| [1] Robert F. Tissue engineers build new bone. Science. 2000;289: 1498-1500.
[2] Kim HM, Uenoyama M, Kobubo T, et al. Biomimetic apatite formation on polyethylene photografted with vinyltrimethxysilane and hydrolyzed. Biomaterials. 2001;22(18): 2489-2494.
[3] Wei J, Li YB. Tissue engineering scaffold material of nano-apatite crystals and polyamide composite. Eur Polymer J. 2004;40:509-515.
[4] Kondo N, Ogose A, Tokunaga K, et al. Osteoinduction with highly purified b-tricalcium phosphate in dog dorsal muscles and the proliferation of osteoclasts before heterotopic bone formation. Biomaterials. 2006;27:4419-4427.
[5] Bauer TW, Muschler GF. Bone graft material: an overview of the basic science. Clin Orthop. 2000;(371): 10-27.
[6] Hosseinkhani H,Hosseinkhani M, Gabrielson NP, et al. DNA nanoparticles encapsulated in 3D tissue-engineered scaffolds enhance osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells .Biomed Mater Res. 2007;85A(1):47-60.
[7] Hosseinkhani H, Inatsugu Y, Hiraoka Y, et al. Impregnation of plasmid DNA into three-dimensional scaffolds and medium perfusion enhance in vitro DNA expression of mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2005,11(9-10):1459-1475.
[8] Gugala Z, Davis AR, Fouletier-Dilling CM, et al. Adenovirus BMP2-induced osteogenesis in combination with collagen carriers. Biomaterials. 2012;28(30):4469-4479.
[9] Park J, Lutz R, Felszeghy E, et al. The effect on bone regeneration of a liposomal v ector to deliver BMP2 gene to bone grafts in peri-implant bone defects. Biomaterials. 2007;28(17):2772-2782.
[10] Parsons B, Strauss E. Surgical management of chronic osteomyelitis. Am J Surg. 2004;188: 57-64.
[11] 范丽,卢岩,林慧平,等.骨形成蛋白-2转染MG-63细胞增加其对壳聚糖膜的粘附[J].材料科学与工程学报,2011,29(6):911-915.
[12] Zou C, Weng W, Deng X, et al. Preparation and characterization of porous b-tricalcium phosphaye/ collagen composites with an integrated structure. Biomaterials. 2005;26:5276-5284.
[13] Silva GA,Ducheyne P,Reis RL.Materials in particulate form for tissue engineering.1.Basic concepts. J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2007;1(1):4-24.
[14] Lu K, Zeng D, Zhang Y,et al.BMP-2 Gene Modified Canine bMSCs Promote Ectopic Bone Formation Mediated by a Nonviral PEI Derivative. Ann Biomed Eng. 2011;39(6):1829-1839.
[15] Zeng D,Xia L,Zhang W,et al. Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Using a Tissue-Engineered Bone with Calcium-Magnesium Phosphate Cement and Bone Marrow Stromal Cells in Rabbits. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(7-8):870-881.
[16] 王晓娜,赵静辉,储顺礼,等.骨替代材料在口腔种植领域中的成骨效果[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志,2016,43(1):113-117.
[17] Chen H, Zhao G, Ye J. Autosolidifying calcium phosphate cement in the repair of bone defects due to different etiology among 94 cases. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res. 2008;12(19): 3779-3781.
[18] Joosten U, Joist A, Gosheger G, et al. Burkhard Brandt.Christof von Eiff. Effectiveness of hydroxyapatite- vancomycin bone cement in thetreatment of Staphylococcus aureus induced chronic osteomyelitis. Biomaterials. 2005;26: 5251-5258.
[19] Hartman GA, Arnold RM,mills MP, et al. Clinical and histologic evaluation of anorganic bovine bone collagen with or without a collagen barrier. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2004;24(2):127-135.
[20] Chen D, Zhao M, Mundy GR. Bone morphogenetic Proteins. Growth Factors. 2004;22(4):233-241.
[21] Urist MR.Bone formation by autoinduction. Science. 1965;150(3698):893-899.
[22] Shimer AL, Oner FC, Vaccaro AR. Spinal reconstruction and bone morphogenetic proteins: open questions. Injury. 2009;40(3):32-38.
[23] Wegman F, Bijenhof A, Schuijll L, et al. Osteogenic differentiation as a result of BMP-2 plasmid DNA based gene therapy in vitro and in vitro and in vivo. Eur Cell Mater. 2011;15(21):230-242
[24] Lee JH, Kim CS. The induction of bone form ation in rat calvarial defects and subcutaneous tissues by recombinant human BMP-2, produced in Escherichia coli. Biomaterials. 2010;31(13):3512-3519.
[25] Bozidar M,Hari S,Michael D,et al. β-tricalcium phosphate-type I collagen cones with or without a barrier membrane in hume extraction socket healing-clinical, histologic, histomorph- ometric, and immunohistochemical evaluation. Clin Oral Invest. 2012;16(10):581-590.
[26] Zou C, Weng WJ, Deng XL, et al. Preparation and characterization of porous β-tricalcium phosphaye/ collagen composites with an integrated structure. Biomaterials. 2005;26:5276-5284.
[27] Cao X, Deng W, Wei Y, et al. Encapsulation of plasmid DNA in ralrium phosphate nanoparticles:stemcell uptake and gene transfer efficiency.Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6: 333-3349.
[28] Liu T, Tang A, Zhang G, et al. Calcium phosphate nanoparticles as a novel nonviral vector for efficient transfection of DNA in cancer gene therapy. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2005;20:141-149.
[29] Keeney M, van den Beucken LL,van der Kraan PM, et al. The ability of a collagen/calcium phosphate scaffold to act as its own vector for gene delivery and to promote bone formation via transfection with VECF(165). Biomaterials. 2010; 31(10):2893-902.
[30] Glassman SD,Carreon LY,Campbell MJ,et al.The perioperative cost of Infuse bone graft in posterolateral lumbar spine fusion.Spine J. 2008;8:443-448.
[31] Chamberlain JR,Schwarze U,Wang PR,et al.Gene targeting instem cells from individuals with osteogenesis imperfecta.Science.2004;303(5661): 1198-1201.
[32] Zhang JY,Doll BA,Beckman EJ,et al. Three-dimensional biocompatible ascorbic acid-containing scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. 2003.9(6):1143-1157.
[33] Petite H, Viateau V, Bensaid W,et al.Tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Nature Bioteehnology. 2000;18(9): 959-963.
[34] Orban JM,Marra KG,Hollinger JO.Composition options for tissue-engineered bone.Tissue Eng. 2002;8(4):529-539.
[35] Bauer TW,Muschler GF.Bone graft matcrials.An overview of the basic science.Clin Orthop. 2000;371:10-27.
[36] Hosseinkhani H,Hosseinkhani M,Gabrielson NP,et al. DNA nanoparticles encapsulated in 3D tissue-engineered scaffolds enhance osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Biomed Mater Res A. 2007; 85A(1):47-60.
[37] Hosseinkhani H,Inatsugu Y,Hiraoka Y,et al. Impregnation of plasmid DNA into three-dimensional scaffolds and medium perfusion enhance in vitro DNA expression of mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(9-10): 1459-1475.
[38] Gugala Z,Davis AR,Fouletier-Dilling CM,et al. Adenovirus BMP2-induced osteogenesis in combination with collagen carriers. Biomaterials. 2012;28(30):4469-4479.
[39] Hinz P,Wolf E,Sehwesinger G,et al.A new resorbable bone void filler intrauma:early clinical experience and histologic evaluation.Orthopedics. 2002;25(S5):597-600.
[40] Sikavitsas VI,Temenoff JS,Mikos AG.Biomaterials and bone mechanotrans Duction. Biomaterials. 2001; 22(19):2581-2593.
[41] Hinz P, Wolf E, Schwesinger G, et al. A new resorbable bone void filler in trauma: early clinical experience and histologic evaluation. Orthopedics. 2002;25(S5):597-600.
[42] Yuan H, Li Y, de Bruijn JD, et al. Tissue responses of calcium phosphate cement: a study in dogs. Biomaterials. 2000;21(12): 1283-1290. |
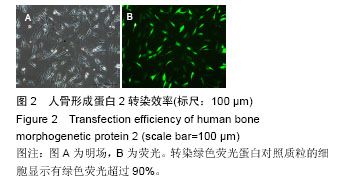
.jpg)

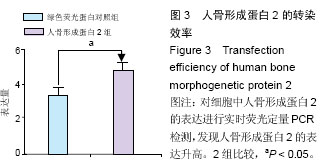
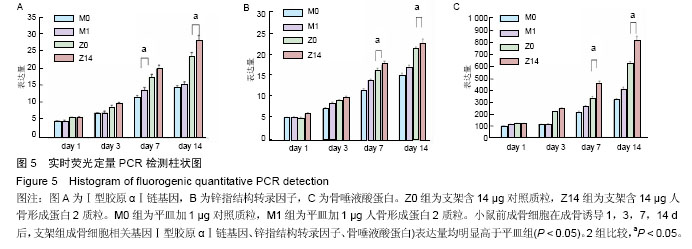
.jpg)
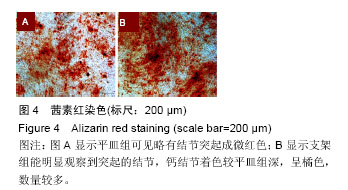
.jpg)