| [1] Malvindi MA,Brunetti V,Vecchio G,et al.SiO2 nanoparticles biocompatibility and their potential for gene delivery and silencing. Nanoscale.2012;4(2):486-495.
[2] Biradar S,Ravichandran P,Gopikrishnan R,et al.Calcium carbonate nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility.J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2011;11(8): 6868-6874.
[3] Tang F,Li L,Chen D.Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: synthesis, biocompatibility and drug delivery.Adv Mater.2012; 24(12):1504-1534.
[4] Alarcon EI,Udekwu K,Skog M,et al.The biocompatibility and antibacterial properties of collagen-stabilized,photochemically prepared silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials.2012; 33(19): 4947-4956.
[5] Huang X,Zhuang J,Teng X,et al.The promotion of human malignant melanoma growth by mesoporous silica nanoparticles through decreased reactive oxygen species. Biomaterials.2010;31(24):6142-6153.
[6] Singh S,Dosani T,Karakoti AS,et al.A phosphate-dependent shift in redox state of cerium oxide nanoparticles and its effects on catalytic properties. Biomaterials.2011;32(28): 6745-6753.
[7] Ladewig K,Niebert M,Xu ZP,et al.Efficient siRNA delivery to mammalian cells using layered double hydroxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials.2010;31(7): 821-1829.
[8] Labouta HI,Schneider M.Interaction of inorganic nanoparticles with the skin barrier: current status and critical review.Nanomedicine.2013 ;9(1):39-54.
[9] Fan K,Cao C,Pan Y,et al.Magnetoferritin nanoparticles for targeting and visualizing tumour tissues.Nat Nanotechnol. 2012;7(7):459-464.
[10] Huang HC,Barua S,Sharma G,et al.Inorganic nanoparticles for cancer imaging and therapy.J Control Release.2011; 155(3):344-357.
[11] Son SJ,Bai X,Lee SB.Inorganic hollow nanoparticles and nanotubes in nanomedicine Part 1. Drug/gene delivery applications.Drug Discov Today. 2007;12(15-16):650-656.
[12] Geidel C,Schmachtel S,Riedinger A,et al.A general synthetic approach for obtaining cationic and anionic inorganic nanoparticles via encapsulation in amphiphilic copolymers. Small.2011;7(20):2929-2934.
[13] Pittella F,Zhang M,Lee Y,et al.Enhanced endosomal escape of siRNA-incorporating hybrid nanoparticles from calcium phosphate and PEG-block charge-conversional polymer for efficient gene knockdown with negligible cytotoxicity. Biomaterials.2011;32(11):3106-3114.
[14] Yang X,Walboomers XF,van den Dolder J,et al.Non-viral bone morphogenetic protein 2 transfection of rat dental pulp stem cells using calcium phosphate nanoparticles as carriers. Tissue Eng Part A.2008;14(1):71-81.
[15] Park EK,Lee YE,Choi JY,et al.Cellular biocompatibility and stimulatory effects of calcium metaphosphate on osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived stromal cells.Biomaterials.2004;25(17):3403-3411.
[16] Lee YM,Seol YJ,Lim YT,et al.Tissue-engineered growth of bone by marrow cell transplantation using porous calcium metaphosphate matrices.J Biomed Mater Res.2001;54(2) : 216-223.
[17] Cho IH,Lee JH,Song YG,et al.Evaluation on the efficacy and safety of calcium metaphosphate coated fixture.J Adv Prosthodont. 2013;5(2):172-178.
[18] 江燕萍,吴岳恒,成安衡.多孔偏磷酸钙生物材料的体外加速降解实验[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(29): 3663-3666.
[19] 岳垂源,唐文洁,戴云,等.人骨髓间质干细胞与新型可降解材料生物相容性的实验研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2005,21(7):1378-1383.
[20] 吴岳恒,汤顺清,毛萱,等.组织工程支架材料偏磷酸钙玻璃陶瓷的多孔性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(1): 130-132.
[21] Lu LX,Zhang XF,Wang YY,et al.Effects of hydroxyapatite-containing composite nanofibers on osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and bone regeneration in vivo.ACS Appl Mater Inter.2013; 5(2): 319-330.
[22] Ning Y,Wei T,Defu C,et al.The research of degradability of a novel biodegradable coralline hydroxyapatite after implanted into rabbit.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2009;88(3): 741-746.
[23] Wetherall KM,Pickup DM,Newport RJ,et al.The structure of calcium metaphosphate glass obtained from x-ray and neutron diffraction and reverse Monte Carlo modelling.J Phys Condens Matter.2009;21(3):035109.
[24] Kasuga T,Ota Y,Nogami M,et al.Surface modification of calcium metaphosphate fibers. J Mater Sci Mat Med.2000; 11(4):223-225.
[25] Salah N,Habib SS,Khan ZH,et al.High-energy ball milling technique for ZnO nanoparticles as antibacterial material.Int J Nanomed.2011;6:863-869.
[26] Maksimenko A,Mougin J,Mura S,et al.Polyisoprenoyl gemcitabine conjugates self assemble as nanoparticles, useful for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett.2013;334(2):346-353.
[27] Bjerre L,Bunger C,Baatrup A,et al.Flow perfusion culture of human mesenchymal stem cells on coralline hydroxyapatite scaffolds with various pore sizes.J Biomed Mater Res A.2011; 97(3):251-263.
[28] Kim JH,Park JS,Yang HN,et al. The use of biodegradable PLGA nanoparticles to mediate SOX9 gene delivery in human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) and induce chondrogenesis. Biomaterials.2011;32(1):268-278.
[29] Greulich C,Kittler S,Epple M,et al.Studies on the biocompatibility and the interaction of silver nanoparticles with human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2009;394(3):495-502.
[30] Shuang-zhi H,Ping S,Xi-ning P.Culture and identification of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells. Chin Med Sci J. 2010;25(4):211-214.
[31] Xiao Y,Chen J.Proteomics approaches in the identification of molecular signatures of mesenchymal stem cells.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2013;129:153-176.
[32] Ranera B,Lyahyai J,Romero A,et al.Immunophenotype and gene expression profiles of cell surface markers of mesenchymal stem cells derived from equine bone marrow and adipose tissue.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2011; 144(1-2):147-154.
[33] Qiu J.Nano-safety studies urged in China.Nature.2012; 489(7416):350.
[34] Monem AS,ElBatal HA,Khalil EM,et al.In vivo behavior of bioactive phosphate glass-ceramics from the system P2O5-Na2O-CaO containing TiO2.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(3):1097-1108.
[35] Hee Soon C,Park SY,Kim S,et al.Effect of different bone substitutes on the concentration of growth factors in platelet-rich plasma.J Biomater Appl.2008;22(6):545-557.
[36] Shundo C,Zhang H,Nakanishi T,et al.Cytotoxicity evaluation of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles in mouse embryonic stem cells.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2012;97:221-225.
[37] Park KS,Tae J,Choi B,et al.Characterization, in vitro cytotoxicity assessment,and in vivo visualization of multimodal, RITC-labeled, silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles for labeling human cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Nanomedicine.2010;6(2):263-276.
[38] Tang ZB,Cao JK,Wen N,et al.Posterolateral spinal fusion with nano-hydroxyapatite-collagen/PLA composite and autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit model.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2012;6(4):325-336.
[39] Phipps MC,Clem WC,Grunda JM,et al.Increasing the pore sizes of bone-mimetic electrospun scaffolds comprised of polycaprolactone, collagen I and hydroxyapatite to enhance cell infiltration.Biomaterials.2012; 33(2):524-534.
[40] Dickinson LE,Kusuma S,Gerecht S.Reconstructing the differentiation niche of embryonic stem cells using biomaterials.Macromol Biosci. 2011;11(1):36-49. |

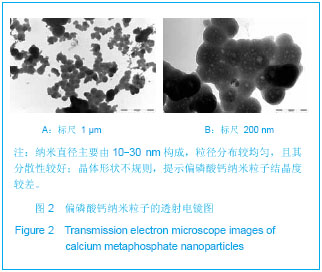
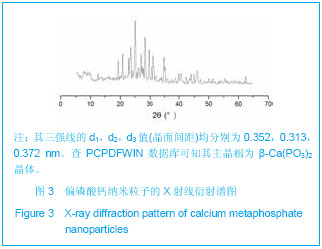
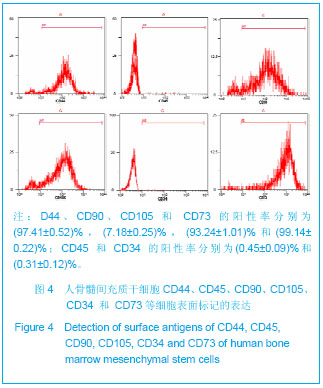
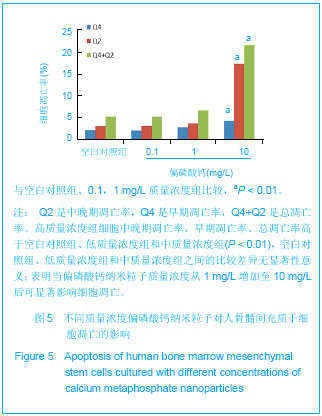
.jpg)