中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (15): 2148-2155.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.15.003
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
活血祛瘀法干预激素性股骨头坏死骨组织的修复
陈雷雷1,2,陈晓波2,3,洪郭驹2,3,陈 达2,3,杨 鹏2,3,何 伟1,2
- 1广州中医药大学第一附属医院关节骨科,广东省广州市 510000;2广州中医药大学国家重点学科中医骨伤科学实验室,广东省广州市 510000;3广州中医药大学第一临床医学院,广东省广州市 510000
“Removing Blood Stasis” Method for bone repair in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral heads
Chen Lei-lei1, 2, Chen Xiao-bo2, 3, Hong Guo-ju2, 3, Chen Da1, 2, Yang Peng2, 3, He Wei1, 2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2the National Key Discipline and the Orthopedic Laboratory of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 3the First Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
激素性股骨头坏死:在国内外报道越来越多,是激素在广泛应用中近年被公认的并发症,其发病率目前已超过了创伤所致的股骨头坏死,机制尚不十分清楚,一般认为激素在体内长期蓄积造成血液黏稠度增加,血脂增高,脂肪栓塞,脂肪肝,造成骨的微细血管阻塞,缺血,骨质合成减少,钙吸收障碍,骨质疏松及微细骨折的积累,最后导致激素性股骨头坏死。使用糖皮质激素如地塞米松最短有7 d导致股骨头坏死的,使用激素后发病时间不一,有使用激素后不到2个月就发生股骨头坏死的报道。
活血化瘀:用具有消散作用的、或能攻逐体内瘀血的药物治疗中医诊断为瘀血病证的方法。
背景:激素性股骨头坏死的发病机制尚不明确,该病所伴随的塌陷破坏和重建性修复或与“骨形成-吸收”偶联失效所引起微观骨结构改变有关。活血祛瘀法经临床证实对该病有积极作用。但目前针对活血祛瘀法促进骨坏死修复的作用机制尚不清楚,相关国内外文献报道较少。
目的:制备激素性股骨头坏死兔模型,探究活血祛瘀法对激素性股骨头坏死修复的干预作用。
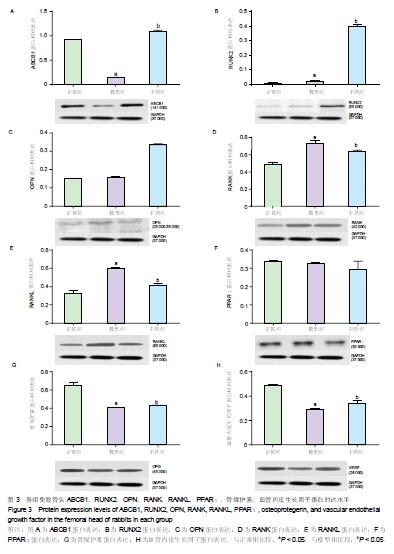
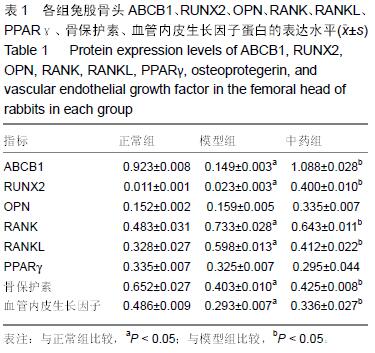
方法:50只新西兰兔随机分为3组:正常组10只、模型组和中药组(桃红四物汤组)各20只,采用内毒素联合甲强龙的方法制备激素性股骨头坏死模型,最后一次肌肉注射甲强龙后24 h,中药组给予 0.3 g/kg桃红四物汤混悬液灌胃,正常组和模型组灌服等体积超纯水,连续8周。实验第8周分别进行高分辨率MRI检查和病理学组织检测以评估建模效果,采用Western Blot检测兔股骨头ABCB1、RUNX2、OPN、RANK、RANKL、PPAR、骨保护素、血管内皮生长因子的蛋白表达水平。
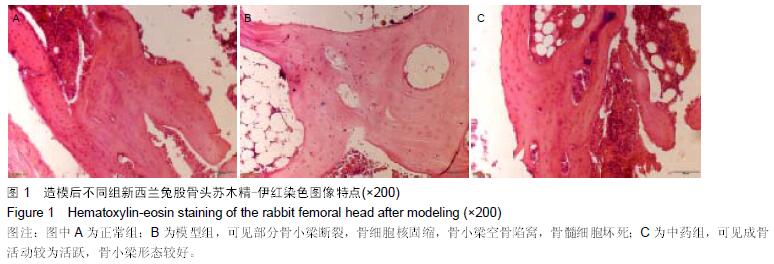
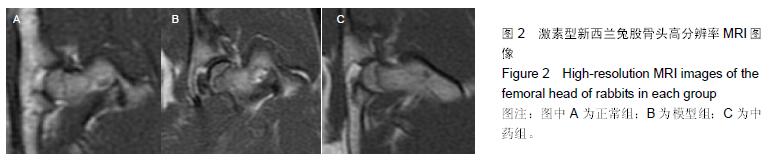
结果和结论:①经苏木精-伊红染色显示:模型组可见部分骨小梁断裂,骨细胞核固缩,骨小梁空骨陷窝,骨髓细胞坏死,与正常组相比空骨陷窝率差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),中药组可见成骨活动仍较为活跃,骨小梁形态较好,说明活血祛瘀法可改善坏死区域组织修复。②高分辨率MRI显示:模型组股骨头外形基本正常,股骨头内可见低信号带;中药组股骨头外形趋于正常,股骨头内近骨骺处有小块低密度区,大部分骨组织灰度值正常,提示活血祛瘀法可改善坏死区域影像学改变。③Western Blot检测结果:模型组与正常组相比RUNX2、RANK、RANKL的蛋白表达升高,ABCB1、骨保护素、血管内皮生长因子蛋白表达下降;中药组与模型组相比,除RANK、RANKL表达下降外,其余均升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。④结果说明:活血祛瘀法促进兔激素性股骨头坏死的修复可能与调节ABCB1、RUNX2、RANK、RANKL、骨保护素、血管内皮生长因子蛋白的表达水平有关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-5610-5245(何伟)
.jpg)