| [1] Ikeuchi K, Hasegawa Y, Seki T, et al. Epidemiology of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Japan. Mod Rheumatol. 2015;25(2):278-281. [2] Mont MA, Cherian JJ, Sierra RJ, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today? A Ten-Year Update. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(19):1604-1627. [3] Yuan HF, Von Roemeling C, Gao HD, et al. Analysis of altered microRNA expression profile in the reparative interface of the femoral head with osteonecrosis. Exp Mol Pathol. 2015;98(2):158-163. [4] Nicoli S, Standley C, Walker P, et al. MicroRNA- mediated integration of haemodynamics and Vegf signalling during angiogenesis. Nature. 2010;464 (7292):1196-1200. [5] Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2): 281-297. [6] Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431(7006):350-355. [7] Inui M, Martello G, Piccolo S. MicroRNA control of signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(4): 252-263. [8] Gámez B, Rodriguez-Carballo E, Ventura F. MicroRNAs and post-transcriptional regulation of skeletal development. J Mol Endocrinol. 2014;52(3): R179-197. [9] Mizuno Y, Yagi K, Tokuzawa Y, et al. miR-125b inhibits osteoblastic differentiation by down-regulation of cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008; 368(2):267-272. [10] [Rippe C, Blimline M, Magerko KA, et al. MicroRNA changes in human arterial endothelial cells with senescence: relation to apoptosis, eNOS and inflammation. Exp Gerontol. 2012;47(1):45-51. [11] Kane NM, Thrasher AJ, Angelini GD, et al. Concise review: MicroRNAs as modulators of stem cells and angiogenesis. Stem Cells. 2014;32(5):1059-1066. [12] 赵丁岩,俞庆声,郭万首,等.淫羊藿苷对激素诱导损伤人股骨头骨微血管内皮细胞蛋白质表达谱的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2016,96(13):1026-1030. [13] Montgomery RL, van Rooij E. Therapeutic advances in MicroRNA targeting. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2011; 57(1): 1-7. [14] Nagpal JK, Rani R, Trink B, et al. Targeting miRNAs for drug discovery: a new paradigm. Curr Mol Med. 2010; 10(5):503-510. [15] 路玉峰,俞庆声,郭万首,等.人股骨头骨微血管内皮细胞的分离培养方法[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(10):843-847. [16] Hashemipour M, Dehkordi EH, Javanmard SH, et al. Von Willebrand factor, and soluble intercellular and vascular cell adhesion molecules as indices of endothelial activation in patients with congenital hypothyroidism. Horm Res Paediatr. 2011;76(2): 99-103. [17] Gregg AJ, Schenkel AR. Cloning and structural analysis of equine platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM, CD31) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1, CD106). Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2008;122(3-4):295-308. [18] Wang X, Qian W, Wu Z, et al. Preliminary screening of differentially expressed circulating microRNAs in patients with steroid?induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Mol Med Rep. 2014;10(6):3118-3124. [19] Suzuki O, Bishop AT, Sunagawa T, et al. VEGF-promoted surgical angiogenesis in necrotic bone. Microsurgery. 2004;24(1):85-91. [20] Yamasaki K, Nakasa T, Miyaki S, et al. Angiogenic microRNA-210 is present in cells surrounding osteonecrosis. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(8):1263-1270. [21] Bouletreau PJ, Warren SM, Spector JA, et al. Hypoxia and VEGF up-regulate BMP-2 mRNA and protein expression in microvascular endothelial cells: implications for fracture healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109(7):2384-2397. [22] Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C, Pober JS, et al. Dicer dependent microRNAs regulate gene expression and functions in human endothelial cells. Circ Res. 2007;100(8):1164-1173. [23] Kuehbacher A, Urbich C, Zeiher AM, et al. Role of Dicer and Drosha for endothelial microRNA expression and angiogenesis. Circ Res. 2007;101(1):59-68. [24] Wang KC, Garmire LX, Young A, et al. Role of microRNA-23b in flow-regulation of Rb phosphorylation and endothelial cell growth Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(7):3234-3239. [25] Zhang H, Hao Y, Yang J, et al. Genome-wide functional screening of miR-23b as a pleiotropic modulator suppressing cancer metastasis. Nat Commun. 2011;2: 554. [26] Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, et al. miR-23b represses proto-oncogene Src kinase and functions as methylation-silenced tumor suppressor with diagnostic and prognostic significance in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2012;72(24):6435-6446. [27] Zhou Q, Gallagher R, Ufret-Vincenty R, et al. Regulation of angiogenesis and choroidal neovascularization by members of microRNA- 23~27~24 clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011; 108(20):8287-8292. [28] Ham O, Song BW, Lee SY, et al. The role of microRNA-23b in the differentiation of MSC into chondrocyte by targeting protein kinase A signaling. Biomaterials. 2012;33(18):4500-4507. [29] Ma Y, Yu S, Zhao W, et al. miR-27a regulates the growth, colony formation and migration of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting Sprouty2. Cancer Lett. 2010; 298(2):150-158. [30] Walker JC, Harland RM. microRNA-24a is required to repress apoptosis in the developing neural retina. Genes Dev. 2009;23(9):1046-1051. [31] Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, et al. miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(Database issue):D154-158. |
.jpg)
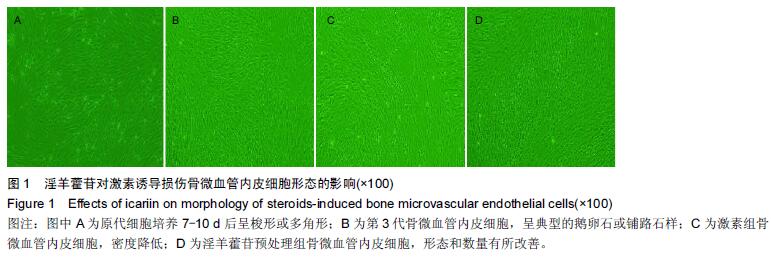
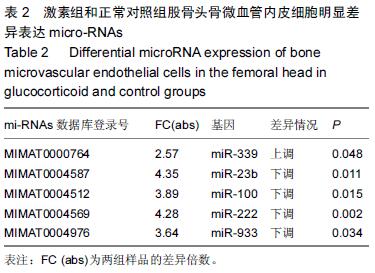
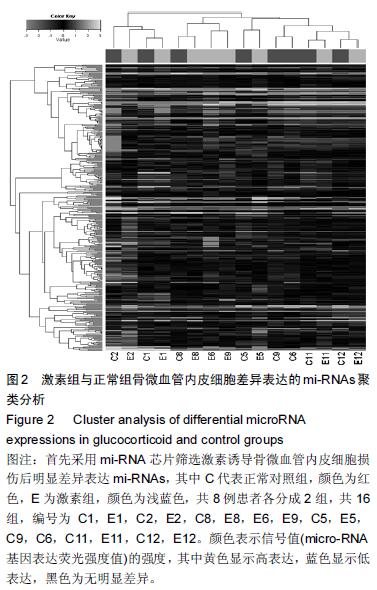
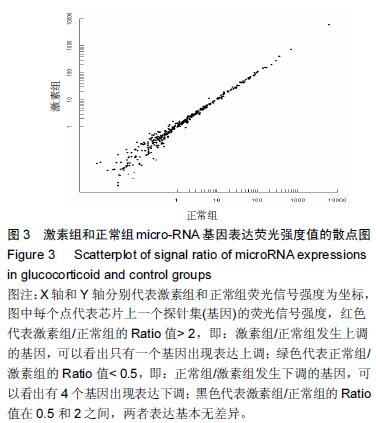
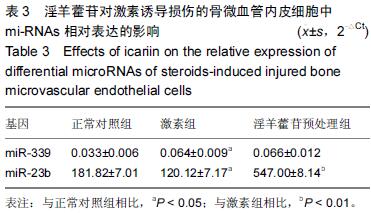

.jpg)
.jpg)