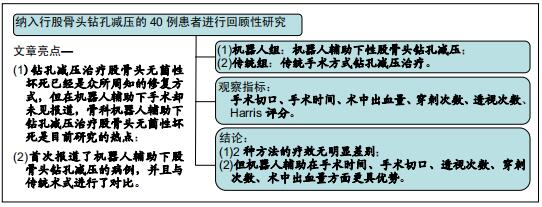
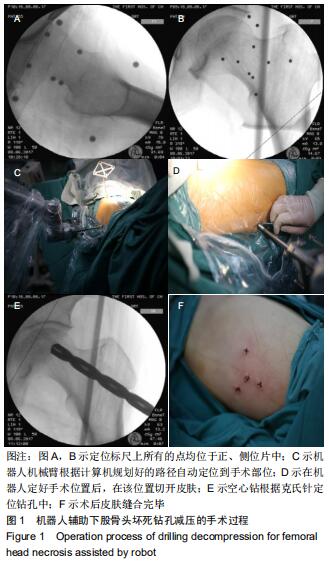
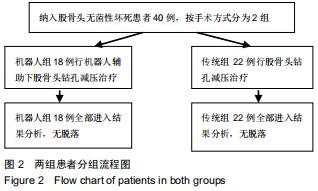
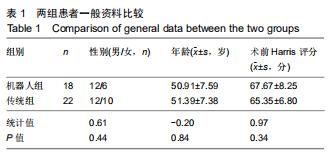
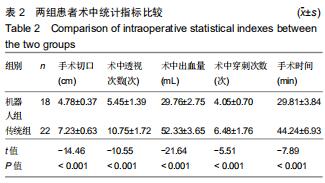
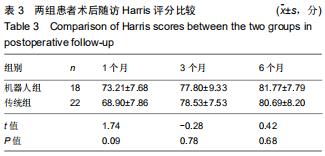
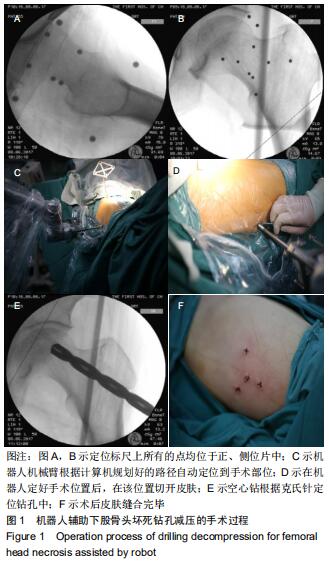
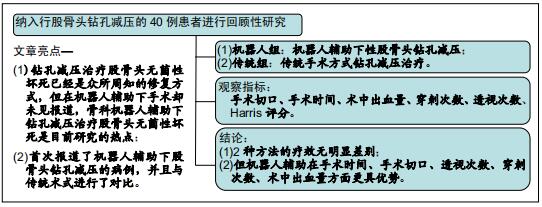
|
[1] WANG G, LI Y, SUN T, et al. BMSC affinity peptide-functionalized β-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds promoting repair of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):204.
[2] 郭红斌.CT和核磁共振诊断股骨头坏死的临床价值对比分析[J].实用中西医结合临床,2017,17(8):98-99.
[3] 随义,于兴玲,贾志祥,等. CT与MRI诊断早期股骨头缺血坏死的多中心对比分析[J].影像研究与医学应用,2018,2(8):170-172.
[4] 许珂,蔡元真,杨治,等.髓芯减压术治疗不同类型股骨头坏死的疗效分析[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(4):24-28.
[5] 王旭,王亚康,郭建斌,等.髓芯减压术及其辅助疗法在股骨头坏死治疗中作用的研究进展[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2018, 32(11):104-106.
[6] 袁明武,罗瀚文,方怀玺,等.髓芯减压联合富血小板血浆及β-磷酸三钙陶瓷骨治疗早期股骨头坏死疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(6):596-598.
[7] 盛东,张庆文,陈达,等.青少年创伤后股骨头坏死的临床特点及保髋手术治疗效果分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(10): 55-57.
[8] 杨元庆,夏军,王思群,等.早期股骨头坏死保头手术治疗进展[J].复旦学报(医学版),2017,44(1):117-121.
[9] 王骏,葛乔枫,武壮壮,等.股骨头坏死手术治疗最新进展:如何达到保髋治疗的目的[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(31): 5056-5061.
[10] 中华医学会骨科分会显微修复学组及中国修复重建外科专业委员会骨缺损及骨坏死学组.成人股骨头坏死诊疗标准专家共识(2012年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(6):185-192.
[11] LONG T, LI KN, GAO JH, et al. Comparative study of percutaneous sacroiliac screw with or without tirobot assistance for treating pelvic posterior ring fractures. Orthop Surg. 2019;11:386-396.
[12] 蒋侃凌,田维,贾健. TiRobot手术机器人辅助经皮骶髂螺钉固定治疗骨盆后环不稳定损伤[J].天津医科大学学报,2017,23(3): 69-73.
[13] 李子荣.股骨头坏死临床诊疗规范[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2015,8(1):49-54.
[14] 王洪伟,赵忆文,韩建达,等.机器人系统在脊柱外科手术中的研究与应用进展[J].中华外科杂志,2012,50(9):856-858.
[15] STAARTJES VE, MOLLIQAJ G, VAN KAMPEN PM, et al. The European Robotic Spinal Instrumentation (EUROSPIN) study: protocol for a multicentre prospective observational study of pedicle screw revision surgery after robot-guided, navigated and freehand thoracolumbar spinal fusion. BMJ Open. 2019; 9: e030389.
[16] 陈良飞,胡盼盼,郭会卿.郭会卿教授治疗非创伤性股骨头坏死经验总结[J]. 风湿病与关节炎,2019,8(8):44-46.
[17] 田志,徐朝健,冯毅,等.早期非创伤性股骨头坏死诊断及治疗的研究现状[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2016,31(s1):116-118.
[18] 文良元,黄公怡.创伤性和激素性股骨头坏死的病理学研究及进展[J].中华骨科杂志,1997,17(2):140-143.
[19] 杨静,康鹏德,沈彬,等.小孔径多通道髓芯钻孔减压治疗早中期股骨头坏死[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(1):58-61.
[20] HUA KC, YANG XG, FENG JT, et al. The efficacy and safety of core decompression for the treatment of femoral head necrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14:306.
[21] 段丹,宁宁,李佩芳,等.加速康复外科下骨科患者围手术期深静脉血栓形成的预防及管理新进展[J].华西医学,2017,32(9):49-52.
[22] 赵永恒.加速康复外科理念的临床应用[J].临床外科杂志,2015, 23(10):739-741.
[23] 杨鹏,张帆,朱磊,等.一种新型微创骨盆后环固定系统的设计与手术模拟及其安全性评估[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(4): 278-283.
[24] 龙涛,彭超,何智勇,等.机器人辅助下经皮骶髂螺钉固定手术的优势及安全性研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2019, 21(1):10-15.
[25] LIU HS, DUAN SJ, LIU SD, et al. Robot-assisted percutaneous screw placement combined with pelvic internal fixator for minimally invasive treatment of unstable pelvic ring fractures. Int J Med Robot. 2018;14(5):e1927.
[26] LAN H,TAN Z,LI KN, et al. Intramedullary nail fixation assisted by orthopaedic robot navigation for intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients. Orthop Surg. 2019;11:255-262.
[27] 佚名.骨科手术机器人辅助经皮椎弓根钉内固定治疗Levine- Edward Ⅰ、Ⅱ型Hangman骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2019,34(5):449-452.
[28] 黄波,荣绍远,李建华,等.双平面机器人导航辅助下空心钉内固定治疗股骨颈骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(9):528-534.
[29] 赵春鹏,王军强,王豫,等.双平面骨科机器人系统辅助股骨颈骨折空心螺钉内固定术的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(1): 50-55.
[30] 苏云,胡春明,莫丽娟,等.髓心减压术治疗早期股骨头缺血性坏死的疗效观察(附90例报告)[J].吉林医学,2005,26(10):1086-1087.
|