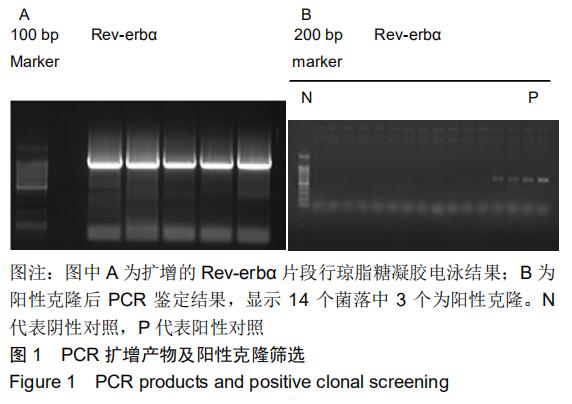
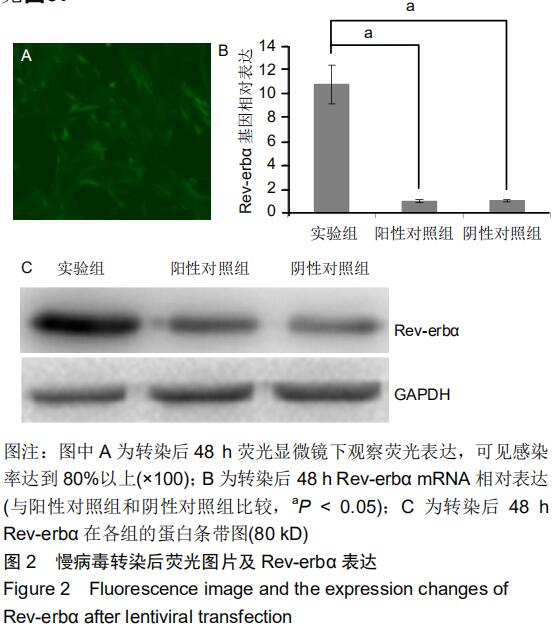
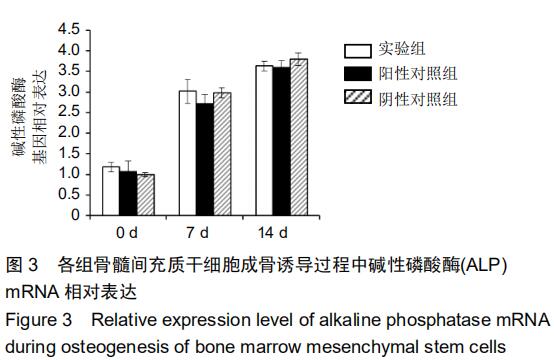
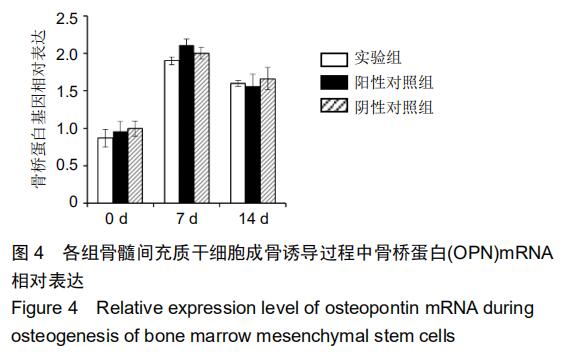
|
[1] RUIZ M, COSENZA S, MAUMUS M, et al. Therapeutic application of mesenchymal stem cells in osteoarthritis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016; 16(1):33-42.
[2] YIM RL, LEE JT, BOW CH, et al. A systematic review of the safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells for disc degeneration: insights and future directions for regenerative therapeutics. Stem Cells Dev. 2014; 23(21):2553-2567.
[3] KARSENTY G, KRONENBERG HM, SETTEMBRE C. Genetic control of bone formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2009;25:629-648.
[4] ZUO C, HUANG Y, BAJIS R, et al. Osteoblastogenesis regulation signals in bone remodeling. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(6):1653-1663.
[5] LIAN JB, JAVED A, ZAIDI SK, et al. Regulatory controls for osteoblast growth and differentiation: role of Runx/Cbfa/AML factors. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2004;14(1-2):1-41.
[6] MARIE PJ, KASSEM M. Osteoblasts in osteoporosis: past, emerging, and future anabolic targets. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011;165(1):1-10.
[7] SÉVÈRE N, DIEUDONNÉ FX, MARIE PJ. E3 ubiquitin ligase-mediated regulation of bone formation and tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e463.
[8] MARGOLIS RN. Nuclear receptors and bone. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007; 1116:327-334.
[9] WEIKUM ER, LIU X, ORTLUND EA. The nuclear receptor superfamily: A structural perspective. Protein Sci. 2018;27(11):1876-1892.
[10] PIKE JW, MEYER MB, WATANUKI M, et al. Perspectives on mechanisms of gene regulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its receptor. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;103(3-5):389-395.
[11] KURT O, YILMAZ-AYDOGAN H, UYAR M, et al. Evaluation of ERα and VDR gene polymorphisms in relation to bone mineral density in Turkish postmenopausal women. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(6): 6723-6730.
[12] YE CF, PAN YM, ZHOU H. Regulation of vitamin D receptor and Genistein on bone metabolism in mouse osteoblasts and the molecular mechanism of osteoporosis. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2018;32(3):497-505.
[13] PAN JM, WU LG, CAI JW, et al. Dexamethasone suppresses osteogenesis of osteoblast via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2019;39(1):80-86.
[14] DENG S, DAI G, CHEN S, et al. Dexamethasone induces osteoblast apoptosis through ROS-PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:602-608.
[15] BONNELYE E, AUBIN JE. Estrogen receptor-related receptor alpha: a mediator of estrogen response in bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 90(5):3115-3121.
[16] GIAGINIS C, TSANTILI-KAKOULIDOU A, THEOCHARIS S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligands as bone turnover modulators. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;16(2):195-207.
[17] FONTAINE C, DUBOIS G, DUGUAY Y, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor Rev-Erbalpha is a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma target gene and promotes PPARgamma-induced adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(39):37672-37680.
[18] CHO H, ZHAO X, HATORI M, et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by REV-ERB-α and REV-ERB-β. Nature. 2012;485 (7396):123-127.
[19] 林富伟,徐晓梅,崔琰,等.小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中的核受体Rev-erbα及Rorα[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(17):2625-2630.
[20] SHEARER RF, SAUNDERS DN. Experimental design for stable genetic manipulation in mammalian cell lines: lentivirus and alternatives. Genes Cells. 2015;20(1):1-10.
[21] JOGLEKAR AV, SANDOVAL S. Pseudotyped Lentiviral Vectors: One Vector, Many Guises. Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2017;28(6):291-301.
[22] GEISLER A, FECHNER H. MicroRNA-regulated viral vectors for gene therapy. World J Exp Med. 2016;6(2):37-54.
[23] DE ANDRADE PEREIRA B, FRAEFEL C. Novel immunotherapeutic approaches in targeting dendritic cells with virus vectors. Discov Med. 2015;20(109):111-119.
[24] HU B, TAI A, WANG P. Immunization delivered by lentiviral vectors for cancer and infectious diseases. Immunol Rev. 2011;239(1):45-61.
[25] FERNÁNDEZ-RUBIO P, TORRES-RUSILLO S, MOLINA IJ. Regulated expression of murine CD40L by a lentiviral vector transcriptionally targeted through its endogenous promoter. J Gene Med. 2015;17 (10-12):219-228.
[26] EBRAHIMABADI S, SHAHBAZI M, AKBARI M, et al. Design and construction of a recombinant lentiviral vector with specific tropism to human epidermal growth factor-overexpressed cancer cells: Developing a new retargeting system for lentivirus vectors. J Gene Med. 2019;21(6):e3095.
[27] PENG W, ZHANG J, ZHANG H, et al. Effects of lentiviral transfection containing bFGF gene on the biological characteristics of rabbit BMSCs. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(10):8389-8397.
[28] GERHART-HINES Z, LAZAR MA. Rev-erbα and the circadian transcriptional regulation of metabolism. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015; 17 Suppl 1:12-16.
[29] LIN F, CHEN Y, LI X, et al. Over-expression of circadian clock gene Bmal1 affects proliferation and the canonical Wnt pathway in NIH-3T3 cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 2013;31(2):166-172.
[30] FENG G, ZHENG K, SONG D, et al. SIRT1 was involved in TNF-α-promoted osteogenic differentiation of human DPSCs through Wnt/β-catenin signal. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2016;52(10): 1001-1011.
[31] SODEK J, GANSS B, MCKEE MD. Osteopontin. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2000;11(3):279-303.
[32] GIACHELLI CM. Inducers and inhibitors of biomineralization: lessons from pathological calcification. Orthod Craniofac Res.2005;8(4):229-231.
[33] KAZANECKI CC, UZWIAK DJ, DENHARDT DT. Control of osteopontin signaling and function by post-translational phosphorylation and protein folding. J Cell Biochem. 2007;102(4):912-924.
[34] STAINS JP, CIVITELLI R. A Functional Assay to Assess Connexin 43-Mediated Cell-to-Cell Communication of Second Messengers in Cultured Bone Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1437:193-201.
[35] 王春玉,龙丰云,陈香,等.骨钙素介导的骨内分泌系统[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2013,6(3):196-202.
[36] KOJETIN DJ, BURRIS TP. A role for rev-erbα ligands in regulation of adipogenesis. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(4):320-324.
|