| [1] Maeno S, Niki Y, Matsumoto H, et al. The effect of calcium ion concentration on osteoblast viability, proliferation and differentiation in monolayer and 3D culture. Biomaterials. 2005;26:4847-4855.
[2] Key JA, Odell RT. Failure of excess minerals in the diet to accelerate the healing of experimental fractures. J Bone Joint Surg.1955;37A:37.
[3] Singh LM, Della Rosa RJ, Dumphy JE. Mobilization of calcium in fractured bones in rats. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1963;126(2):243-248.
[4] Lu Y,Markel MD,Nemke B,et al.Influence of hydroxyapatite-coated and growth factor-releasing interference screws on tendon-bone healing in an ovine model. Arthroscopy.2009; 25(12):1427-1435.
[5] Wen CY,Qin L,Lee KM,et al.The use of brushite calcium phosphate cement for enhancement of bone-tendon integration in an anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction rabbit model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2009; 89(2):466-474.
[6] Huangfu X,Zhao J.Tendon-bone healing enhancementusing injectable tricalcium phosphate in a dog anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction model. Arthroscopy. 2007; 23: 455-462.
[7] Mutsuzaki H,Sakane M,Nakajima H,et al. Calcium-phosphate-hybridized tendon directly promotes regeneration of tendon-bone insertion. J Biomed Mater Res A.2004; 70:319-327.
[8] Berland S,Delattre O,Borzeix S, et al.Nacre/bone interface changes in durable nacre endosseous implants in sheep. Biomaterials.2005; 26(15):2767-2773.
[9] Tang Z,Kotov NA,Magonov S, et al .Nanostructured artificial nacre. Nat Mater. 2003;2(6):413-418.
[10] Balmain J,Hannoyer B,Lopez E. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray diffraction analyses of mineral and organic matrix during heating of mother of pearl (nacre) from the shell of the mollusc Pinctada maxima. J Biomed Mater Res.1999;48(5):749-754.
[11] Westbroek P,Marin F.A marriage of bone and nacre.Nature. 1998; 392(6679):861-862.
[12] 薛恩兴,徐华梓,彭磊.牡蛎壳材料的生物相容性研究[J].浙江临床医学, 2007,9(2):175-176.
[13] 杨春露,陈建庭,王建钧,等.珍珠层人工骨与人骨髓基质细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(1):37-40.
[14] 薛恩兴,徐华梓.牡蛎壳材料填充兔股骨骨缺损的实验研究[J]. 浙江创伤外科,2009,14(5):437-439.
[15] 李振威,谢丽丽,曹阳,等.天然牡蛎壳纳米体复合型骨材料修复桡骨缺损的研究[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2012, 18(9):807-812.
[16] Zhang W, Wang W, Chen QY,et al.Effect of calcium citrate on bone integration in a rabbit femur defect model. Asian Pac J Trop Med.2012;5(4):310-314.
[17] 王伟, 李秀翠, 张伟, 等.柠檬酸钙载体复合骨形态发生蛋白-2成骨的实验研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2011,13(10):951-955.
[18] 蔡汝汝,杨云,孙珍珍,等.牡蛎壳纳米羟基磷灰石的制备与表征[J].厦门大学学报:自然科学版,2010,49(5):666-670.
[19] 潘荣楷, 文健, 林丽丽, 等.以贝壳为原料制备苹果酸钙的研究[J].现代食品科技, 2009, 25(7):790-791.
[20] Tong H,Hu J,Ma W,et al. In situ analysis of the organic framework in the prismatic layer of mollusc shell.Biomaterials. 2002;23:2593-2594
[21] 郑伟航,陈淑婉,衷明华.从贝壳中制取乳酸钙的工艺条件研究[J].广东化工,2005,32(11):42.
[22] Brecevic LJ, Füredi-Milhofer H.Precipitation of calcium phosphates from electrolyte solutions V. The influence of citrate ions.Calcif Tissue Int. 1979;28:131.
[23] Misra DN. Interaction of citric acid with hydroxyapatite: surface exchange of ions and precipitation of calcium citrate.J Dent Res.1996;75(6): 1418-1425.
[24] Tenhuisen KS, Brown PW.The effects of citric and acetic acids on the formation of calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite at 38 °C. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1994;(5):291-298
[25] Hu YY,Rawal A,Schmidt-Rohr K.Strongly bound citrate stabilizes the apatite nanocrystals in bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2010;52 : 22425-22429. |
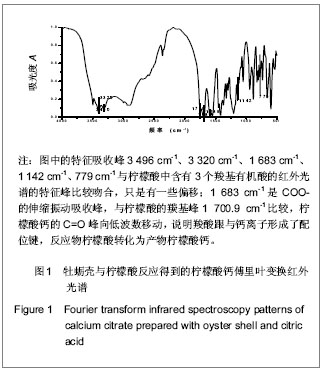
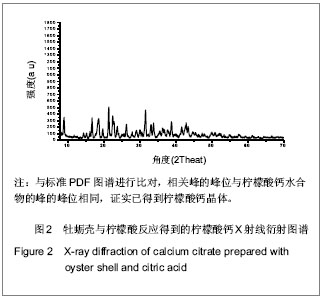

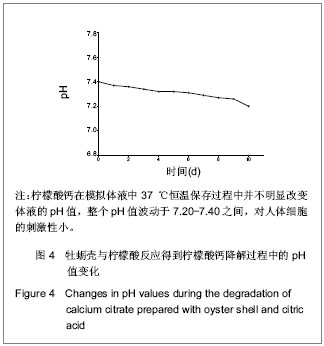
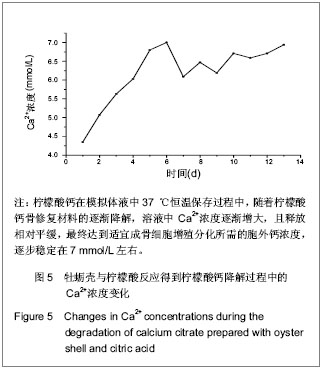
.jpg)