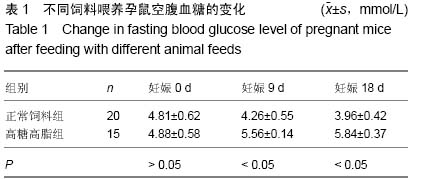
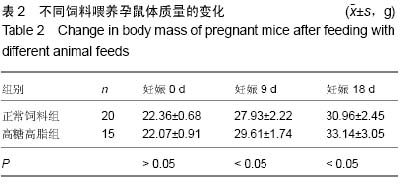
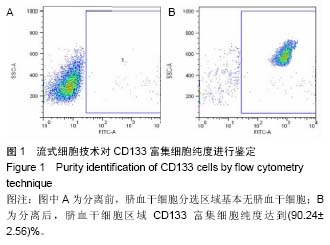
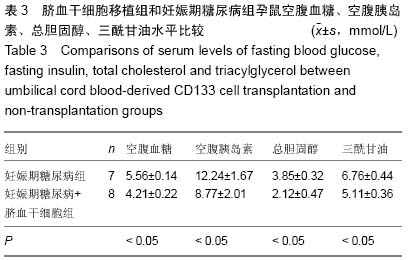
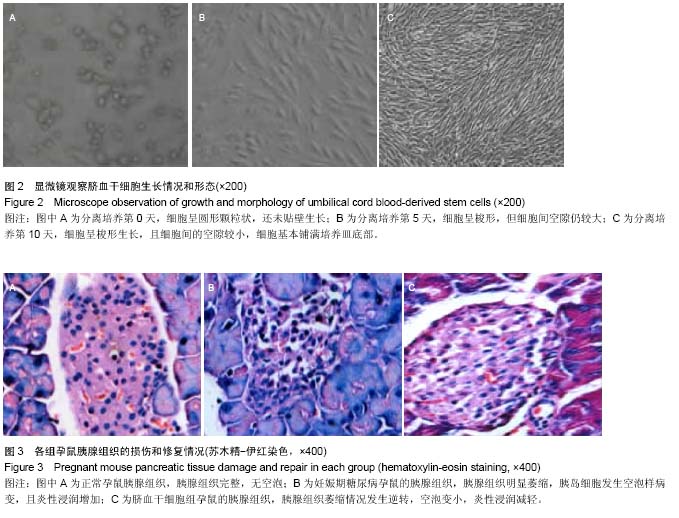
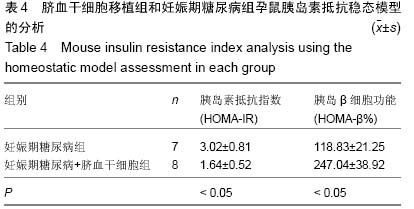
| [1] Wang G, Li Y, Wang Y, et al. Roles of the co-culture of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells with rat pancreatic cells in the treatment of rats with diabetes mellitus. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8(5):1389- 1396.
[2] Van Pham P, Thi-My Nguyen P, Thai-Quynh Nguyen A, et al. Improved differentiation of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-producing cells by PDX-1 mRNA transfection. Differentiation. 2014;87(5): 200-208.
[3] Qu H, Liu X, Ni Y, et al. Laminin 411 acts as a potent inducer of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into insulin-producing cells. J Transl Med. 2014;12:135.
[4] Fong CY, Tam K, Cheyyatraivendran S, et al. Human Wharton's jelly stem cells and its conditioned medium enhance healing of excisional and diabetic wounds. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(2):290-302.
[5] Boroujeni ZN, Aleyasin A. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells can secrete insulin in vitro and in vivo. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2014;61(2):82-92.
[6] Shen WC, Liang CJ, Wu VC, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells derived from Wharton's jelly of the umbilical cord reduces ischemia-induced hind limb injury in diabetic mice by inducing HIF-1α/IL-8 expression. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(9): 1408- 1418.
[7] Wang HW, Lin LM, He HY, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton's jelly differentiate into insulin-producing cells in vitro. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124(10):1534-1539.
[8] Phuc PV, Nhung TH, Loan DT, et al. Differentiating of banked human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-secreting cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011; 47(1):54-63.
[9] Acosta JC, Haas DM, Saha CK, et al. Gestational diabetes mellitus alters maternal and neonatal circulating endothelial progenitor cell subsets. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011;204(3): 254.e8-254.e15.
[10] Buemi M, Allegra A, D'Anna R, et al. Concentration of circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) in normal pregnancy and in pregnant women with diabetes and hypertension. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;196(1):68.e1-6.
[11] Hess DA, Meyerrose TE, Wirthlin L, et al. Functional characterization of highly purified human hematopoietic repopulating cells isolated according to aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. Blood. 2004;104(6):1648-1655.
[12] Chao KC, Chao KF, Fu YS, et al. Islet-like clusters derived from mesenchymal stem cells in Wharton's Jelly of the human umbilical cord for transplantation to control type 1 diabetes. PLoS One. 2008;3(1):e1451.
[13] Abbasi P, Shamsasenjan K, Movassaghpour Akbari AA, et al. The Effect of Baicalin as A PPAR Activator on Erythroid Differentiation of CD133(+)Hematopoietic Stem Cells in Umbilical Cord Blood. Cell J. 2015;17(1):15-26.
[14] Yang JF, Cao HC, Pan QL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from the human umbilical cord ameliorate fulminant hepatic failure and increase survival in mice. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2015;14(2):186-193.
[15] Radtke S, Görgens A, Kordelas L, et al. CD133 allows elaborated discrimination and quantification of haematopoietic progenitor subsets in human haematopoietic stem cell transplants. Br J Haematol. 2015;169(6):868-878.
[16] González-González M, Rito-Palomares M. Application of affinity aqueous two-phase systems for the fractionation of CD133(+) stem cells from human umbilical cord blood. J Mol Recognit. 2015;28(3):142-147.
[17] Qiu L, Onoyama S, Low HP, et al. Effect of preeclampsia on umbilical cord blood stem cells in relation to breast cancer susceptibility in the offspring. Carcinogenesis. 2015;36(1): 94-98.
[18] Zhang C, Zhou C, Wu XJ, et al. Human CD133-positive hematopoietic progenitor cells initiate growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(12): 2771-2777.
[19] Joseph M, Das M, Kanji S, et al. Retention of stemness and vasculogenic potential of human umbilical cord blood stem cells after repeated expansions on PES-nanofiber matrices. Biomaterials. 2014;35(30):8566-8575.
[20] González-González M, Rito-Palomares M, Méndez Quintero O. Partition behavior of CD133(+) stem cells from human umbilical cord blood in aqueous two-phase systems: In route to establish novel stem cell primary recovery strategies. Biotechnol Prog. 2014;30(3):700-707.
[21] Maslova EV, Andreeva ER, Andrianova IV, et al. Enrichment of umbilical cord blood mononuclears with hemopoietic precursors in co-culture with mesenchymal stromal cells from human adipose tissue. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2014;156(4): 584-589.
[22] Paczkowska E, Kaczyńska K, Pius-Sadowska E, et al. Humoral activity of cord blood-derived stem/progenitor cells: implications for stem cell-based adjuvant therapy of neurodegenerative disorders. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e83833.
[23] Kamei N, Kwon SM, Alev C, et al. Ex-vivo expanded human blood-derived CD133+ cells promote repair of injured spinal cord. J Neurol Sci. 2013;328(1-2):41-50.
[24] Shahaduzzaman M, Golden JE, Green S, et al. A single administration of human umbilical cord blood T cells produces long-lasting effects in the aging hippocampus. Age (Dordr). 2013;35(6):2071-2087.
[25] Vasilyev SA, Kubes M, Markova E, et al. DNA damage response in CD133 + stem/progenitor cells from umbilical cord blood: low level of endogenous foci and high recruitment of 53BP1. Int J Radiat Biol. 2013;89(4):301-309.
[26] Hafizi M, Atashi A, Bakhshandeh B, et al. MicroRNAs as markers for neurally committed CD133+/CD34+ stem cells derived from human umbilical cord blood. Biochem Genet. 2013;51(3-4):175-188.
[27] Ratajczak J, Kucia M, Mierzejewska K, et al. Paracrine proangiopoietic effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived purified CD133+ cells--implications for stem cell therapies in regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(3):422-430.
[28] Dai N, Li D, Shi Q, et al. Influence of vascular endothelial growth factor on endothelial components in human bone marrow and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012;20(3):717-721.
[29] Monga R, Buck S, Sharma P, et al. Effect of preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction on endothelial progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;25(11):2385-2389.
[30] Burger D, Gutsol A, Carter A, et al. Human cord blood CD133+ cells exacerbate ischemic acute kidney injury in mice. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(10):3781-3789. |