| [1] 王颖,李楠.分子印迹技术及其应用[J].化工进展,2010,29(12): 2315-2323.
[2] 史瑞雪,郭成海,邹小红,等.分子印迹技术研究进展[J].化学进展,2002,14(3):182-191.
[3] 闫有旺,于汝生.分子印迹技术及其应用[J].化学教学,2005,27(4): 28-30.
[4] Puoci F,Cirillo G,Curcio M,et al.Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) in Biomedical Applications.Biopolymers. 2010;28:547-574.
[5] Langer R,Peppas NA.Advances in biomaterials, drug delivery, and bionanotechnology.AIChE J.2003;49(12):2990-3006.
[6] 张粉艳,郝红,粱国正.应用于药物控释系统中的生物降解高分子材料[J].离子交换与吸附,2003,19(2):189-192.
[7] Cunliffe D,Kirby A,Alexander C.Molecularly imprinted drug delivery systems.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2005;57:1836-1853.
[8] 张勇,周建平.分子印迹给药系统研究进展[J].中国药学杂志, 2006, 41(21):1605-1609.
[9] Hilt JZ,Byrne ME.Configurational biomimesis in drug delivery: molecular imprinting of biologically significant molecules.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2004; 56:1599-1620.
[10] Singh B,Chauhan N.Preliminary evaluation of Molecular Imprinting of 5-fluorouracil within hydrogels for use as drug delivery systems.Acta Biomaterialia.2008;4(5):1244-1254.
[11] Van-nostrum CF.Molecular imprinting:a new tool for drug innovation. Drug Discov Today Technol.2005;2(1):119-124.
[12] Norell MC,Andersson HS,Nicholls IA.Theophylline molecularly imprinted polymer dissociation kinetics: a novel sustained release drug dosage mechanism.J Mol Recognit. 1998;11:98-102.
[13] Cirillo G,Curcio M,Parisi OI,et al. Gastro-intestinal sustained release of phytic acid by molecularly imprinted microparticles. Pharm Dev Technol.2010;15(5):526-531.
[14] Cirillo G,Parisi OI,Curcio M,et al.Molecularly imprinted polymers as drug delivery systems for the sustained release of glycyrrhizic acid.J Pharm Pharmacol.2010;62(5):577-582.
[15] Cirillo G,Iemma F,Puoci F,et al.Imprinted hydrophilic nanospheres as drug delivery systems for 5-fluorouracil sustained release.J Drug Target.2009;17(1):72-77.
[16] Yin J,Cui Y,Yang G,Wang H.Molecularly imprinted nanotubes for enantioselective drug delivery and controlled release.Chem Commun (Camb). 2010;46(41):7688-7690.
[17] Kan X,Geng Z,Zhao Y,et al.Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for aspirin recognition and controlled release. Nanotechnology. 2009;20(16):165601.
[18] 凌霞,李红萍,郭娟,等.左旋甲基多巴分子印迹微球给药系统的合成、表征及药物缓释研究[J].化学学报,2010,68(1):95-101.
[19] Jantarat C,Tangthong N,Songkro S,et al.S-Propranolol imprinted polymer nanoparticle-on-microsphere composite porous cellulose membrane for the enantioselectively controlled delivery of racemic propranolol.Int J Pharm. 2008;349:212-215.
[20] Suedee R,Jantarat C,Lindner W,et al.Development of a pH-responsive drug delivery system for enantioselective-controlled delivery of racemic drugs.J Control Release.2010;142(1):122-131.
[21] Suedee R,Bondhibukkana C,Tangthong N,et al.Development of a reservoir-type transdermal enantioselective-controlled delivery system for racemic propranolol using a molecularly imprinted polymer composite membrane.J Control Release. 2008;129(3):170-178.
[22] 王晓青,高永良.手性控释给药系统的研究进展[J].中国医药导刊, 2008,10(3):426-427.
[23] Yañez F,Martikainen L,Braga ME,et al.Supercritical fluid-assisted preparation of imprinted contact lenses for drug delivery.Acta Biomater.2011;7(3):1019-1130.
[24] Ali M,Byrne ME.Controlled release of high molecular weight hyaluronic Acid from molecularly imprinted hydrogel contact lenses.Pharm Res. 2009;26(3):714-726.
[25] Wang C,Javadi A,Ghaffari M,et al. A pH-sensitive molecularly imprinted nanospheres/hydrogel composite as a coating for implantable biosensors. Biomaterials.2010;31(18):4944-4951.
[26] 艾哈麦提•玉素甫,王振斌,朱良.可生物降解材料聚己内酯在医学上的应用进展[J].国外医学:生物医学工程分册,2005,28(1): 19-23.
[27] 宋存先,王彭延,孙洪范,等.聚己内酯在体内的降解、吸收和排泄[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2000,17(1):25-29.
[28] 王永亮,易国斌,康正,等.聚己内酯的合成与应用研究进展[J].化学与生物工程,2006,26(3):1-3.
[29] 刘峰,卓仁禧.水凝胶的制备及应用[J].高分子通报,1995,12(4): 205-216.
[30] 王铁,张黎明.医用高分子水凝胶的设计与合成[J].功能高分子学报,2004,17(2):330-336.
[31] 许志峰,吴双,吴小辉,等.二茂铁甲酸分子印迹聚合物的制备、识别机理和结合特性[J].应用化学,2010,27(4):384-389.
[32] 蒲家志,李丹.非洛地平分子印迹聚合物的制备及其识别特性[J].凯里学院学报,2009,27(3):37-38.
[33] Kweon H,Yoo MK,Park IK,et al.A novel degradable polycaprolactonenetweeks for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2003;24:801-808.
[34] Woodward SC,Brewer PS,Moatamed F,et al.The intracellular degradation of poly(ε-caprolactone).J Biomed Mater Res. 1985;19(4):437-444.
[35] Pitt CG,Gratzei MM,Kimmei GL,et al.Aliphatic polyesters Ⅱ: the degradation of poly(DL-lactide),poly(ε-caprolactone), and their copolymers in vivo.Biomaterials.1981;2:215-220. |

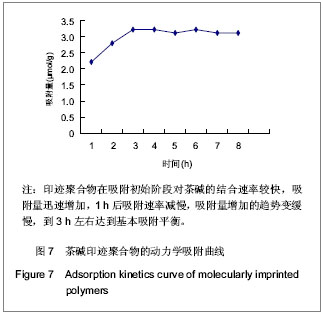
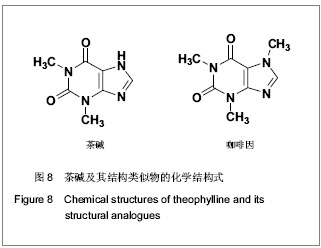
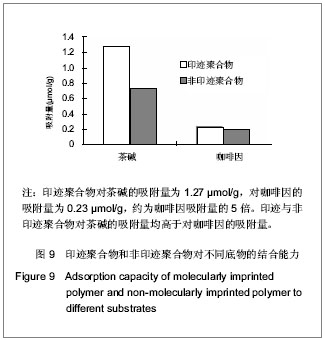
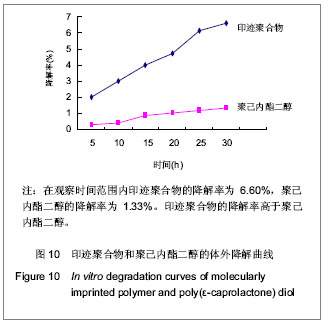
.jpg)