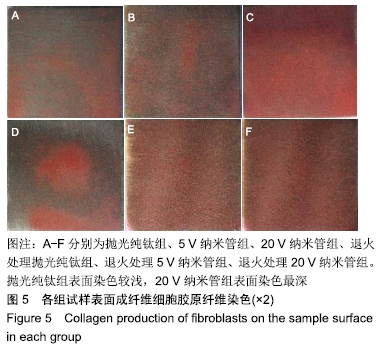
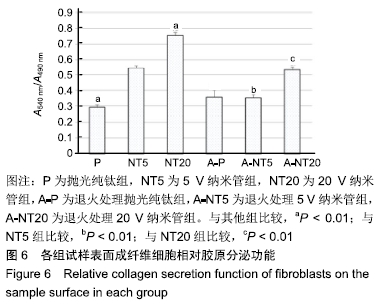
[1] KULKARNI M, MAZARE A, GONGADZE E, et al.Titanium nanostructures for biomedical applications.Nanotechnology. 2015;26(6):062002.
[2] 李红彩,马壮.TiO_2纳米管对种植体周细胞影响的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(52):7899-7904.
[3] ZHANG L, LIAO X, FOK A, et al. Effect of crystalline phase changes in titania (TiO2) nanotube coatings on platelet adhesion and activation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2018;82(1):91-101.
[4] 杨修春,崔晓琳,任鹏,等.后处理工艺对阳极氧化钛生物活性的影响[J].功能材料,2015,46(1):1135-1140,1143.
[5] PARK S, MIN D, LIM H, et al. Effect of heat treatment on phase transition of nanotubular titanium oxide arrays.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11(2):1476-1479.
[6] OH S, DARAIO C, CHEN LH, et al. Significantly accelerated osteoblast cell growth on aligned TiO2 nanotubes.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;78(1):97-103.
[7] AN SH, NARAYANAN R, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Crystallinity of anodic TiO2 nanotubes and bioactivity.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11(6): 4910-4918.
[8] YU WQ, ZHANG YL, JIANG XQ, et al. In vitro behavior of MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast with different annealing temperature titania nanotubes. Oral Dis.2010;16(7):624-630.
[9] MINAGAR S, WANG J, BERNDT CC, et al. Cell response of anodized nanotubes on titanium and titanium alloys.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(9):2726-2739.
[10] NAIR M, ELIZABETH E. Applications of Titania Nanotubes in Bone Biology.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2015;15(2):939-955.
[11] SHOKUHFAR T, HAMLEKHAN A, CHANG JY, et al. Biophysical evaluation of cells on nanotubular surfaces: the effects of atomic ordering and chemistry.Int J Nanomedicine.2014;12(9):3737-3748.
[12] ZHU Y, ZHANG CN, GU YX, et al. The responses of human gingival fibroblasts to magnesium-doped titanium.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(2):267-278.
[13] 赖颖真,卢薛冠,蔡艺煌.钛及氧化锆表面微沟槽结构对人牙龈成纤维细胞生物学行为的影响[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志,2019,54(10):676-682.
[14] PHAM MH, HAUGEN HJ, RINNA A, et al. Hydrofluoric acid treatment of titanium surfaces enhances the proliferation of human gingival fibroblasts.J Tissue Eng.2019;10:204173141982895.
[15] 包崇云.牙种植体穿龈部位表面微结构对生物密封的影响[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2017,26(3):113-117.
[16] 江瑶,黎红.钛表面粗糙度对成纤维细胞生长影响的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(8):738-740.
[17] RADTKE A, BAL M, JĘDRZEJEWSKI T. Novel Titania Nanocoatings Produced by Anodic Oxidation with the Use of Cyclically Changing Potential: Their Photocatalytic Activity and Biocompatibility. Nanomaterials (Basel).2018;8(9).pii: E712. doi: 10.3390/nano8090712.
[18] FADEYEV FA, KHRUNYK YY, BELIKOV SV, et al. The Adhesion of Human Dermal Fibroblasts on Anodized Nanotube-layered Titanium, Modified for Implantology Application.Dokl Biol Sci.2019;486(1):91-93.
[19] 李宝娥,李军,梁春永,等.阳极氧化处理对钛表面粗糙度和亲水性的影响[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2016,45(4):858-862.
[20] 李红彩,张玉梅,孙海平.不同管径Ti-TiO2纳米管对成纤维细胞和成骨细胞黏附的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2012,47(2):122-126.
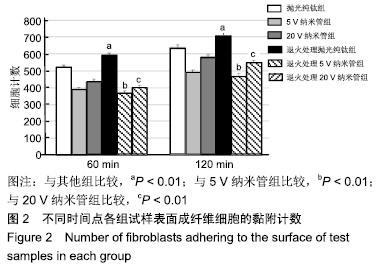
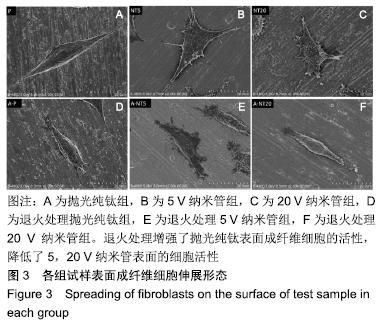
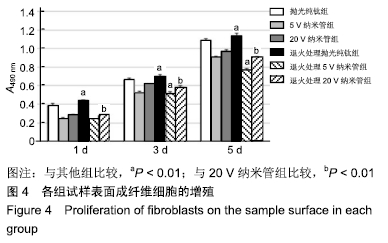
[21] 李红彩,马壮.不同管径钛纳米管对成纤维细胞增殖、伸展和胶原分泌功能的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2017,33(05):612-616.
[22] 梁砚琴,杨贤金,崔振铎,等.钛和钛合金表面TiO2纳米管研究进展[J].科技导报,2009,27(14):94-101.
[23] HYAM RS, LEE J, CHO E, et al. Effect of annealing environments on self-organized TiO2 nanotubes for efficient photocatalytic applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2012;12(12):8908-8912.
[24] 梅盛林,张玉梅,赵领洲,等.近β钛合金TLM表面阳极氧化对成骨细胞早期附着的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2010,26(5):597-601.
[25] PARK J, BAUER S, SCHMUKI P, et al. Narrow window in nanoscale dependent activation of endothelial cell growth and differentiation on TiO2 nanotube surfaces. Nano Lett. 2009; 9(9):3157-3164.
[26] HUANG Q, YANG Y, ZHENG D, et al. Effect of construction of TiO2 nanotubes on platelet behaviors: Structure-property relationships.Acta Biomater.2017;51(15):505-512.
[27] 石萍,于千.退火温度及TiO_2结构对羟基磷灰石的沉积诱导作用[J].材料热处理学报,2010,31(1):44-47.
[28] 顾迎新,赖红昌,张志勇.钛基种植体表面纳米管改性的研究进展[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2012,21(3):145-148.
[29] POPAT KC, ELTGROTH M, LATEMPA TJ, et al. Titania nanotubes: a novel platform for drug-eluting coatings for medical implants? Small. 2007;3(11):1878-1881.
[30] WEI H, WU S, FENG Z, et al. Increased fibroblast functionality on CNN2-loaded titania nanotubes. Int J Nanomedicine.2012;7:1091-100.
[31] LV L, LI K, XIE Y, et al. Enhanced osteogenic activity of anatase TiO2 film: Surface hydroxyl groups induce conformational changes in fibronectin. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;78(1):96-104.
[32] LEE SJ, OH TJ, BAE TS, et al. Effect of bisphosphonates on anodized and heat-treated titanium surfaces: an animal experimental study.J Periodontol.2011;82(7):1035-1042.
[33] MORAVEC H, VANDROVCOVA M, CHOTOVA K, et al. Cell interaction with modified nanotubes formed on titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;65(1):313-322.
[34] FAN X, FENG B, LIU Z, et al. Fabrication of TiO2 nanotubes on porous titanium scaffold and biocompatibility evaluation in vitro and in vivo.J Biomed Mater Res A.2012; 100(12):3422-3427.
[35] HUANG Q, YANG Y, HU R,et al. Reduced platelet adhesion and improved corrosion resistance of superhydrophobic TiO₂-nanotube- coated 316L stainless steel.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;125(1): 134-141.
[36] TIAN A, QIN X, WU A, et al. Nanoscale TiO2 nanotubes govern the biological behavior of human glioma and osteosarcoma cells.Int J Nanomedicine.2015;10(25):2423-2439.
[37] AMIN YAVARI S, CHAI YC, BÖTTGER AJ, et al. Effects of anodizing parameters and heat treatment on nanotopographical features, bioactivity, and cell culture response of additively manufactured porous titanium.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2015;51:132-138.
|