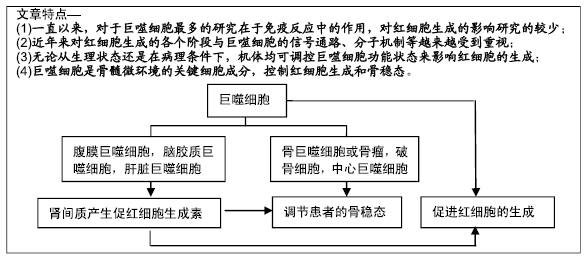
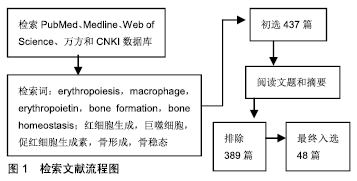
[1] DOULATOV S, NOTTA F, LAURENTI E, et al. Hematopoiesis: a human perspective. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(2):120-136.
[2] PAUL F, ARKIN Y, GILADI A, et al. Transcriptional Heterogeneity and Lineage Commitment in Myeloid Progenitors.Cell.2015;163(7): 1663-1677.
[3] RODRIGUEZ-FRATICELLI AE, WOLOCK SL, WEINREB CS, et al. Clonal analysis of lineage fate in native haematopoiesis.Nature.2018; 553(7687):212-216.
[4] TUSI BK, WOLOCK SL, WEINREB C, et al. Population snapshots predict early haematopoietic and erythroid hierarchies.Nature.2018; 555(7694):54-60.
[5] VOSKARIDOU E, NTANASIS-STATHOPOULOS I, CHRISTOULAS D, et al. Denosumab effects on serum levels of the bone morphogenetic proteins antagonist noggin in patients with transfusion-dependent thalassemia and osteoporosis. Hematology. 2019;24(1):318-324.
[6] EGGOLD JT, RANKIN EB. Erythropoiesis, EPO, macrophages, and bone. Bone. 2019;119:36-41.
[7] VALDERRABANO RJ, LEE J, LUI LY, et al. Older Men With Anemia Have Increased Fracture Risk Independent of Bone Mineral Density. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(7):2199-2206.
[8] FARMER S, HORVATH-PUHO E, VESTERGAARD H, et al. Chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms and risk of osteoporotic fractures; a nationwide population-based cohort study. Br J Haematol. 2013;163(5): 603-610.
[9] OIKONOMIDOU PR, CASU C, YANG Z, et al. Polycythemia is associated with bone loss and reduced osteoblast activity in mice. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(4):1559-1568.
[10] JELKMANN W. Molecular biology of erythropoietin. Intern Med. 2004; 43(8):649-659.
[11] MELASHCHENKO OV, MENIAILO ME, MALASHCHENKO VV, et al. Erythropoietin Directly Affects Human Macrophage Functionality. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2018;19(11):902-909.
[12] ELLIOTT S, SINCLAIR AM. The effect of erythropoietin on normal and neoplastic cells. Biologics.2012;6:163-189.
[13] WU H, LEE SH, GAO J, et al. Inactivation of erythropoietin leads to defects in cardiac morphogenesis.Development.1999;126(16):3597-3605.
[14] KOBAYASHI H, LIU Q, BINNS TC, et al. Distinct subpopulations of FOXD1 stroma-derived cells regulate renal erythropoietin. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(5):1926-1938.
[15] RANKIN EB, WU C, KHATRI R, et al. The HIF signaling pathway in osteoblasts directly modulates erythropoiesis through the production of EPO. Cell. 2012;149(1):63-74.
[16] HIRAM-BAB S, NEUMANN D, GABET Y. Context-Dependent Skeletal Effects of Erythropoietin. Vitam Horm. 2017;105:161-179.
[17] WAN L, ZHANG F, HE Q, et al. EPO promotes bone repair through enhanced cartilaginous callus formation and angiogenesis. PloS one. 2014;9(7):e102010.
[18] SHIOZAWA Y, JUNG Y, ZIEGLER AM, et al. Erythropoietin couples hematopoiesis with bone formation. PloS one. 2010;5(5):e10853.
[19] ROLFING JH, BENDTSEN M, JENSEN J, et al. Erythropoietin augments bone formation in a rabbit posterolateral spinal fusion model. J Orthop Res.2012;30(7):1083-1088.
[20] LI D, DENG L, XIE X, et al. Evaluation of the osteogenesis and angiogenesis effects of erythropoietin and the efficacy of deproteinized bovine bone/recombinant human erythropoietin scaffold on bone defect repair. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(6):101.
[21] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):323-328.
[22] RAMASAMY SK, KUSUMBE AP, WANG L, et al. Endothelial Notch activity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):376-380.
[23] KERTESZ N, WU J, CHEN TH, et al. The role of erythropoietin in regulating angiogenesis. Dev Biol. 2004;276(1):101-110.
[24] ROLFING JH, JENSEN J, JENSEN JN, et al. A single topical dose of erythropoietin applied on a collagen carrier enhances calvarial bone healing in pigs. Acta orthopaedica. 2014;85(2):201-209.
[25] HOLSTEIN JH, MENGER MD, SCHEUER C, et al. Erythropoietin (EPO): EPO-receptor signaling improves early endochondral ossification and mechanical strength in fracture healing. Life Sci. 2007;80(10):893-900.
[26] HIRAM-BAB S, NEUMANN D, GABET Y. Erythropoietin in bone- Controversies and consensus. Cytokine. 2017;89:155-159.
[27] SIMS NA, MARTIN TJ. Coupling Signals between the Osteoclast and Osteoblast: How are Messages Transmitted between These Temporary Visitors to the Bone Surface? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015;6:41.
[28] HIRAM-BAB S, LIRON T, DESHET-UNGER N, et al. Erythropoietin directly stimulates osteoclast precursors and induces bone loss. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 2015;29(5):1890-1900.
[29] CLINKENBEARD EL, HANUDEL MR, STAYROOK KR, et al. Erythropoietin stimulates murine and human fibroblast growth factor-23, revealing novel roles for bone and bone marrow. Haematologica. 2017;102(11):e427-e430.
[30] HEIDEVELD E, VAN DEN AKKER E. Digesting the role of bone marrow macrophages on hematopoiesis.Immunobiology. 2017;222(6):814-822.
[31] JACOME-GALARZA CE, LEE SK, LORENZO JA, et al. Identification, characterization, and isolation of a common progenitor for osteoclasts, macrophages, and dendritic cells from murine bone marrow and periphery. J Bone Miner Res.2013;28(5):1203-1213.
[32] CHOW A, HUGGINS M, AHMED J, et al. CD169(+) macrophages provide a niche promoting erythropoiesis under homeostasis and stress. Nat Med. 2013;19(4):429-436.
[33] MILLOT S, ANDRIEU V, LETTERON P, et al. Erythropoietin stimulates spleen BMP4-dependent stress erythropoiesis and partially corrects anemia in a mouse model of generalized inflammation. Blood. 2010; 116(26):6072-6081.
[34] SINGBRANT S, RUSSELL MR, JOVIC T, et al. Erythropoietin couples erythropoiesis, B-lymphopoiesis, and bone homeostasis within the bone marrow microenvironment. Blood. 2011;117(21):5631-5642.
[35] SAKHNO LV, SHEVELA EY, LYKOV AP, et al. Effect of Apoptotic Neutrophils on the Production of Erythropoietin, MMP-9, and TIMP-1 in Cultures of Human Macrophages. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2019;167(6): 755-758.
[36] CHOU YH, LIAO FL, CHEN YT, et al. Erythropoietin modulates macrophages but not post-ischemic acute kidney injury in mice. J Formos Med Assoc. 2019;118(1 Pt 3): 494-503.
[37] LUO B, GAN W, LIU Z, et al. Erythropoeitin Signaling in Macrophages Promotes Dying Cell Clearance and Immune Tolerance. Immunity. 2016;44(2):287-302.
[38] WOOD MA, GOLDMAN N, DEPIERRI K, et al. Erythropoietin increases macrophage-mediated T cell suppression.Cellular Immunology. 2016; 306-307:17-24.
[39] WANG S, ZHANG C, LI J, et al. Erythropoietin protects against rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury by modulating macrophage polarization. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(4):e2725.
[40] WANG R, LI J, DUAN Y, et al. Effects of Erythropoietin on Gliogenesis during Cerebral Ischemic/Reperfusion Recovery in Adult Mice. Aging Dis. 2017;8(4):410-419.
[41] TAMURA T, AOYAMA M, UKAI S, et al. Neuroprotective erythropoietin attenuates microglial activation, including morphological changes, phagocytosis, and cytokine production. Brain Res. 2017;1662:65-74.
[42] GILBOA D, HAIM-OHANA Y, DESHET-UNGER N, et al. Erythropoietin enhances Kupffer cell number and activity in the challenged liver. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):10379.
[43] DE LUISI A, BINETTI L, RIA R, et al. Erythropoietin is involved in the angiogenic potential of bone marrow macrophages in multiple myeloma. Angiogenesis. 2013;16(4):963-973.
[44] KLEI TR, MEINDERTS SM, VAN DEN BERG TK, et al. From the Cradle to the Grave: The Role of Macrophages in Erythropoiesis and Erythrophagocytosis. Front Immunol. 2017;8:73.
[45] TODA S, SEGAWA K, NAGATA S. MerTK-mediated engulfment of pyrenocytes by central macrophages in erythroblastic islands. Blood. 2014;123(25):3963-3971.
[46] KOROLNEK T, HAMZA I. Macrophages and iron trafficking at the birth and death of red cells. Blood. 2015;125(19):2893-2897.
[47] JACOBSEN RN, PERKINS AC, LEVESQUE JP. Macrophages and regulation of erythropoiesis. Curr Opin Hematol. 2015;22(3):212-219.
[48] PRADEEP S, HUANG J, MORA EM, et al. Erythropoietin Stimulates Tumor Growth via EphB4. Cancer Cell. 2015;28(5):610-622.
|