生成能力要比5 μm的筛孔材料降低近100倍[42],因此在设计水凝胶屏障时对孔径大小需要特别注意。另外,组织内氧气的扩散距离大约为100 μm[43],而胰岛细胞团的平均直径为200 μm,所以用水凝胶封装后的胰岛体积不能过大,否则会极大影响胰岛的活性。
为了解决胰岛移植物封装的问题,水凝胶需要具备稳定的细胞结合能力、免疫隔离能力、促血管生成能力、组织微环境融入能力等[15]。虽然合成水凝胶缺乏生物容性功能,但可以通过在其表面交联某些生物活性分子来进行补偿。常用于增加合成水凝胶功能的分子有血管内皮生长因子、骨形成蛋白及各种活性肽。由于生物材料还可以作为药物控释载体,如果将生物活性分子引入封装材料中还可以提升对生物活性分子释放时间和空间的控制能力[12]。细胞外基质蛋白中的精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸肽(RGD肽)能够和胰岛细胞表面的整合素结合,从而产生细胞内信号促进胰岛细胞的存活和胰岛素的释放,所以用RGD肽修饰封装材料再用于胰岛移植能够极大提高胰岛移植的效果[44]。胰高血糖素样肽不仅能够刺激胰岛细胞分泌胰岛素,还能够促进胰岛β细胞的增殖,抑制其凋亡[45-46]。胰高血糖素样肽修饰过的聚乙二醇水凝胶材料可以有效抑制炎症因子介导的胰岛β细胞凋亡[47]。胰岛素样生长因子是β细胞分泌的一种激素,用胰岛素样生长因子修饰移植物封装材料能够促进胰岛的存活和其分化,并提高胰岛对血糖的反应[48-49]。如果将免疫活性分子引入到水凝胶封装材料中,还可以实现对胰岛移植物的免疫调节。如将带有死亡受体配体FasL的纳米微粒与胰岛进行共移植,可以显著降低受体的免疫攻击,延长胰岛移植物的存活时间[50]。用抗CD4的聚乙二醇-聚乳酸纳米颗粒可以将白血病抑制因子靶向运输给T细胞,能刺激T细胞向调节性T细胞方向分化[51]。当然,胰岛移植物会诱发受体的固有免疫应答,导致异物反应的发生,在移植物周围形成纤维囊[52],不利于移植物的存活和胰岛功能的发挥。巨噬细胞是异物反应的重要参与者[53],通过在材料中加入某些细胞因子促进巨噬细胞向抗炎的M2型方向极化,或者采用自身可以诱导巨噬细胞极化的纳米材料也是缓解异物反应的手段[54],能够达到调节局部炎症反应的作用[55]。ZAKERI SIAVASHANI等[56]制作了一种具有免疫调节功能的蚕丝支架,在支架上负载烟酸进行移植,发现能够极大地降低异物反应。
除了将生物活性分子与水凝胶结合以提高胰岛封装的功能外,水凝胶也可以作为连接媒介将其他细胞与胰岛进行共移植。由于一些细胞可以分泌多种免疫调节的生物因子,所以这种多细胞共移植的方案比单纯负载生物活性分子的方法更具有优势[12]。如将胰岛与Tregs进行共移植,植入的Tregs能够建立免疫耐受,可以提高胰岛移植的效果。间充质干细胞是一种多功能干细胞,将它同胰岛移植联合起来,能够产生多方面的作用[57]。KUPPAN等[58]将人脂肪来源的间充质干细胞与新生猪胰岛共移植到糖尿病小鼠的皮下和肾包膜内,发现相比于单独移植胰岛,共移植间充质干细胞能够显著提高小鼠的糖耐量,血清猪胰岛素水平也更高。在缺氧条件下将间充质干细胞与胰岛进行混合培养,可显著诱导胰岛的抗凋亡信号分子和抗缺氧分子的表达[59-60]。将间充质干细胞与胰岛进行共移植不仅可以加快改善受体的血糖控制,还能够提高胰岛移植物内的血管密度[61]。当然,间充质干细胞除了能改善胰岛存活和促进血管生成以外,还具有免疫调节功能[62]。当它与胰岛共移植时,既能够显著诱导Treg分泌白细胞介素10减少移植物的炎症细胞浸润[63],还能够抑制自然杀伤细胞的活性[62]。
2.6 胰岛的水凝胶封装模型
2.6.1 双层结构水凝胶封装模型 MARCHIOLI等[64]以聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯为基础,联合多种天然高分子材料设计了一种包含胰岛层和血管层的双层结构水凝胶模型,该模型可以促进胰岛移植物的血管重建,目前有2种设计方案。第一种方案是先将胰岛细胞、Ⅳ型胶原和层粘连蛋白加入聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯溶液中,运用光引发剂2959在356 nm的紫外线下将聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯交联成网,由此制作成封装模型的胰岛层;血管层则用水凝胶作为生长因子的运载工具,在聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯成胶之前把血管内皮生长因子和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子加入到巯基化的明胶、肝素和透明质酸混合液中,然后使用交联剂使聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯成胶形成血管层;胰岛层和血管层之间通过迈克尔加成反应使两者共价结合,使这两层成为一个多功能的整体。第二种方案是先用聚乙二醇将胰岛封装成胶囊,再将其嵌入血管层中。两种方案都能保证生长因子持续释放14 d以上,并且过程中没有释放高峰出现。这种双层设计模型的优势在于将聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯水凝胶与天然高分子材料及多种生长因子结合在一起,形成了一个多功能结构。透明质酸、胶原和层粘连蛋白可以通过与整合素和CD44等特异性受体结合来增加聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯水凝胶的细胞黏附力,有利于维持胰岛的空间结构[65]。聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯层加入巯基化肝素、透明质酸、明胶等细胞外基质成分,不仅能够增加了材料的细胞黏附性,使胰岛附近的内皮细胞重新排列,也可以为生长因子的缓释提供载体,最终到达促进血管生成的作用。但这类封装模型对胰岛功能会有一定的影响,如双层结构模型的厚度为3 mm,不利营养的扩散;胰岛细胞表面的聚乙二醇化可能使葡萄糖感应相关蛋白(如GLUT2受体)发生构象变化[66],阻断高血糖信号向细胞内的传递。因此在设计这类胰岛封装模型时,需要重点考虑偶联的聚乙二醇浓度、反应基团、聚合链的长度、偶联反应中的胰岛数量及状态等。
2.6.2 双夹层结构封装模型 WEAVER等[67]用末端马来酰亚胺化的聚乙二醇大分子单体,设计了一种双夹层结构的胰岛移植模型。该模型的核心层是由不可降解的交联剂二巯基聚乙二醇交联聚乙二醇得到,结构稳定,用于封装胰岛。核心层外部包裹可降解的血管层,血管层是由可降解的交联剂双半胱氨酸肽VPM或GDQ交联聚乙二醇得到的,并且加入了血管内皮生长因子。这种可降解的血管层能促进血管形成,在降解之后观察发现核心层表面的血管也有所增加。将此胰岛封装模型植入大鼠大网膜14周后,核心层依然能保持相对的稳定,体、内外实验均表明,这种模型的稳定性和转运效率都与传统海藻酸盐微胶囊相当。聚乙二醇封装过的胰岛相比于未封装的胰岛对于血糖的反应性有所降低,但WEAVER等在该模型的核心层中加入RGD肽可以改善聚乙二醇封装胰岛导致的血糖反应性差的缺点。该模型设计的优势在于可降解水凝胶外层增加了核心层形成的血管的密度和长度,在封装模型的表面和内部均产生更大的氧张力,从而促进水凝胶核心层中胰岛细胞的生存。
2.6.3 丙交酯乙交酯支架负载模型 SALVAY等[68]运用气体发泡的方法将丙交酯和乙胶酯以75∶25的比例制成丙交酯乙交酯水凝胶支架[69],并将丙交酯乙交酯水凝胶支架分别负载细胞外基质相关蛋白(如Ⅳ型胶原、纤连蛋白、层粘连蛋白332)和血清蛋白56,然后再将胰岛吸附到各支架上。细胞外基质蛋白能够增加支架的蛋白黏附特性,从而保持胰岛的正常结构,可防止胰岛脱落[70]。将该模型移植到同系小鼠附睾的脂肪垫上,40周后发现负载IV型胶原的移植物依然能够维持受体正常血糖水平。对移植物进行免疫组化发现,用支架负载细胞外基质蛋白能够促进移植物中内皮细胞的生长和血管的重建。
2.6.4 逐层组装的细胞球模型 FUKUDA等[71]建立了一种逐层组装的胰岛封装技术,这种技术是将MIN-6细胞反复与纤连蛋白和明胶溶液混合,使得细胞表面能够被纤连蛋白和明胶逐层包裹,最终使MIN-6细胞聚集制成形似胰岛的细胞团。这种MIN-6细胞球直径大概为300 μm,略大于最佳胰岛细胞团的直径(<250 μm)[72-73],但是这种MIN-6细胞球的氧供和营养物质交换并不受影响。这种封装细胞的技术效率很高,可以保证98.3%的MIN-6胰岛细胞被成功封装,而且也不会对胰岛细胞造成损伤。将封装好的MIN-6细胞球移植入同系糖尿病小鼠的肾包囊中,移植35 d后发现胰岛移植物的高糖刺激反应性非常好,使用这种逐层封装的胰岛细胞球移植比不封装的胰岛细胞团能更好地控制糖尿病小鼠血糖。
2.6.5 胰岛多层修饰封装模型 HAQUED等[74]巧妙地用聚乙二醇衍生物设计了一种可以对猪胰岛表面进行多层修饰的方法。第一层由巯基-6臂-聚乙二醇-脂质和明胶-儿茶酚通过疏水作用锚定在胰岛细胞膜的脂质双分子层上,直接与胰岛细胞膜相连增强封装的稳定性,防止胰岛细胞解离;第二层旨在模拟细胞外基质层,并与第一层的巯基形成共价键连接在一起;第三层包括3种聚乙二醇层,分别是6臂-聚乙二醇-巯基层、6臂-聚乙二醇-儿茶酚胺层和线性聚乙二醇-巯基层,其中6臂-聚乙二醇-儿茶酚胺层可以形成免疫隔离屏障,而最外面的线性聚乙二醇-巯基层可以防止未交联的儿茶酚胺基团与体内蛋白质发生反应[75]。这3层聚乙二醇之间相互通过化学键结合使胰岛封装结构更为稳定。这种胰岛表面多层修饰方法形成的封装很薄(0.5 μm),有利于氧气和营养物质的交换,也使得胰岛更灵敏地对葡萄糖产生反应,所以相比海藻酸盐封装胰岛更具有优势。另外,封装厚度的降低也会减少血小板的聚集和血液凝固,从而降低经血液介导的炎性反应。将这种修饰封装的猪胰岛移植到糖尿病小鼠肾包膜下,能维持糖尿病小鼠正常血糖(13.0±1.8)d,展示出这种修饰封装的胰岛具有很强的免疫隔离作用。这种多层修饰封装在不影响胰岛存活和功能的条件下,既可以阻止胰岛的分散又能够达到免疫隔离的作用。当然这种封装方法的免疫隔离作用是有限的,并不能完全抑制免疫细胞的活化,所以必须联合使用免疫抑制剂才能达到更好的移植效果。
2.6.6 星状聚乙二醇-肝素薄膜封装模型 LOU等[76]研制了一种能与胰岛结合的星状聚乙二醇-肝素薄膜。此方法先利用肝素-N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺和星状8臂聚乙二醇-NH2合成肝素聚乙二醇薄膜,肝素聚乙二醇薄膜再通过N-羟基丁二酰亚胺与胰岛表面的氨基基团发生共价结合,从而封装胰岛细胞。这种薄膜的优点在于薄膜的厚度仅为30 nm,结合到胰岛表面之后对胰岛的影响很小。肝素的加入能够促进胰岛移植物的血管生成,并有利于胰岛释放胰岛素。另外,这种封装模型还具有免疫调节作用,主要体现在2方面:薄膜表面有直径100-200 nm的筛孔,可以有效地防止免疫细胞的攻击;肝素聚乙二醇薄膜具有抗凝血的作用,能够降低经血液介导的炎性反应。虽然封装后的胰岛在体外培养14 d依然具有良好的活性和功能,但该封装模型尚未进行体内实验验证。LOU等的实验中设计了3组不同肝素含量的聚乙二醇-肝素(3,7.5,15 g/L),发现用高浓度15 g/L组的聚乙二醇-肝素封装胰岛时胰岛的活性最好,而3 g/L组的胰岛对高低血糖刺激最敏感,分泌胰岛素的能力最强,这说明最适宜胰岛封装的肝素浓度还亟待探索。

| [1] VANTYGHEM MC, DE KONING EJP, PATTOU F, et al. Advances in Β-Cell Replacement Therapy for the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Lancet. 2019;394(10205):1274-1285. [2] ESPONA-NOGUERA A, CIRIZA J, CANIBANO-HERNANDEZ A, et al. Review of Advanced Hydrogel-Based Cell Encapsulation Systems for Insulin Delivery in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(11):597. [3] WEBSTER AC, HEDLEY JA, ANDERSON PF, et al. Australia and New Zealand Islet and Pancreas Transplant Registry Annual Report 2018-Islet Donations, Islet Isolations, and Islet Transplants. Transplant Direct.2019;5(2):e421. [4] LILJEBACK H, QUACH M, CARLSSON PO, et al. Fewer Islets Survive from a First Transplant Than a Second Transplant: Evaluation of Repeated Intraportal Islet Transplantation in Mice. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(11): 1455-1460. [5] GOLEBIEWSKA JE, BACHUL PJ, WANG LJ, et al. Validation of a New North American Islet Donor Score for Donor Pancreas Selection and Successful Islet Isolation in a Medium-Volume Islet Transplant Center. Cell Transplant.2019;28(2):185-194. [6] WILLIAMS J, JACUS N, KAVALACKAL K, et al. Over Ten-Year Insulin Independence Following Single Allogeneic Islet Transplant without T-Cell Depleting Antibody Induction. Islets.2018;10(4):168-174. [7] SHAPIRO AM, LAKEY JR, RYAN EA, et al. Islet Transplantation in Seven Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Using a Glucocorticoid-Free Immunosuppressive Regimen. N Engl J Med.2000;343(4):230-238. [8] JAMES SHAPIRO AM, POKRYWCZYNSKA M, RICORDI C. Clinical Pancreatic Islet Transplantation. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(5): 268-277. [9] RYAN EA, PATY BW, SENIOR PA, et al.Five-Year Follow-up after Clinical Islet Transplantation.Diabetes.2005;54(7):2060-2069. [10] PEPPER AR, BRUNI A, SHAPIRO AMJ. Clinical Islet Transplantation: Is the Future Finally Now? Curr Opin Organ Transplant.2018;23(4):428-439. [11] DESAI T, SHEA LD.Advances in Islet Encapsulation Technologies. Nat Rev Drug Discov.2017;16(5):367. [12] ERNST AU, BOWERS DT, WANG LH, et al. Nanotechnology in Cell Replacement Therapies for Type 1 Diabetes. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2019; 139:116-138. [13] KORSGREN O. Islet Encapsulation: Physiological Possibilities and Limitations. Diabetes.2017;66(7):1748-1754. [14] FARNEY AC, SUTHERLAND DE, OPARA EC. Evolution of Islet Transplantation for the Last 30 Years. Pancreas.2016;45(1):8-20. [15] SHRESTHA P, REGMI S, JEONG JH. Injectable Hydrogels for Islet Transplantation: A Concise Review. J Pharm Investig.2019;50(1):29-45. [16] SCHASCHKOW A, SIGRIST S, MURA C, et al. Extra-Hepatic Islet Transplantation: Validation of the H-Omental Matrix Islet Filling (Homing) Technique on a Rodent Model Using an Alginate Carrier. Cell Transplant.2018;27(8):1289-1293. [17] FENORADOSOA TA, ALI G, DELATTRE C, et al. Extraction and Characterization of an Alginate from the Brown Seaweed Sargassum Turbinarioides Grunow. J Appl Phycol.2010;22(2):131-137. [18] GUAN X, AVCI‐ADALI M, ALARçIN E, et al. Development of Hydrogels for Regenerative Engineering. Biotechnol J. 2017;12(5):1600394. [19] CRUISE GM, SCHARP DS, HUBBELL JA. Characterization of Permeability and Network Structure of Interfacially Photopolymerized Poly (Ethylene Glycol) Diacrylate Hydrogels. Biomaterials.1998;19(14):1287-1294. [20] WILSON JT, HALLER CA ,QU Z, et al. Biomolecular Surface Engineering of Pancreatic Islets with Thrombomodulin. Acta Biomater.2010;6(6): 1895-1903. [21] ORIVE G, HERNáNDEZ RM, GASCóN AR, et al. Encapsulation of Cells in Alginate Gels. In Guisan JM.Immobilization of Enzymes and Cells.Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2006:345-355. [22] YAMAMOTO T, TERAMURA Y, ITAGAKI T, et al. Interaction of Poly (Ethylene Glycol)-Conjugated Phospholipids with Supported Lipid Membranes and Their Influence on Protein Adsorption. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2016;17(1):677-684. [23] TERAMURA Y, OOMMEN OP, OLERUD J, et al. Microencapsulation of Cells, Including Islets, within Stable Ultra-Thin Membranes of Maleimide-Conjugated Peg-Lipid with Multifunctional Crosslinkers. Biomaterials.2013;34(11):2683-2693. [24] TERAMURA Y, IWATA H. Improvement of Graft Survival by Surface Modification with Poly (Ethylene Glycol)-Lipid and Urokinase in Intraportal Islet Transplantation. Transplantation. 2011;91(3):271-278. [25] TERAMURA Y,IWATA H. Islets Surface Modification Prevents Blood-Mediated Inflammatory Responses. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19(7): 1389-1395. [26] KRISHNAMURTHY M, LI J, FELLOWS GF, et al. Integrin Α3, but Not Β1, Regulates Islet Cell Survival and Function Via Pi3k/Akt Signaling Pathways. Endocrinology.2011;152(2):424-435. [27] KAIDO T, YEBRA M, CIRULLI V, et al. Regulation of Human Β-Cell Adhesion, Motility, and Insulin Secretion by Collagen Iv and Its Receptor Α1β1. J Biol Chem.2004;279(51):53762-53769. [28] VLAHOS AE, COBER N, SEFTON MV. Modular Tissue Engineering for the Vascularization of Subcutaneously Transplanted Pancreatic Islets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(35):9337-9342. [29] ZHU Q, LU C, JIANG X, et al. Using Recombinant Human Collagen with Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor to Provide a Simulated Extracellular Matrix Microenvironment for the Revascularization and Attachment of Islets to the Transplantation Region. Front Pharmacol. 2020;10: 1536-1536. [30] MINARDI S, GUO M, ZHANG X, et al. An Elastin-Based Vasculogenic Scaffold Promotes Marginal Islet Mass Engraftment and Function at an Extrahepatic Site. J Immunol Regen Med.2019;3:1-12. [31] ECHALIER C, JEBORS S, LACONDE G, et al. Sol–Gel Synthesis of Collagen-Inspired Peptide Hydrogel. Mater Today.2017;20(2):59-66. [32] AN D, CHIU A, FLANDERS JA, et al. Designing a Retrievable and Scalable Cell Encapsulation Device for Potential Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2018;115(2):E263-E272. [33] SCHARP DW, MARCHETTI P. Encapsulated Islets for Diabetes Therapy: History, Current Progress, and Critical Issues Requiring Solution. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2014;67-68:35-73. [34] PARETA R, MCQUILLING JP, FARNEY AC, et al. Bioartificial Pancreas: Evaluation of Crucial Barriers to Clinical Application. In book: Organ Donation and Transplantation - Public Policy and Clinical Perspectives.2012:241-266. [35] O’SULLIVAN ES, VEGAS A, ANDERSON DG, et al. Islets Transplanted in Immunoisolation Devices: A Review of the Progress and the Challenges That Remain. Endocr Rev.2011;32(6):827-844. [36] JAIN K, ASINA S, YANG H, et al. Glucose Control and Long-Term Survival in Biobreeding/Worcester Rats after Intraperitoneal Implantation of Hydrophilic Macrobeads Containing Porcine Islets without Immunosuppression. Transplantation.1999;68(11):1693-1700. [37] SYED F, BUGLIANI M, NOVELLI M, et al. Conformal Coating by Multilayer Nano-Encapsulation for the Protection of Human Pancreatic Islets: In-Vitro and in-Vivo Studies. Nanomedicine.2018;14(7):2191-2203. [38] DIMITRIOGLOU N, KANELLI M, PAPAGEORGIOU E, et al. Paving the Way for Successful Islet Encapsulation. Drug Discov Today.2019;24(3): 737-748. [39] SELAWRY HP, WHITTINGTON K. Extended Allograft Survival of Islets Grafted into Intra-Abdominally Placed Testis. Diabetes.1984;33(4): 405-406. [40] BRANGE J, OWENS DR, KANG S, et al. Monomeric Insulins and Their Experimental and Clinical Implications. Diabetes Care.1990;13(9): 923-954. [41] HOSOYA O, CHONO S, SASO Y, et al. Determination of Diffusion Coefficients of Peptides and Prediction of Permeability through a Porous Membrane. J Pharm Pharmacol.2004;56(12):1501-1507. [42] SONG S, ROY S. Progress and Challenges in Macroencapsulation Approaches for Type 1 Diabetes (T1d) Treatment: Cells, Biomaterials, and Devices. Biotechnol Bioeng.2016;113(7):1381-1402. [43] YOLCU ES, ZHAO H, BANDURA-MORGAN L, et al. Pancreatic Islets Engineered with Sa-Fasl Protein Establish Robust Localized Tolerance by Inducing Regulatory T Cells in Mice. J Immunol.2011;187(11): 5901-5909. [44] LEE KM, KIM JH, CHOI ES, et al. Rgd-Containing Elastin-Like Polypeptide Improves Islet Transplantation Outcomes in Diabetic Mice. Acta Biomater. 2019;94:351-360. [45] ZHU L, DATTAROY D, PHAM J, et al. Intra-Islet Glucagon Signaling Is Critical for Maintaining Glucose Homeostasis. JCI Insight.2019;5. [46] SVENDSEN B, LARSEN O, GABE MBN, et al. Insulin Secretion Depends on Intra-Islet Glucagon Signaling. Cell Rep.2018;25(5):1127-1134.e2. [47] LIN CC,ANSETH KS. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Functionalized Peg Hydrogels Promote Survival and Function of Encapsulated Pancreatic Β-Cells. Biomacromolecules.2009;10(9):2460-2467. [48] PETRIK J, ARANY E, MCDONALD T, et al. Apoptosis in the Pancreatic Islet Cells of the Neonatal Rat Is Associated with a Reduced Expression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Ii That May Act as a Survival Factor. Endocrinology.1998;139(6):2994-3004. [49] LEE KL, AITKEN JF, HSU HL, et al. Glucoregulatory Activity of Vesiculin in Insulin Sensitive and Resistant Mice. Peptides.2019;116:1-7. [50] HEADEN DM, WOODWARD KB, CORONEL MM, et al. Local Immunomodulation Fas Ligand-Engineered Biomaterials Achieves Allogeneic Islet Graft Acceptance. Nat Mater.2018;17(8):732-739. [51] WANG W, SHAHZAD KA, LI M, et al. An Antigen-Presenting and Apoptosis-Inducing Polymer Microparticle Prolongs Alloskin Graft Survival by Selectively and Markedly Depleting Alloreactive Cd8(+) T Cells. Front Immunol.2017;8:657. [52] ANDERSON JM,RODRIGUEZ A, CHANG DT.Foreign Body Reaction to Biomaterials.Seminars in Immunology.2008;20(2):86-100. [53] BRYERS JD, GIACHELLI CM, RATNER BD. Engineering Biomaterials to Integrate and Heal: The Biocompatibility Paradigm Shifts. Biotechnol Bioeng.2012;109(8):1898-1911. [54] SHAYAN M,PADMANABHAN J,MORRIS AH,et al.Nanopatterned Bulk Metallic Glass-Based Biomaterials Modulate Macrophage Polarization.Acta Biomater.2018;75:427-438. [55] VAN PUTTEN SM, PLOEGER DT, POPA ER, et al. Macrophage Phenotypes in the Collagen-Induced Foreign Body Reaction in Rats. Acta Biomater.2013;9(5):6502-6510. [56] ZAKERI SIAVASHANI A, MOHAMMADI J, MANIURA-WEBER K, et al. Silk Based Scaffolds with Immunomodulatory Capacity: Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Nicotinic Acid. Biomater Sci.2019;8(1):148-162. [57] FIGLIUZZI M, BONANDRINI B, SILVANI S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Help Pancreatic Islet Transplantation to Control Type 1 Diabetes. World J Stem Cells.2014;6(2):163-172. [58] KUPPAN P, SEEBERGER K, KELLY S, et al. Co-Transplantation of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Neonatal Porcine Islets within a Prevascularized Subcutaneous Space Augments the Xenograft Function. Xenotransplantation.2020:e12581. [59] PARK KS, KIM YS, KIM JH, et al. Influence of Human Allogenic Bone Marrow and Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secreting Trophic Factors on Atp (Adenosine-5’-Triphosphate)/Adp (Adenosine-5’-Diphosphate) Ratio and Insulin Secretory Function of Isolated Human Islets from Cadaveric Donor. Transplant Proc.2009;41(9):3813-3818. [60] LU Y, JIN X, CHEN Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Islets from Hypoxia/Reoxygenation‐Induced Injury. Cell Biochem Funct.2010; 28(8):637-643. [61] FIGLIUZZI M, CORNOLTI R, PERICO N, et al. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Islet Graft Function in Diabetic Rats. Transplant Proc.2009;41(5):1797-1800. [62] ISHIDA N, ISHIYAMA K, SAEKI Y, et al. Cotransplantation of Preactivated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Intraportal Engraftment of Islets by Inhibiting Liver Natural Killer Cells in Mice. Am J Transplant.2019; 19(10):2732-2745. [63] MADEC AM, MALLONE R, AFONSO G, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Nod Mice from Diabetes by Inducing Regulatory T Cells. Diabetologia. 2009;52(7):1391-1399. [64] MARCHIOLI G, ZELLNER L, OLIVEIRA C, et al. Layered Pegda Hydrogel for Islet of Langerhans Encapsulation and Improvement of Vascularization. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2017;28(12):195. [65] WANG R, ROSENBERG L. Maintenance of Beta-Cell Function and Survival Following Islet Isolation Requires Re-Establishment of the Islet-Matrix Relationship. J Endocrinol.1999;163(2):181-190. [66] WU L, FRITZ JD, POWERS AC. Different Functional Domains of Glut2 Glucose Transporter Are Required for Glucose Affinity and Substrate Specificity. Endocrinology.1998;139(10):4205-4212. [67] WEAVER JD, HEADEN DM, HUNCKLER MD, et al. Design of a Vascularized Synthetic Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Macroencapsulation Device for Islet Transplantation. Biomaterials.2018;172:54-65. [68] SALVAY DM, RIVES CB, ZHANG X, et al. Extracellular Matrix Protein-Coated Scaffolds Promote the Reversal of Diabetes after Extrahepatic Islet Transplantation. Transplantation.2008;85(10):1456-1464. [69] JANG JH, BENGALI Z, HOUCHIN TL, et al. Surface Adsorption of DNA to Tissue Engineering Scaffolds for Efficient Gene Delivery. J Biomed Mater Res A.2006;77(1):50-58. [70] SMINK AM, DE VOS P. Therapeutic Strategies for Modulating the Extracellular Matrix to Improve Pancreatic Islet Function and Survival after Transplantation. Curr Diab Rep.2018;18(7):39. [71] FUKUDA Y, AKAGI T, ASAOKA T, et al. Layer-by-Layer Cell Coating Technique Using Extracellular Matrix Facilitates Rapid Fabrication and Function of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Spheroids. Biomaterials. 2018;160: 82-91. [72] ICHIHARA Y, UTOH R, YAMADA M, et al. Size Effect of Engineered Islets Prepared Using Microfabricated Wells on Islet Cell Function and Arrangement. Heliyon.2016;2(6):e00129. [73] TANAKA H, TANAKA S, SEKINE K, et al. The Generation of Pancreatic Β-Cell Spheroids in a Simulated Microgravity Culture System. Biomaterials. 2013;34(23):5785-5791. [74] HAQUE MR, JEONG JH, BYUN Y. Combination Strategy of Multi-Layered Surface Camouflage Using Hyperbranched Polyethylene Glycol and Immunosuppressive Drugs for the Prevention of Immune Reactions against Transplanted Porcine Islets. Biomaterials.2016;84:144-156. [75] JUNG YS, JEONG JH, YOOK S, et al. Surface Modification of Pancreatic Islets Using Heparin-Dopa Conjugate and Anti-Cd154 Mab for the Prolonged Survival of Intrahepatic Transplanted Islets in a Xenograft Model. Biomaterials.2012;33(1):295-303. [76] LOU S, ZHANG X, ZHANG J, et al. Pancreatic Islet Surface Bioengineering with a Heparin-Incorporated Starpeg Nanofilm. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;78:24-31. [77] FORBES S, BOND AR, THIRLWELL KL, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Perivascular Cells Improve Human Pancreatic Islet Transplant Function by Increasing Vascularization. Sci Transl Med.2020;12(526). [78] FIGUEIREDO H, FIGUEROA ALC, GARCIA A, et al. Targeting Pancreatic Islet Ptp1b Improves Islet Graft Revascularization and Transplant Outcomes. Sci Transl Med.2019;11(497):11(497):eaar6294. [79] KELLY SH, SHORES LS, VOTAW NL, et al. Biomaterial Strategies for Generating Therapeutic Immune Responses. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2017; 114:3-18. [80] CLOTMAN K, JANSSENS K, SPECENIER P, et al. Programmed Cell Death-1 Inhibitor-Induced Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2018;103(9):3144-3154. [81] JACOBSEN LM, NEWBY BN, PERRY DJ, et al. Immune Mechanisms and Pathways Targeted in Type 1 Diabetes. Curr Diab Rep.2018;18(10):90. [82] QIN S, XU L, YI M, et al. Novel Immune Checkpoint Targets: Moving Beyond Pd-1 and Ctla-4. Mol Cancer.2019;18(1):155. [83] WAKELEY ME, GRAY CC, MONAGHAN SF, et al. Check Point Inhibitors and Their Role in Immunosuppression in Sepsis. Crit Care Clin. 2020; 36(1):69-88. [84] TSANG VHM, MCGRATH RT, CLIFTON-BLIGH RJ, et al. Response to Letter to the Editor for “Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Autoimmune Diabetes Is Distinct from Type 1 Diabetes”. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105(6):e2317-e2318. [85] ZAMMIT NW, WALTERS SN, SEEBERGER KL, et al. A20 as an Immune Tolerance Factor Can Determine Islet Transplant Outcomes. JCI Insight. 2019;4(21):e131028. [86] DOLOFF JC, VEISEH O, VEGAS AJ, et al. Colony Stimulating Factor-1 Receptor Is a Central Component of the Foreign Body Response to Biomaterial Implants in Rodents and Non-Human Primates. Nat Mater. 2017;16(6):671-680. [87] LIU X, CARTER SD, RENES MJ, et al. Development of a Coaxial 3d Printing Platform for Biofabrication of Implantable Islet-Containing Constructs. Adv Healthc Mater.2019;8(7):e1801181. [88] DUIN S, SCHUTZ K, AHLFELD T, et al. 3d Bioprinting of Functional Islets of Langerhans in an Alginate/Methylcellulose Hydrogel Blend. Adv Healthc Mater.2019;8(7):e1801631. [89] YANG J, ZHOU F, XING R, et al. Development of Large-Scale Size-Controlled Adult Pancreatic Progenitor Cell Clusters by an Inkjet-Printing Technique. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2015;7(21):11624-11630. |
| [1] | 蒋红英, 朱 亮, 余 曦, 黄 靖, 向小娜, 兰正燕, 何红晨. 富血小板血浆干预脊髓损伤患者压力性损伤的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [2] | 唐 辉, 姚志浩, 罗道文, 彭双麟, 杨双林, 王 浪, 肖金刚. 高脂高糖饮食结合链脲佐菌素建立2型糖尿病性骨质疏松症大鼠模型[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [3] | 王晗月, 李富荣, 杨晓菲, 胡巢凤. 高效靶向激活肝细胞内源基因直接重编程为胰岛样细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [4] | 何祥忠, 陈海云, 刘 军, 吕 阳, 潘建科, 杨文斌, 何静雯, 黄俊翰. 富血小板血浆联合微骨折对比微骨折治疗膝关节软骨病变的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [5] | 张 宾, 孙丽华, 张俊花, 刘玉三, 崔彩云. 改良翻瓣即刻种植有利于上颌前牙区的软硬组织重建[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 707-712. |
| [6] | 付拴虎, 秦 凯, 卢大汉, 覃海飚, 谷 金, 陈勇喜, 覃浩然, 韦家鼎, 伍 亮, 宋泉生. 载链霉素硫酸钙人工骨椎间孔镜下植入联合经皮置钉治疗腰椎结核[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 493-498. |
| [7] | 李文静, 李浩渤, 刘从娜, 程东梅, 陈惠珍, 张志勇. 不同生物活性支架治疗年轻恒牙再生牙髓活力的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 499-503. |
| [8] | 王玉姣, 刘 丹, 孙 嵩, 孙 勇. 改良型富血小板纤维蛋白复合双相磷酸钙可促进兔骨髓间充质干细胞的活性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [9] | 陈俊毅, 王 宁, 彭称飞, 朱伦井, 段江涛, 王 烨, 贝朝涌. 脱钙骨基质与慢病毒介导沉默P75神经营养因子受体转染骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [10] | 李晨杰, 吕林蔚, 宋 阳, 刘静娜, 张春秋. 预紧力作用下钛合金人工假体界面骨小梁形态参数测量与统计分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 516-520. |
| [11] | 孙 启, 周亚男, 董 鑫, 李 宁, 颜家振, 石浩江, 许 胜, 张 幖. 激光选区熔化钴铬烤瓷合金金瓷结合界面的特性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 521-525. |
| [12] | 柳 扬, 龚 毅, 范 伟. 构建靶向型Pluronic F127/芒柄花黄素纳米复合体系体外抗肝癌活性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| [13] | 周继辉, 姚 猛, 王岩松, 李新志, 周 游, 黄 卫, 陈文瑶. 新型纳米支架对神经干细胞生物行为及相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [14] | 张国梅, 祝 军, 胡 杨, 焦红卫. E-Max瓷嵌体三维有限元模型粘接界面应力分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 537-541. |
| [15] | 刘江锋. 纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合材料联合锁定钢板治疗股骨骨纤维异常增殖症[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
1.2 纳入和排除标准
纳入标准:①与胰岛移植封装有关的文献;②与胰岛移植水凝胶有关的研究。
排除标准:①内容重复的文献;②与主题相关性不高的文献。
1.3 质量评估 首先阅读所有检索文献,并对所有文献的主题进行评估。文献检索和筛选结果的输出采用文献的引用形式。
只依靠在胰岛表面形成一层物理免疫隔离屏障的封装模型,并不能完全保护胰岛不受宿主免疫系统的攻击[71]。随着药物控释高分子材料和免疫检查点药物的研究进展,将免疫耐受性药物与高分子材料相结合[79],通过材料将所负载的药物进行局部缓释能极大地提高移植物的免疫耐受能力,有利于移植胰岛的长期存活。目前已有临床研究证实,免疫调节性药物可以有效治疗1型糖尿病或者延缓1型糖尿病的发病[80-81]。如细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关蛋白4、程序性死亡受体1、程序性死亡配体及B、T淋巴细胞衰减因子、T细胞免疫球蛋白粘蛋白3、T细胞免疫球蛋白和ITIM结构域蛋白[82]、T细胞活化V结构域Ig抑制剂等免疫检查点是T淋巴细胞激活的关键调节分子[83],在维持中枢和外周免疫耐受中发挥重要作用[84]。泛素编辑酶A20也可以作为免疫耐受因子提高胰岛移植的效果。研究表明,泛素编辑酶A20在人胰岛中高表达时可有效降低炎症递质的水平,而对葡萄糖刺激的胰岛素分泌无影响[85]。集落刺激因子1受体在宿主对移植生物材料的异物反应中发挥了重要作用,在未来也可能作为应用局部免疫抑制药物的靶点[86]。
近年也有将生物材料制成生物墨水,运用3D打印技术模拟胰岛的微环境的研究,但是仍然处于起步阶段[87-89]。在今后的研究中可以将3D打印技术运用于胰岛封装中,促进胰岛移植物的存活。
对高分子材料进行更好的修饰,并将免疫检查点药物、促血管生成因子或促胰岛生存或功能的相关因子等巧妙地结合到生物材料中,并且联合可以促进胰岛功能的其他细胞共移植,设计出更合理的胰岛封装模型,使之成为有免疫隔离或耐受功能和血管生成功能的新材料,是未来使用生物材料封装胰岛进行移植的关键。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程

文题释义:#br# 胰岛移植:是指将从供者胰腺中分离出来的胰岛移植到受者体内,从而重建受者的胰岛素分泌功能,使其脱离使用胰岛素的一种治疗方法。#br# 胰岛移植封装材料:指可用于胰岛封装的天然高分子或合成高分子等生物材料,具有在胰岛表面营造免疫隔离的微环境、促进移植后局部血管的生成和增加移植后的黏附性等功能。
文章概述了近年来有关封装胰岛移植物的材料和封装策略的相关研究进展,列举了常用的几种胰岛移植物封装模型,对其封装的优缺点进行了总结,并对胰岛移植物的封装水凝胶的发展进行了展望,这些内容还未见其他文献有报道。还提出了有利于解决胰岛封装目前存在的问题的解决新策略,帮助读者在设计胰岛移植物封装水凝胶时,能够运用这些策略进行更好的构思。#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||