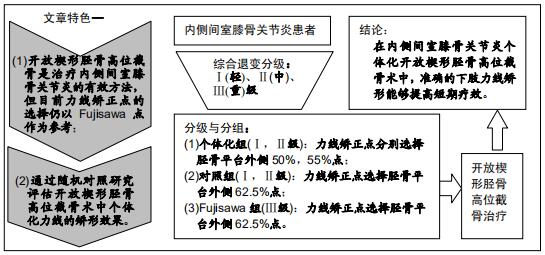
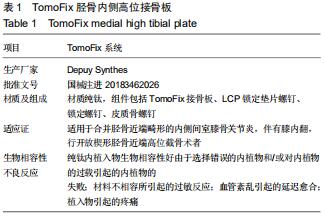
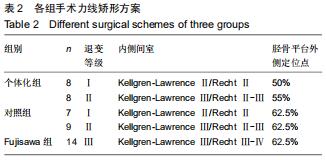
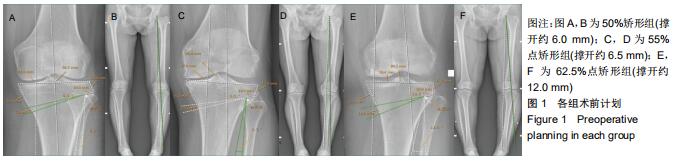
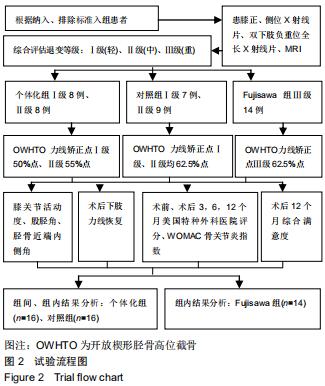
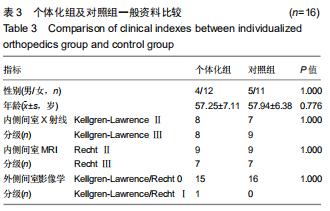
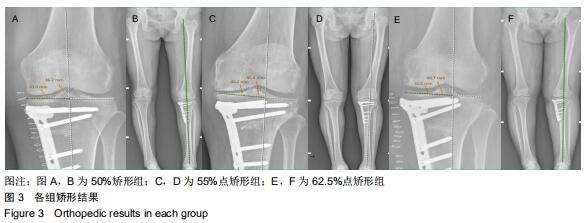
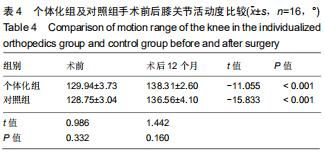
|
[1] SLEMENDA CW. The epidemiology of osteoarthritis of the knee. Curr Opin Rheumatol.1992;4(4):546-451.
[2] 于沂阳,常恒瑞,张英泽.保膝治疗的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2017,11(1):73-77.
[3] DOROFEEV A, TYLLA A, DRESCHER W, et al. Complication analysis after angle-stable CW and OW high tibial osteotomy. Der Orthopade. 2020;49(1):18-25.
[4] PANNELL WC, HEIDARI KS, MAYER EN, et al. High tibial osteotomy survivorship: a population-based study. Orthop J Sports Med. 2019;7(12): 2325967119890693.
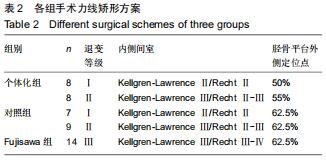
[5] FUJISAWA Y, MASUHARA K, SHIOMI S. The effect of high tibial osteotomy on osteoarthritis of the knee. An arthroscopic study of 54 knee joints. Orthop Clin North Am. 1979;10(3): 585-608.
[6] ALTMAN R, ASCH E, BLOCH D, et al. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and therapeutic criteria committee of the american rheumatism association. Arthritis Rheum. 1986;29(8):1039-1049.
[7] RECHT MP, KRAMER J, MARCELIS S, et al. Abnormalities of articular cartilage in the knee: analysis of available MR techniques. Radiology. 1993;187(2):473-478.
[8] SLEVIN O, AYENI OR, HINTERWIMMER S, et al. The role of bone void fillers in medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(11):3584-3598.
[9] 魏伟,沈计荣.双平面胫骨高位截骨术治疗膝关节内侧间室骨关节炎[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(11):1406-1410.
[10] HUANG SC, CHEN YF, LIU XD, et al. The efficacy and safety of opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy in treating unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2019;98(12): e14927.
[11] 张子琦,梁佳林,樊立宏,等.开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术治疗膝关节内侧间室骨关节炎疗效观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018, 32(8):997-1000.
[12] RODRIGUEZ-MERCHAN EC. Unicompartmental Knee Osteoarthritis (UKOA): unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA) or high tibial osteotomy (HTO)? Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2016;4(4): 307-313.
[13] 黄野.胫骨高位截骨术治疗膝关节骨关节炎的现状[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2016,10(5): 470-473.
[14] 周青,张辉.胫骨高位截骨术治疗膝关节骨关节炎的长期随访[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2000,7(9):6-10+106.
[15] COTTER EJ, GOWD AK, BOHL DD, et al. Medical comorbidities and functional dependent living are independent risk factors for short-term complications following osteotomy procedures about the knee. Cartilage. 2018:1947603518798889.
[16] TRIEB K, GROHS J, HANSLIK-SCHNABEL B, et al. Age predicts outcome of high-tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14(2): 149-152.
[17] JIN C, SONG EK, SANTOSO A, et al. Survival and risk factor analysis of medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy for unicompartment knee osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy. 2019; 19: 30760-30761.
[18] FLAMME CH, RUHMANN O, SCHMOLKE S, et al. Long-term outcome following high tibial osteotomy with tension bend principle. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2003;123(1): 12-16.
[19] LEE SC, JUNG KA, NAM CH, et al. The short-term follow-up results of open wedge high tibial osteotomy with using an Aescula open wedge plate and an allogenic bone graft: the minimum 1-year follow-up results. Clin Orthop Surg. 2010; 2(1): 47-54.
[20] HERNIGOU P, MEDEVIELLE D, DEBEYRE J, et al. Proximal tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis with varus deformity. A ten to thirteen-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987; 69(3): 332-354.
[21] HERNIGOU P. A 20-year follow-up study of internal gonarthrosis after tibial valgus osteotomy. Single versus repeated osteotomy. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1996;82(3):241-250.
[22] BENZAKOUR T, HEFTI A, LEMSEFFER M, et al. High tibial osteotomy for medial osteoarthritis of the knee: 15 years follow-up. Int Orthop. 2010;34(2): 209-215.
[23] SETHI G, ALJAWADI A, ELMAJEE M, et al. Determination of the postoperative limb alignment following a high tibial osteotomy in patients with uni-compartmental knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop. 2019;19: 30624-30625.
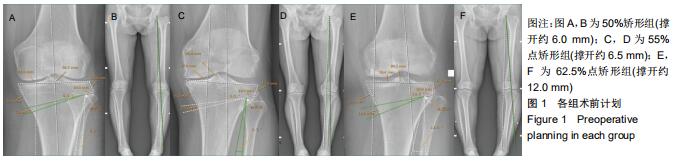
[24] YIN Y, LI S, ZHANG R, et al. What is the relationship between the "Fujisawa point" and postoperative knee valgus angle? A theoretical, computer-based study. Knee. 2019;19: 30244-30243.
[25] JUNG WH, TAKEUCHI R, CHUN CW, et al. Second-look arthroscopic assessment of cartilage regeneration after medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Arthroscopy. 2014; 30(1): 72-79.
[26] NAKAMURA R, TAKAHASHI M, SHIMAKAWA T, et al. High tibial osteotomy solely for the purpose of return to lifelong sporting activities among elderly patients: A case series study. Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol. 2019;19: 17-21.
[27] LEE SS, LEE HI, CHO ST, et al. Comparison of the outcomes between two different target points after open wedge high tibial osteotomy: The Fujisawa point versus the lateral tibial spine. Knee. 2020. pii: S0968-0160(20)30006-5.
[28] 包学智,赵蓬,刘培来,等. 胫骨内侧开放楔形高位截骨治疗膝关节内侧间室骨关节炎的短期疗效[J].山东大学学报(医学版), 2016,54(10): 85-89.
[29] SAWAGUCHI T, TAKEUCHI R, NAKAMURA R, et al. Outcome after treatment of osteoarthritis with open-wedge high-tibial osteotomy with a plate: 2-year results of a Japanese cohort study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2020; 28(1): 2309499019887997.
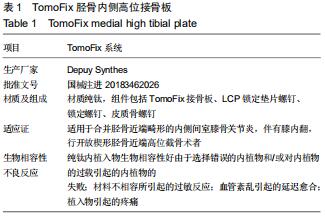
[30] DAREES M, PUTMAN S, BROSSET T, et al. Opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy performed with locking plate fixation (TomoFix) and early weight-bearing but without filling the defect. A concise follow-up note of 48 cases at 10 years' follow-up. Orthop Traum Surg Res. 2018;104(4): 477-480.
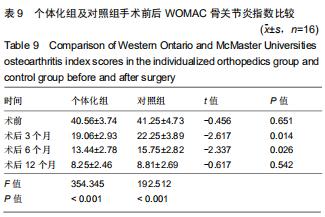
[31] 陈蔚,郭燕梅,李晓英,等. 西安大略和麦克马斯特大学骨关节炎指数的重测信度[J].中国康复理论与实践,2010,16(1): 23-24.
[32] 朱兵,裴保安,高万里,等.开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术后膝关节软骨修复的影响因素研究进展[J].山东医药, 2019, 59(3): 102-105.
[33] KIM HJ, KYUNG HS. Comparison of the method using 3D printing model and PACS in preoperative planning for open wedge high tibial osteotomy. Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol. 2017; 9: 13-14.
[34] AGARWALLA A, CHRISTIAN DR, LIU JN, et al. Return to work following high tibial osteotomy with concomitant osteochondral allograft transplantation. Arthroscopy. 2019;19: 30788-30791.
[35] KIM YS, KOH YG. Comparative matched-pair analysis of open-wedge high tibial osteotomy with versus without an injection of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for varus knee osteoarthritis: clinical and second-look arthroscopic results. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(11): 2669-2677.
|