中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (32): 5140-5145.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.32.010
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
自身骨髓间充质干细胞治疗慢性移植物肾病的安全性与可行性
张 磊1,陈 正1,谢斯盛1,2,马俊杰1,方佳丽1,李光辉1,徐 璐1,张异蕊1,郭予和1,潘光辉1
- 1广州医科大学附属第二医院器官移植科,广东省广州市 510260;2东莞市人民医院泌尿外科,广东省东莞市 523000
Safety and feasibility of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in treating chronic allograft nephropathy
Zhang Lei1, Chen Zheng1, Xie Si-sheng1, 2, Ma Jun-jie1, Fang Jia-li1, Li Guang-hui1, Xu Lu1, Zhang Yi-rui1, Guo Yu-he1, Pan Guang-hui1
- 1Department of Organ Transplantation, Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510260, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Urology, Dongguan People’s Hospital, Dongguan 523000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
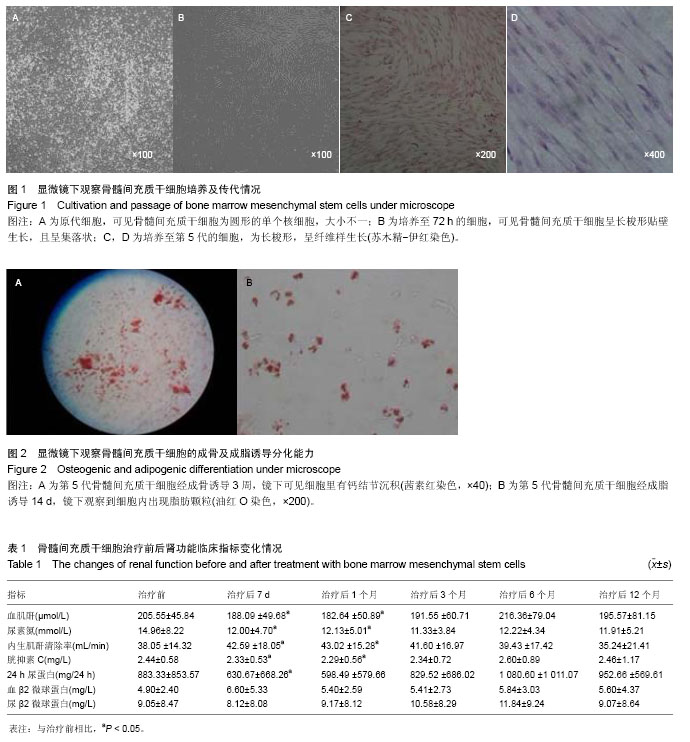
背景:慢性移植物肾病是肾移植领域较难处理的一种临床并发症,大多数最终会发展为移植肾失功。骨髓间充质干细胞作为一种低免疫原性的特殊细胞群,已证实具有分化、转分化、旁分泌等多种功能,在临床其他领域已有成功应用的基础。基于此特点,将其应用于慢性移植物肾病的患者可能会起到一定的治疗作用。 目的:探讨数字减影动脉造影引导下经移植肾动脉输注及之后经静脉输注自身骨髓间充质干细胞治疗慢性移植物肾病的安全性与可行性。 方法:选择2011年3月至2013年1月间确诊慢性移植物肾病且符合入组标准的患者11例,行1次数字减影动脉造影引导下经移植肾动脉输注及之后2次经静脉输注骨髓间充质干细胞。观察治疗后1年内患者血肌酐、尿素氮、内生肌酐清除率、胱抑素C、24 h尿蛋白、血/尿β2微球蛋白的变化情况。 结果与结论:11例患者未发生出血、移植肾动脉栓塞、假性动脉瘤等相关并发症。骨髓间充质干细胞治疗后1周、1个月时血肌酐、尿素氮、胱抑素C水平与治疗前相比明显下降,其差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);治疗3个月后,各指标与治疗前比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。骨髓间充质干细胞治疗后1周、1个月时内生肌酐清除率较治疗前升高,其差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);而治疗3个月后与治疗前比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。治疗7 d时24 h尿蛋白水平与治疗前相比明显下降,其差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),而治疗1个月后差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);血/尿β2微球蛋白治疗前后均无明显变化。结果可见数字减影动脉造影引导下经移植肾动脉输注及经静脉输注骨髓间充质干细胞治疗慢性移植物肾病是安全的,对患者肾功能改善有一定效果,输注细胞剂量及后续输注方式的选择尚有待研究。
中图分类号: