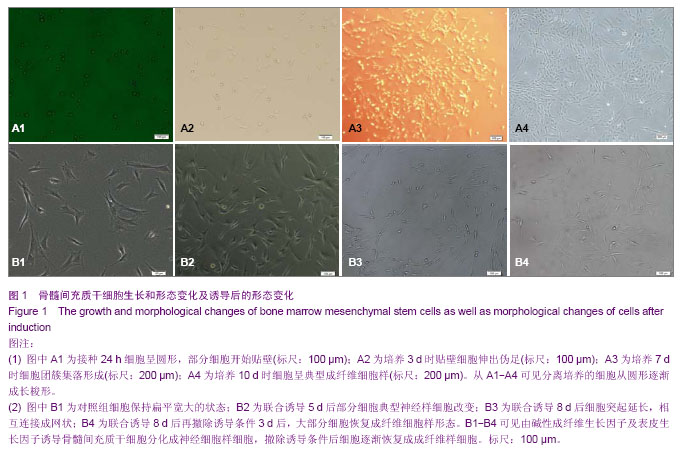
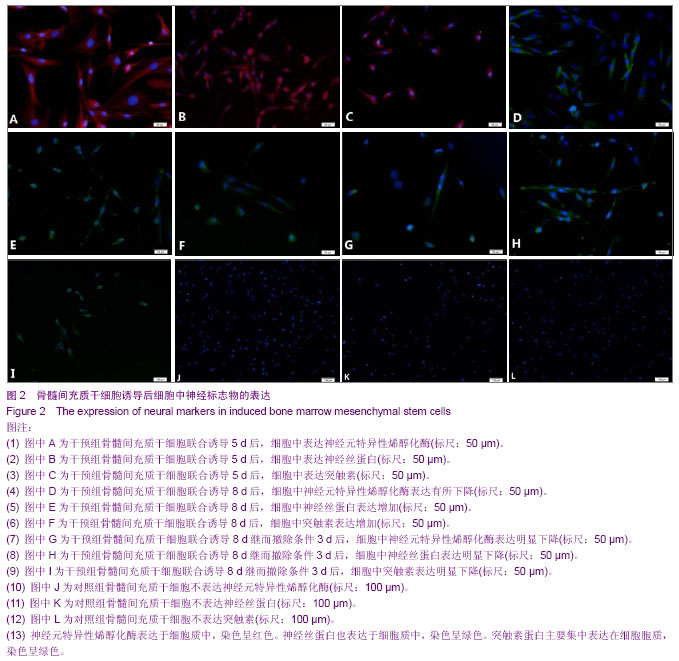
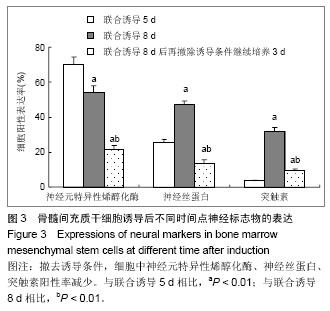
| [1] Erakat MS, Chuang SK, Shanti RM, et al. Interval between injury and lingual nerve repair as a prognostic factor for success using type I collagen conduit. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(5):833-838.[2] He J, Gu D, Wu X, et al. Major causes of death among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(11):1124-1134.[3] Jiang J, Lv Z, Gu Y, et al. Adult rat mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neuronal-like phenotype and express a variety of neuro-regulatory molecules in vitro. Neurosci Res. 2010;66(1):46-52. [4] Hom DB. Growth factors in wound healing. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1995;28(5):933-953.[5] 姜琨,秦樾,童坦君.erbB-2表达抑制与表皮生长因子刺激对信号转导与转录激活分子及细胞周期蛋白D1的影响[J].北京医科大学学报,1998,30(3):205-208. [6] 王阁,汪思应,许望翔,等.肝部分切除及表皮生长因子迅速诱导PC3基因的表达[J].科学通报,2000,45(20):2005-2009.[7] Leslie CC, McCormick-Shannon K, Shannon JM, et al. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor is a mitogen for rat alveolar type II cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997;16(4): 379-387.[8] Chia CM, Winston RM, Handyside AH. EGF, TGF-alpha and EGFR expression in human preimplantation embryos. Development. 1995;121(2):299-307.[9] Stubbs SC, Hargreave TB, Habib FK. Localization and characterization of epidermal growth factor receptors on human testicular tissue by biochemical and immunohistochemical techniques. J Endocrinol. 1990;125(3):485-492.[10] Hongo M, Itoi M, Yamaguchi N, et al. Distribution of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors in rabbit corneal epithelial cells, keratocytes and endothelial cells, and the changes induced by transforming growth factor-beta 1. Exp Eye Res. 1992; 54(1): 9-16.[11] Parelman JJ, Nicolson M, Pepose JS. Epidermal growth factor in human aqueous humor. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990; 109(5):603-604.[12] 赵培林,王慧敏,李肇特.下颌下腺切除对大鼠胃粘膜影响的组织学和组织化学观察[J].解剖学报,1994,25(3):318-321.[13] Calabrò A, Orsini B, Brocchi A, et al. Gastric juice immunoreactive epidermal growth factor levels in patients with peptic ulcer disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990;85(4): 404-407.[14] 周欣,黄志华,林汉华. 表皮生长因子与小儿消化性溃疡[J].华中医学杂志,2000,24(2):79-81. [15] 董光龙,王俊义,王为忠,等.表皮生长因子减少腹部辐射肠外营养大鼠肠道细菌移位[J].第四军医大学学报,2000,21(1):76-79.[16] 王涛,王俊义,陈冬利,等. 表皮生长因子对胰腺炎相关蛋白基因表达及胰腺炎的影响[J].第四军医大学学报,2000,21(11):1357- 1360.[17] 孙秀,陈先文,陈生弟.FGF和EGF对神经干细胞增殖及分化的影响[J].中国神经科学杂志,2000,16(2):170-173.[18] Okumura M, Okuda T, Nakamura T, et al. Acceleration of wound healing in diabetic mice by basic fibroblast growth factor. Biol Pharm Bull. 1996;19(4):530-535.[19] Takeuchi K, Takehara K, Tajima K, et al. Impaired healing of gastric lesions in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: effect of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997; 281(1):200-207.[20] Satoh H, Asano S, Maeda R, et al. Prevention of gastric ulcer relapse induced by indomethacin in rats by a mutein of basic fibroblast growth factor. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1997;73(3): 229- 241.[21] Rieck P, Denis J, Peters D, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 2, heparin and suramin reduce epithelial ulcer development in experimental HSV-1 keratitis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1997;235(11):733-740.[22] Nakamura K, Kawaguchi H, Aoyama I, et al. Stimulation of bone formation by intraosseous application of recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor in normal and ovariectomized rabbits. J Orthop Res. 1997;15(2):307-313.[23] Allouche M, Bikfalvi A. The role of fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) in hematopoiesis. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1995; 6(1):35-48.[24] Kaye DM, Kelly RA, Smith TW. Cytokines and cardiac hypertrophy: roles of angiotensin II and basic fibroblast growth factor. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl. 1996;3: S136-141.[25] Schumacher B, Pecher P, von Specht BU, et al. Induction of neoangiogenesis in ischemic myocardium by human growth factors: first clinical results of a new treatment of coronary heart disease. Circulation. 1998;97(7):645-350.[26] Nakagami Y, Saito H, Matsuki N. Basic fibroblast growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor promote survival and neuronal circuit formation in organotypic hippocampal culture. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1997;75(4):319-326.[27] Müller HW, Junghans U, Kappler J. Astroglial neurotrophic and neurite-promoting factors. Pharmacol Ther. 1995;65(1): 1-18.[28] Stachowiak MK, Moffett J, Maher P, et al. Growth factor regulation of cell growth and proliferation in the nervous system. A new intracrine nuclear mechanism. Mol Neurobiol. 1997;15(3):257-283.[29] Marini AM, Spiga G, Mocchetti I. Toward the development of strategies to prevent ischemic neuronal injury. In vitro studies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997;825:209-219.[30] Shimada J, Fushiki S, Tsujimura A, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2 expression is up-regulated after denervation in rat lung tissue. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1997;49(1-2):295-298.[31] Yoshida K, Toya S. Neurotrophic activity in cytokine-activated astrocytes. Keio J Med. 1997;46(2):55-60.[32] Sieber-Blum M, Zhang JM. Growth factor action in neural crest cell diversification. J Anat. 1997;191 ( Pt 4):493-499.[33] Adolphe M, Parodi AL. Ethical issues in animal experimentation. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2009;193(8): 1803-1804.[34] 胡辉,张伟才,黄继锋,等.新型神经导管复合材料与骨髓间充质干细胞的相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(16):2913-2920.[35] Lamers KJ, Vos P, Verbeek MM, et al. Protein S-100B, neuron-specific enolase (NSE), myelin basic protein (MBP) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and blood of neurological patients. Brain Res Bull. 2003; 61(3):261-264.[36] Uchida K, Baba H, Maezawa Y, et al. Progressive changes in neurofilament proteins and growth-associated protein-43 immunoreactivities at the site of cervical spinal cord compression in spinal hyperostotic mice. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(5):480-486.[37] Ferreira A, Chin LS, Li L, et al. Distinct roles of synapsin I and synapsin II during neuronal development. Mol Med. 1998;4(1): 22-28.[38] Kim SS, Yoo SW, Park TS, et al. Neural induction with neurogenin1 increases the therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells in the ischemic brain. Stem Cells. 2008;26(9):2217-2228. [39] Wang Y, Zhao Z, Ren Z, et al. Recellularized nerve allografts with differentiated mesenchymal stem cells promote peripheral nerve regeneration. Neurosci Lett. 2012;514(1): 96-101. [40] Wang X, Luo E, Li Y, et al. Schwann-like mesenchymal stem cells within vein graft facilitate facial nerve regeneration and remyelination. Brain Res. 2011;1383:71-80. [41] Ao Q, Fung CK, Tsui AY, et al. The regeneration of transected sciatic nerves of adult rats using chitosan nerve conduits seeded with bone marrow stromal cell-derived Schwann cells. Biomaterials. 2011;32(3):787-796.[42] Moyse E, Segura S, Liard O, et al. Microenvironmental determinants of adult neural stem cell proliferation and lineage commitment in the healthy and injured central nervous system. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2008;3(3): 163- 184.[43] Sun D, Bullock MR, McGinn MJ, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor-enhanced neurogenesis contributes to cognitive recovery in rats following traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2009;216(1):56-65. [44] Weiss S, Reynolds BA, Vescovi AL, et al. Is there a neural stem cell in the mammalian forebrain? Trends Neurosci. 1996; 19(9):387-393.[45] Murrey HE, Gama CI,Kalovidouris SA,et al. Protein fucosylation regulates synapsin Ia/Ib expression and neuronal morphology in primary hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:21-26. |
.jpg)