| [1] Liu W, Cui L, Cao YL. A closer view of tissue engineering in China-The experience of tissue construction in immunocompetent animals. Tissue Eng. 2003;9(Suppl1): S17-31.[2] Cai G, Zhang Y, Liu W, et al. Zhonghua Yixue Zazhi. 2003; 83(19):1676-1681. 柴岗,张燕,刘伟,等.组织工程骨在颅颌面骨缺损临床修复中的应用[J].中华医学杂志,2003,83(19):1676-1681.[3] Brittberg M, Tallheden T, Sjorgren-Jansson B, et al. Autologous chondrocytes used for articular cartilage repair: an update. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;391(Suppl):S337-348.[4] Shi SS, Xu ST. Beijing: People Military Medical Press. 2002. 时述山,胥少汀.实用骨与软骨移植[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2002. [5] Cheng LZ, Zhong CP, Cai WQ. Shanghai: Shanghai Kexuejishu Wenxian Chubanshe. 2003. 成令忠,钟翠平,蔡文琴.现代组织学[M].上海:上海科学技术文献社,2003.[6] Bai SL. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House. 2004. 柏树令.系统解剖学[M].6版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2004.[7] Susan Standring. Beijing: Peking University Medical Press. 2008. 徐群渊.格氏解剖学[M].39版.北京:北京大学医学出版社, 2008.[8] Ge C, Zhang ZG, Xiang P. Zhongshan Daxue Xuebao(Yixue Kexueban). 2006;27(4):387-390. 葛成,张志光,项鹏.体外培养大鼠耻骨联合软骨细胞的生物学特性[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2006,27(4):387-390. [9] Ge C, Zhang ZG, Xiang P. Linchuang Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2005;21(11):662-664. 葛成,张志光,项鹏.耻骨联合软骨细胞的体外培养及形态学观察[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2005,21(11):662-664. [10] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. [11] Zhang JZ, Shu YK. Beijing: Kexue Chubanshe. 2007. 张继宗,舒永康.人体骨骼测量方法[M].北京:科学出版社,2007. [12] Hao Q, Chen HZ, Lin L. Fuzhou: Fujian Kexue Jishu Chubanshe. 2003. 郝强,陈宏颉,林玲.影像解剖学[M].第1版.福州:福建科学技术出版社,2003.[13] Scott JE, Dorling J. Differential staining of acid glycoaminoglycansy alcian blue in salt solutions. Histochemie. 1965;5:221-233.[14] Gao GX, Wei XC, Li K, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu Yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(24):4385-4389. 高改霞,卫小春,李凯,等.大鼠膝关节软骨不同染色方法的差异[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(24):4385-4389.[15] Ortega HH, Munoz-de-Toro MM, Luque EH, et al. Morphological characteristics of the interpubic joint (Symphysis pubica) of rats, guinea pigs and mice in different physiological situations. A comparative study. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;173(2):105-114. [16] Pinheiro MC, Moraes SG, Battlehner CN, et al. Histochemical and ultrastructural study of collagen fibers in mouse pubic symphysis during late pregnancy. Micron. 2004;35(8): 685-693.[17] Putnis SE, Pearce R, Wali UJ, et al.Open reduction and internal fixation of a traumatic diastasis of the pubic symphysis: one-year radiological and functional outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(1):78-84. [18] Sgambati E, Stecco A, Capaccioli L, et al. Morphometric evaluation of the symphysis pubis joint. Ital J Anat Embryol. 1996;101(3):195-201. [19] Wang SW, Yue L. Tianjin: Tianjin Keji Fanyi Chubangongsi. 2003. 王淑雯,岳琏.中国女性骨盆图集[M].天津:天津科技翻译出版公司出版,2003. [20] Alicioglu B, Kartal O, Gurbuz H, et al. Symphysis pubis distance in adults: a retrospective computed tomography study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2008;30(2):153-157.[21] Diduch DR, Jordan LC, Mierisch CM, et al. Marrow stromal cells embedded in alginate for repair of osteochondral defects. Arthroscopy. 2000;16(6):571-577. [22] Lin HR, Yeh YJ. Porous alginate/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: preparation, characterization, and in vitro studies. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004;71(1):52-65.[23] Choi BY, Park HJ, Hwang SJ, et al. Preparation of alginate beads for floating drug delivery system: effects of CO(2) gas-forming agents. Int J Pharm. 2002;239(1-2):81-91.[24] Wong M, Siegrist M, Gaschen V, et al. Collagen fibrillogenesis by chondrocytes in alginate. Tissue Eng. 2002;8(6):979-986.[25] Dembczynski R, Jankowski T. Determination of pore diameter and molecular weight cut-off of hydrogel-membrane liquid-core capsules for immunoisolation. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2001;12(9):1051-1058.[26] Dvir-Ginzberg M, Gamlieli-Bonshtein I, Agbaria R, et al. Liver tissue engineering within alginate scaffolds: effects of cell-seeding density on hepatocyte viability, morphology, and function. Tissue Eng. 2003;9(4):757-766.[27] Almarza AJ, Athanasiou KA. Effects of initial cell seeding density for the tissue engineering of the temporomandibular joint disc. Ann Biomed Eng. 2005;33(7):943-950.[28] Benya PD, Shaffer JD. Dedifferentiated chondrocytes reexpress the differentiated collagen phenotype when cultured in agarose gels. Cell. 1982;30(1):215-224.[29] Beekman B, Verzijl N, Bank RA, et al. Synthesis of collagen by bovine chondrocytes cultured in alginate: posttranslational modifications and cell-matrix interaction. Exp Cell Res. 1997; 237(1):135-141. [30] Bonaventure J, Kadhom N, Cohen-Solal L, et al. Reexpression of cartilage-specific genes by dedifferentiated human articular chondrocytes cultured in alginate beads. Exp Cell Res. 1994;212(1):97-104.[31] He Qingyi. Chongqing: Disan Junyi Daxue. 2002. 何清义.软骨组织工程的种子细胞研究-人关节软骨细胞的永生化及其生物学特性[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2002.[32] Steck E, Bertram H, Abel R, et al. Induction of intervertebral disc-like cells from adult mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2005;23(3):403-411. [33] Richardson SM, Curran JM, Chen R, et al. The differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocyte-like cells on poly-l-lactic acid (PLLA) scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2006;27(22):4069-4078. [34] Banfi A, Bianchi G, Notaro R, et al. Replicative aging and gene expression in long-term culture of human bone marrow stromal cells. Tissue Eng. 2002;8(6):901-910. [35] Owen M. Marrow stromal stem cells. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1988; 10:63-76. [36] Yoo JU, Johnstone B. The role of osteochondral progenitor cells in fracture repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; 355 (Suppl): S73-81. [37] Lin JH, Chen XD, Deng LX. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2007;21(11):1155-1160. 林建华,陈晓东,邓凌霄,等.大鼠软骨细胞复制性老化的体外观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(11):1155-1160. |
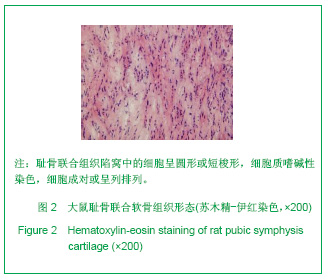



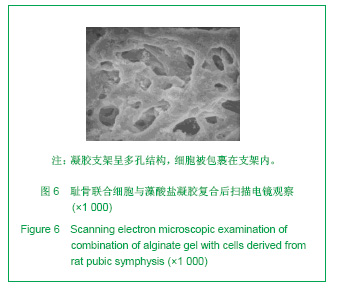
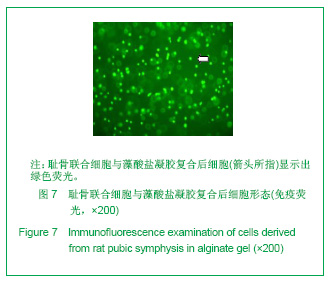
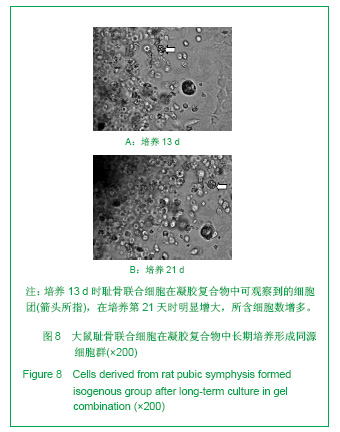

.jpg)
.jpg)