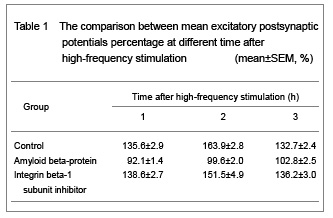
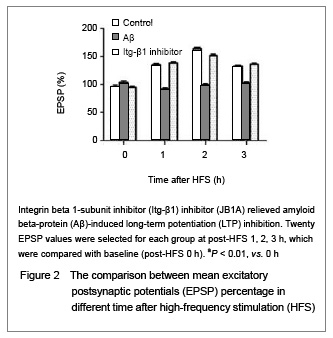
| [1] Blennow K, de Leon MJ, Zetterberg H. Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 2006;368(9533):387-403.[2] Lee HG, Moreira PI, Zhu X, et al. Staying connected: synapses in Alzheimer disease. Am J Pathol. 2004;165(5): 1461-1464.[3] Doherty GH, Beccano-Kelly D, Yan SD, et al. Leptin prevents hippocampal synaptic disruption and neuronal cell death induced by amyloid β. Neurobiol Aging. 2013;34(1): 226-237. [4] Tyan SH, Shih AY, Walsh JJ, et al. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) regulates synaptic structure and function. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2012;51(1-2):43-52. [5] Chapman TR, Barrientos RM, Ahrendsen JT, et al. Synaptic correlates of increased cognitive vulnerability with aging: peripheral immune challenge and aging interact to disrupt theta-burst late-phase long-term potentiation in hippocampal area CA1. J Neurosci. 2010;30(22): 7598-7603.[6] Hamilton A, Holscher C. The effect of ageing on neurogenesis and oxidative stress in the APP(swe)/PS1(deltaE9) mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 2012;1449:83-93. [7] Lisman J, Spruston N. Postsynaptic depolarization requirements for LTP and LTD: a critique of spike timing-dependent plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(7): 839-841.[8] Malenka RC, Bear MF. LTP and LTD: an embarrassment of riches. Neuron. 2004;44(1):5-21.[9] Puzzo D, Arancio O. Fibrillar beta-amyloid impairs the late phase of long term potentiation. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2006; 3(3):179-183.[10] Townsend M, Shankar GM, Mehta T, et al. Effects of secreted oligomers of amyloid beta-protein on hippocampal synaptic plasticity: a potent role for trimers. J Physiol. 2006; 572(Pt 2):477-492. [11] Scopes DI, O’Hare E, Jeggo R, et al. Aβ oligomer toxicity inhibitor protects memory in models of synaptic toxicity. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;167(2):383-392. [12] Klein WL. Synaptotoxic amyloid-β oligomers: a molecular basis for the cause, diagnosis, and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease? J Alzheimers Dis. in press.[13] Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E. Integrin signaling. Science. 1999;285(5430):1028-1032.[14] Chavis P, Westbrook G. Integrins mediate functional pre- and postsynaptic maturation at a hippocampal synapse. Nature. 2001;411(6835):317-321.[15] Rohrbough J, Grotewiel MS, Davis RL, et al. Integrin-mediated regulation of synaptic morphology, transmission, and plasticity. J Neurosci. 2000;20(18): 6868-6878.[16] Sabo S, Lambert MP, Kessey K, et al. Interaction of beta-amyloid peptides with integrins in a human nerve cell line. Neurosci Lett. 1995;184(1):25-28.[17] Huang Z, Shimazu K, Woo NH, et al. Distinct roles of the beta 1-class integrins at the developing and the mature hippocampal excitatory synapse. J Neurosci. 2006;26(43): 11208-11219.[18] Bernard-Trifilo JA, Kramár EA, et al. Integrin signaling cascades are operational in adult hippocampal synapses and modulate NMDA receptor physiology. J Neurochem. 2005;93(4):834-849.[19] McGeachie AB, Cingolani LA, Goda Y. Stabilising influence: integrins in regulation of synaptic plasticity. Neurosci Res. 2011;70(1):24-29.[20] Lin B, Arai AC, Lynch G, et al. Integrins regulate NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents. J Neurophysiol. 2003;89(5):2874-2878.[21] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.[22] Wang Q, Klyubin I, Wright S, et al. Alpha v integrins mediate beta-amyloid induced inhibition of long-term potentiation. Neurobiol Aging. 2008;29(10):1485-1493.[23] Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297(5580):353-356.[24] Anderson KL, Ferreira A. alpha1 Integrin activation: a link between beta-amyloid deposition and neuronal death in aging hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2004;75(5): 688-697. |