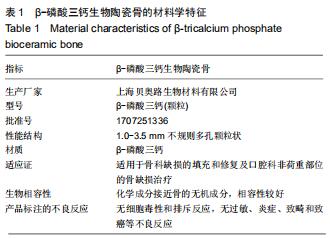
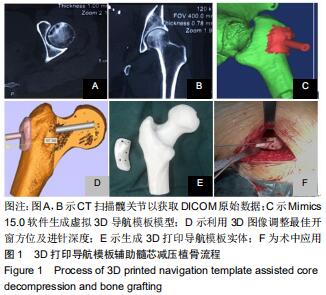
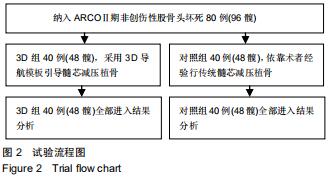
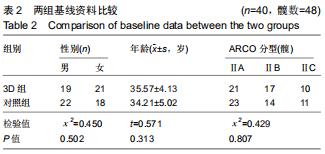
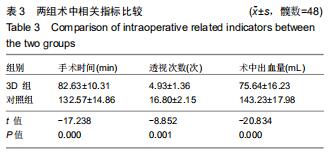
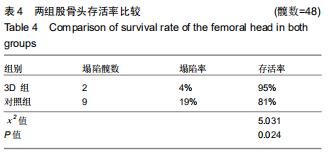
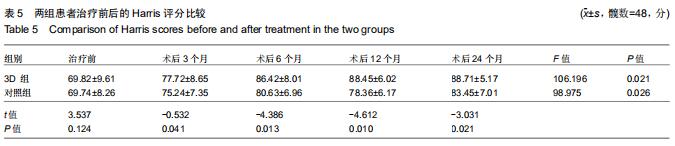
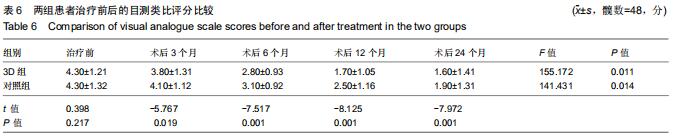
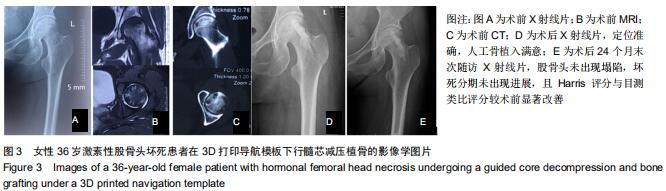
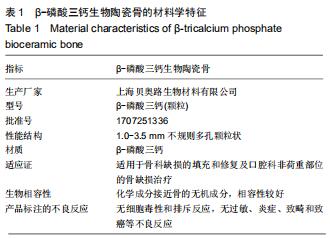
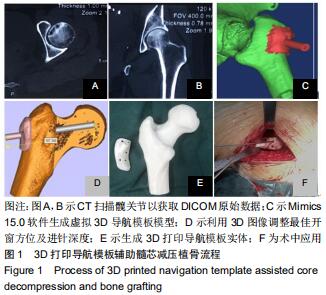
|
[1] 中华医学会骨科分会显微修复学组, 中国修复重建外科专业委员会骨缺损及骨坏死学组. 成人股骨头坏死诊疗标准专家共识(2012年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,4(6):51-56.
[2] GANGJI V, SOYFOO MS, HEUSCHLING A, et al. Non traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head is associated with low bone mass. Bone.2018;107:88-92.
[3] 白浩波,朱卫文,路倩,等.股骨头坏死患者基因表达的转录组学高通量分析[J].重庆医科大学学报,2019,44(9):1149-1154.
[4] ZHU W, QI MQ, BORG S, et al. Cemented injectable multi-phased porous bone grafts for the treatment of femoral head necrosis. J Mater Chem.2019.
[5] JO WL, LEE YK, HA YC, et al. Delay of total hip arthroplasty to advanced stage worsens post-operative hip motion in patients with femoral head osteonecrosis. Int Orthop. 2018;42(7):1-5.
[6] KOBAYASHI S, KUBO T, IWAMOTO Y, et al. Nationwide multicenter follow-up cohort study of hip arthroplasties performed for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Int Orthop. 2018;(6):1-8.
[7] 赵德伟,程亮亮.国内股骨头坏死保留髋关节手术治疗的十年回顾[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2017,37(3):183-192.
[8] TU Y, CHEN Z, LINEAWEAVER WC, et al. Different recipient vessels for free microsurgical fibula flaps in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Plastic Surg. 2017;79(6):583-589
[9] ZHAO D, ZHANG Y, WANG W, et al. Tantalum rod implantation and vascularized iliac grafting for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthopedics. 2013;36(6): 789-795.
[10] ELMALI N, ERTEM K, KARAKAPLAN M, et al. Vascular pedicled iliac bone graft ing is eff ective in patients with an early stage of femoral head avascular necrosis. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2014; 25(1): 2-7.
[11] ZHAO D, LIU B, WANG B, et al. Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells associated with tantalum rod implantation and vascularized iliac grafting for the treatment of end-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015: 240506.
[12] 赵宇驰,曲文庆,张树栋.机器人辅助髓芯减压植骨术治疗早期股骨头缺血性坏死的临床效果[J].中华外科杂志,2018,56(11):849-853.
[13] PAPAGELOPOULOS PJ, SAVVIDOU OD, KOUTSOURADIS P, et al. Three-dimensional technologies in orthopedics. Orthopedics. 2018;41(1):12-20.
[14] 卢鹏,田文.3D打印技术在骨科及手外科领域的应用研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2017,6(5):348-351.
[15] 中国医师协会骨科医师分会显微修复工作委员会, 中国修复重建外科专业委员会骨缺损及骨坏死学组,中华医学会骨科分会显微修复学组.成人股骨头坏死临床诊疗指南(2016)[J].中华骨科杂志,2016, 36(15):945-954.
[16] 陈卫衡.基于X线的股骨头坏死保髋疗效评价方法研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2017,11(3):222-227.
[17] CILLA M, CHECA S, PREININGER B, et al. Femoral head necrosis: A finite element analysis of common and novel surgical techniques. Clin Biomech. 2017; 48:49-56.
[18] 程文俊,王俊文,左伟,等.组织工程化骨结合改良髓芯减压技术治疗早中期股骨头坏死中期疗效研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019, 36(5):954-957.
[19] 李子荣.股骨头坏死临床诊疗规范(2015年版)[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,9(1):133-138.
[20] HARRIS WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. an end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg. 1969;51(4):737-755.
[21] TURNER NM, VAN DE LEEMPUT AJ, DRAAISMA JM, et al. Validity of the visual analogue scale as an instrument to measure self -efficacy in resuscitation skills. Med Educ. 2008;42(5): 503-511.
[22] 赵德伟,谢辉.成人股骨头坏死保髋手术治疗的策略及探讨[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(7):792-797.
[23] 姜良斌,肖伯莲,刘松,等. 富血小板血浆联合高位股骨头颈开窗植骨支撑术治疗早期股骨头坏死的研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2018, 36(4):449-452.
[24] LAI Y, CAO H, WANG X, et al. Porous composite scaffold incorporating osteogenic phytomolecule icariin for promoting skeletal regeneration in challenging osteonecrotic bone in rabbits. Biomaterials. 2018; 153:1-13.
[25] 李杨,冯世庆.早期股骨头缺血性坏死治疗:髓芯减压并钽棒优于并植骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(5):815-820.
[26] 赵宇驰,曲文庆,张树栋.机器人辅助髓芯减压植骨术治疗早期股骨头缺血性坏死的临床效果[J].中华外科杂志,2018,56(11):849-853.
[27] GUO HS, TIAN YJ, LIU G, et al. Arthroscopy-guided core decompression and bone grafting combined with selective arterial infusion for treatment of early stage avascular necrosis of femoral head. China J Orthop Traumatol. 2018;31(1):47-56.
[28] 中华医学会医学工程学分会数字骨科学组, 国际矫形与创伤外科学会(SICOT)中国部数字骨科学组. 3D打印骨科手术导板技术标准专家共识[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(1):6-9.
[29] 周明旺,邓昶,李盛华,等.股骨头坏死的精准医疗:概念与模式[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(7):1133-1139.
[30] 李靖,王臻.骨肿瘤外科修复重建进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018,32(7):838-842.
[31] 余开富,徐永清,谭洪波,等. 3D打印导航模板在带血管蒂髂骨瓣移植治疗股骨头缺血性坏死中的临床应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016(3):373-377.
[32] 章跃,谭杰,饶勇,等. 3D打印导航模块辅助髓芯减压植骨治疗早期股骨头坏死[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(5):22-26.
[33] 吴超,邓佳燕,谭伦,等. 3D打印导航模板辅助枢椎椎弓根拉力螺钉置钉治疗不典型Hangman骨折的初步应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2019,21(4):338-344.
|