| [1] Thorek LJD, Chen AK, Czupryna J, et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging. Ann Biomed Eng. 2006;34(1):23-38.
[2] Berry CC, Curtis ASG. Functionalisation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2003;36:R198-R206.
[3] Ito A, Shinkai M, Honda H, et al. Medical application of functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J Biosci Bioeng. 2005; 100(1):1-11.
[4] Chemla YR, Crossman HL, Poon Y. Ultrasensitive magnetic biosensor for homogeneous immunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:14268-14272.
[5] Mornet S, Vasseur S, Grasset F, et al. Magnetic nanoparticle design for medical applications. Prog Solid State Chem. 2006;34(2):237-247.
[6] Hatakeyama M, Kishi H, Kita Y, et al. A two-step ligand exchange reaction generates highly water-dispersed magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J Mater Chem. 2011;21:5959-5966.
[7] Tassa C, Shaw SY, Weissleder R. Dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles: a versatile platform for targeted molecular imaging, molecular diagnostics, and therapy. Acc Chem Res. 2011;44:842-852.
[8] Easo SL, Mohanan PV. Dextran stabilized iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and in vitro studies. Carbohyd Polym. 2013;92(1):726-732.
[9] Xie J, Xu C, Kohler N, et al. Controlled pegylation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles for reduced non-specific uptake by macrophage cells. Adv Mater. 2007;19: 3163-3166.
[10] Kim DK, Mikhaylova M, Wang FH, et al. Starch-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles as MR contrast agents. Chem Mater. 2003;15:4343-4351.
[11] Quan Q, Xie J, Gao H, et al. HSA coated iron oxide nanoparticles as drug delivery vehicles for cancer therapy. Mol Pharm. 2011;8(5):1669-1676.
[12] Kah JC, Chen J, Zubieta A, et al. Exploiting the protein corona around gold nanorods for loading and triggered release. ACS Nano. 2012;6(8):6730-6740.
[13] Cifuentes-Rius A, de Puig H, Kah JC, et al. Optimizing the properties of the protein corona surrounding nanoparticles for tuning payload release. ACS Nano. 2013;7(11): 10066-10074.
[14] Chen FH, Zhang LM, Chen QT, et al. Synthesis of a novel magnetic drug delivery system composed of doxorubicin- conjugated Fe3O4 nanoparticle cores and a PEG-functionalized porous silica shell. Chem Commun. 2010;46:8633-8635.
[15] Ahmad T, Bae H, Rhee I, et al. Gold-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as a T2 contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging. J Nanosci Nanotechno. 2012;12(7):5132-5137.
[16] Zhu J, Lu YJ, Li YG, et al. Synthesis of Au-Fe3O4 heterostructured nanoparticles for in vivo computed tomography and magnetic resonance dual model imaging. Nanoscale. 2014;6(1):199-202.
[17] Larsen EK, Nielsen T, Wittenborn T, et al. Accumulation of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coated with variably sized polyethylene glycol in murine tumors. Nanoscale. 2012;4(7):2352-2361.
[18] Huang C, Neoh KG, Kang ET. Combined ATRP and ‘Click’ chemistry for designing stable tumor-targeting superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir. 2011;28(1):563-571.
[19] Aphesteguy JC, Jacobo SE. Synthesis of a soluble polyaniline-ferrite composite: magnetic and electric properties. J Mater Sci. 2007;42:7062-7068.
[20] Wang HD, Luo WQ, Chen JC. Fabrication and characterization of thermoresponsive Fe3O4@PNIPAM hybrid nanomaterials by surface-initiated RAFT polymerization. J Mater Sci. 2012;47:5918-5925.
[21] Wang SH, Shi XY, Antwerp MV, et al. Dendrimer-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for specific targeting and imaging of cancer cells. Adv Funct Mater. 2007;17:3043-3050.
[22] Kabanov AV, Batrakova EV, Alakhov VY. Pluronic block copolymers as novel polymer therapeutics for drug and gene delivery. J Controlled Release. 2002;82(2-3):189-212.
[23] Batrakova EV, Kabanov AV. Pluronic block copolymers: evolution of drug delivery concept from inert nanocarriers to biological response modifiers. J Controlled Release. 2008; 130(2):98-106.
[24] Bromberg L. Polymeric micelles in oral chemotherapy. J Controlled Release. 2008;128(2):99-112.
[25] Singh-Joy SD, McLain VC. Safety assessment of poloxamers 101, 105, 108, 122, 123, 124, 181, 182, 183, 184, 185, 188, 212, 215, 217, 231, 234, 235, 237, 238, 282, 284, 288, 331, 333, 334, 335, 338, 401, 402, 403, and 407, poloxamer 105 benzoate, and poloxamer 182 dibenzoate as used in cosmetics. Int J Toxicol. 2008;27:93-128.
[26] Liang S, Wang Y, Yu J, et al. Surface modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: as a new carrier for bio-magnetically targeted therapy. J Mater Sci. 2007;18:2297-2302.
[27] Sun C, Fang C, Stephen Z, et al. Tumor-targeted drug delivery and MRI contrast enhancement by chlorotoxin-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanomed. 2008;3:495-505.
[28] Yang Y, Jiang JS, Du B, et al. Preparation and properties of a novel drug delivery system with both magnetic and biomolecular targeting. J Mater Sci. 2009;20:301-307.
[29] Scarberry KE, Dickerson EB, McDonald JF, et al. Magnetic nanoparticlepeptide conjugates for in vitro and in vivo targeting and extraction of cancer cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:10258-10262.
[30] Lee HY, Li Z, Chen K, et al. PET/MRI dual-modality tumor imaging using arginine–glycine–aspartic (RGD)-conjugated radiolabeled iron oxide nanoparticles. J Nucl Med. 2008;49: 1371-1379.
[31] Zhang J, Rana S, Srivastava RS, et al. On the chemical synthesis and drug delivery response of folate receptor-activated, polyethylene glycol-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2008;4:40-48.
[32] Sun C, Sze R, Zhang M. Folic acid–PEG conjugated superparamagnetic nanoparticles for targeted cellular uptake and detection by MRI. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;78:550-557.
[33] Yang XQ, Pilla S, Grailer JJ, et al. Tumor-targeting, superparamagnetic polymeric vesicles as highly efficient MRI contrast probes. J Mater Chem. 2009;19:5812-5817.
[34] Wang L, Neoh KG, Kang ET, et al. Multifunctional polyglycerol-grafted Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles for targeting ovarian cancer cells. Biomaterials. 2011;32: 2166-2173. |
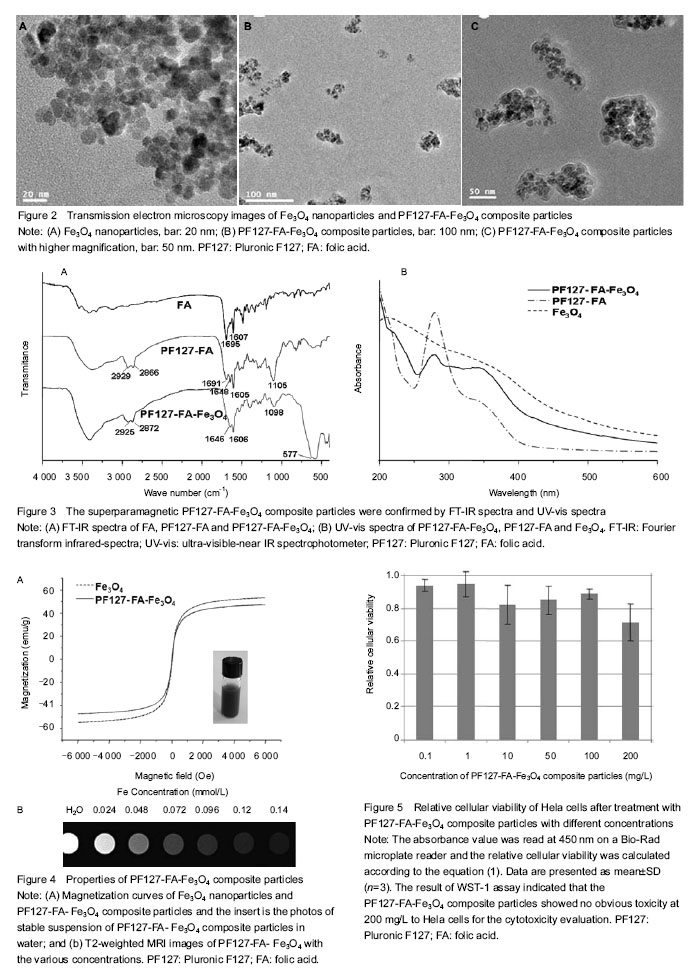
.jpg)