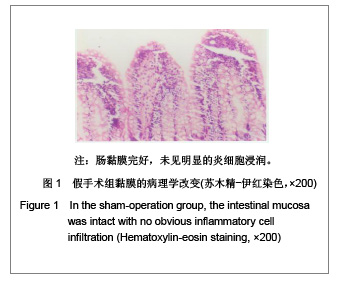
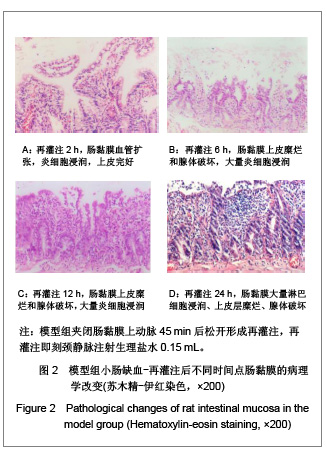
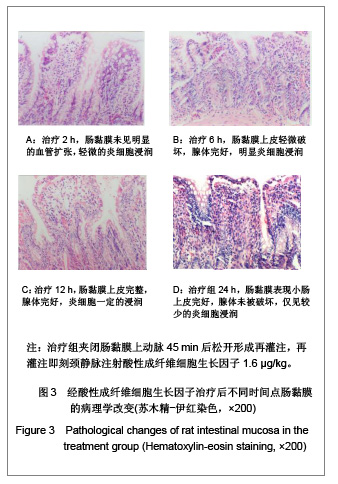
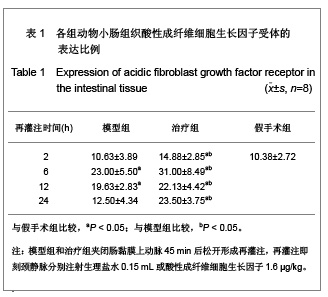
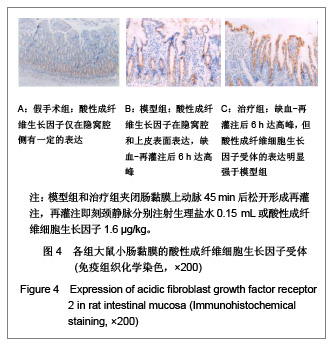
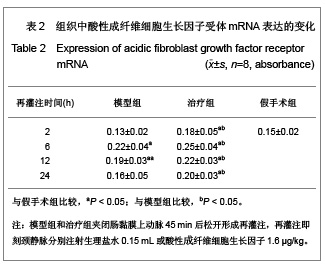
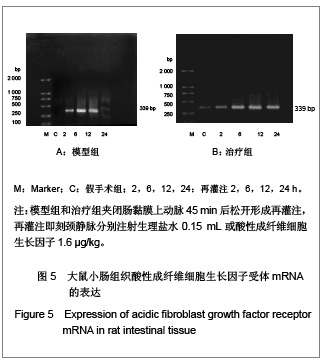
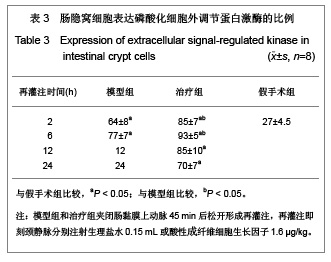
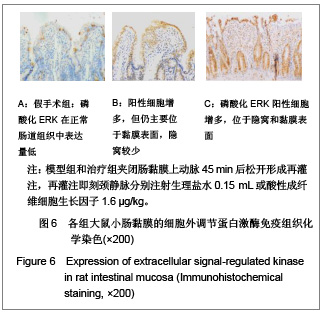
| [1] Feingold KR, Grunfeld C, Heuer JG, et al. FGF21 Is Increased by Inflammatory Stimuli and Protects Leptin-Deficient ob/ob Mice from the Toxicity of Sepsis. Endocrinology. 2012;153(6): 2689-2700.[2] Oh YC, Cho WK, Jeong YH, et al.Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Citrus Unshiu Peel in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells. Am J Chin Med. 2012;40(3):611-629.[3] Friedrich RE, Holstein AF, Middendorff R, et al.Vascular wall cells contribute to tumourigenesis in cutaneous neurofibromas of patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. A comparative histological, ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study. Anticancer Res. 2012;32(5):2139-2158.[4] Niu Y, Ye QF, Xiao JS, et al. Zhongguo Putong Waike Zazhi. 2005;16(5):41-43. 牛英,叶启发,肖建生,等.缺血预处理对大鼠肝缺血再灌注损伤后p38和c-jun蛋白表达的影响[J].中国普通外科杂志, 2005, 16(5): 41-43.[5] Peng HB, Wang XH, Feng L, et al. Effect of p38MAPK on proliferation in human embryonic lung fibroblasts in Vitro.Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2010;28(11):819-821. [6] Zhao JX, Li P, Huang QF, et al. Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2007;23(12) 2448-2450. 赵京霞,李萍,黄启福,等.桂皮醛对NIH3T3细胞p38、c-Myc表达的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2007,23(12) 2448-2450.[7] Xu XY, Ke YB, Ding LP, et al.Effect of cadmium chloride on the expression and phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in normal rat kidney epithelial cells. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;44(12):1131-1135. [8] Shen LJ, Qiu JW, Yu J, et al. Role of p38MAPK in apoptosis of human paratumor cirrhosis hepatocellular cell line QSG-7701 induced by cisplatin. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2010 Dec;18(12):931-935. [9] Ong SL, Garcea G, Thomasset SC, et al.Surrogate markers of resectability in patients undergoing exploration of potentially resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12 (6):1068-1073. [10] Liu RL, Zhang J, Wu W, et al. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Jijiu Zazhi. 2008,15(1):45-47. 刘瑞林,张嘉,吴薇,等.大黄素对肠缺血/再灌注损害保护作用的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志,2008,15(1):45-47.[11] Quermie I, Liwei Lu. Role of leptin in immunity. Cell Mol Immunol. 2007;4(1):1-13. [12] West DA, Valentim LM, Lythgoe MF, et al. MR image-guided investigation of regional signal transducers and activators of transcription-1activation in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 2004;127(2):333-339. [13] Yoshida N, Takagi T, Isozaki Y, et al. Proinflammatory role of protease-activated receptor-2 in intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Med Report. 2011;4(1):81-86. [14] Sonnier DI, Makley AT, Friend LA, et al. Hemorrhagic shock induces a proinflammatory milieu in the gut lumen. J Surg Res. 2011;170(2):272-279. [15] Margaritis EV, Yanni AE, Agrogiannis G, et al. Effects of oral administration of (L)-arginine, (L)-NAME and allopurinol on intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Life Sci. 2011; 88(23-24):1070-1076. [16] Ntinas A, Vrochides D, Iliadis S, et al. Oxygenated perfluorocarbons protect the intestine from the ischemia/ reperfusion injury in rabbits. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2011; 45(5):426-432. [17] Shulga A, Thomas-Crusells J. Posttraumatic GABA(A)-mediated [Ca2+]i increase is essential for the induction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent survival of mature central neurons. J Neurosci. 2008;28(27):6996-7005. [18] Hamarat M, Yenilmez A, Erkasap N, et al. Protective effects of leptin on ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat bladder. Chin J Physiol. 2010;53(3):145-150.[19] Bundzikova J, Pirnik Z, Lackovicova L, et al. Brain-liver interactions during liver ischemia reperfusion injury: a minireview. Endocr Regul. 2011;45(3):163-172. [20] Lu T, Jiang Y, Zhou Z, et al. Intranasal ginsenoside Rb1 targets the brain and ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(8):1319-1324. [21] Balyemez G, Sivasli E, Ceylan H, et al. Protective effects of Y-27632 on hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced intestinal injury in newborn rats. J Pediatr Surg. 2011;46(8):1490-1494. [22] Nedvig K, Zapf I, Fekecs T. Examination of warm and cold ischemic injury of small intestine by differential scanning calorimetry. Magy Seb. 2011;64(4):207-212. [23] Yuan Y, Guo H, Zhang Y, et al. Protective effects of L-carnitine on intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model. J Clin Med Res. 2011;3(2):78-84. [24] He X, Xu X, Fan M, et al. Preconditioning with hyperbaric oxygen induces tolerance against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via increased expression of heme oxygenase-1. J Surg Res. 2011;170(2):271-277. [25] Yuan Y, Guo H, Zhang Y, et al. Protective effects of L-carnitine on intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model. J Clin Med Res. 2011;3(2):78-84. [26] Zhang H, Cui NQ. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Waike Zazhi. 2007,13(3):316. 张浩,崔乃强.肠屏障与多器官功能障碍综合征[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2007,13(3):316.[27] Tapuria N, Kumar Y, Habib MM, et al.Remote ischemic preconditioning: a novel protective method from ischemia reperfusion injury--a review.Surg Res. 2008;150(2):304-330.[28] Ishii A, Fyffe-Maricich SL, Furusho M, et al. EXTRACELLULAR SIGNAL-REGULATED KINASE 1/ EXTRACELLULAR SIGNAL-REGULATED KINASE 2 MAPK Signaling is Required to Increase Myelin Thickness Independent of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Initiation of Myelination.J Neurosci. 2012;32(26):8855-8864. |