| [1] Luu HH, Song WX, Luo X, et al. Distinct roles of bone morphogenetic proteins in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.J Orthop Res. 2007;25(5):665-677. [2] Abula K, Muneta T, Miyatake K, et al. Elimination of BMP7 from the developing limb mesenchyme leads to articular cartilage degeneration and synovial inflammation with increased age. FEBS letters.2015; 589: 1240-1248. [3] Razzouk S, Sarkis R. BMP-2: biological challenges to its clinical use. The New York state dental journal. 2012;78:37-39. [4] Smoljanovic T,Caric D,Bojanic I.RE: Clinical applications of bone morphogenetic proteins: current evidence. Kanakaris, NK; Giannoudis, PV; JSOA 17(3):133-46, 2008.J Surg Orthop Adv. 2010 Summer;19(2): 135-137; author reply 137. [5] Noel D, Gazit D, Bouquet C, et al. Short-term BMP-2 expression is sufficient for in vivo osteochondral differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Stem cells 2004;22:74-85. [6] Tsuji K, Bandyopadhyay A, Harfe BD, et al.BMP2 activity, although dispensable for bone formation, is required for the initiation of fracture healing.Nature genetics.2006;38:1424-1429. [7] Tan TY,Gonzaga-Jauregui C, Bhoj EJ, et al. Monoallelic BMP2 variants predicted to result in haploinsufficiency cause craniofacial, skeletal, and cardiac features overlapping those of 20p12 deletions. Am J Hum Genet. 2017 Dec 7;101(6):985-994. [8] Luo G, Hofmann C, Bronckers AL, et al. BMP-7 is an inducer of nephrogenesis, and is also required for eye development and skeletal patterning. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 15;9(22):2808-2820. [9] Solloway MJ, Dudley AT, Bikoff EK,et al. Mice lacking Bmp6 function. Dev genet.1998;22:321-339. [10] Daluiski A, Engstrand T, Bahamonde ME, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-3 is a negative regulator of bone density. Nature genet.2001; 27:84-88. [11] Celil AB,Hollinger JO,Campbell PG.Osx transcriptional regulation is mediated by additional pathways to BMP2/Smad signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2005 Jun 1;95(3):518-528. [12] Kang Q, Song WX, Luo Q, et al. A comprehensive analysis of the dual roles of BMPs in regulating adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells.Stem cells Dev.2009;18:545-559. [13] Luu HH, Song WX, Luo X, et al. Distinct roles of bone morphogenetic proteins in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res.2007;25:665-677. [14] Hak DJ, Fitzpatrick D, Bishop JA, et al. Delayed union and nonunions: epidemiology, clinical issues, and financial aspects. Injury.2014;45 Suppl 2:S3-7. [15] Xavier JR,Thakur T,Desai P,et al.Bioactive nanoengineered hydrogels for bone tissue engineering: a growth-factor-free approach. ACS nano. 2015;9:3109-3118. [16] Bez M, Sheyn D, Tawackoli W, et al.In situ bone tissue engineering via ultrasound-mediated gene delivery to endogenous progenitor cells in mini-pigs. Sci Transl Med. 2017 May 17;9(390). pii: eaal3128. [17] Li C,Jiang C,Deng Y, et al.RhBMP-2 loaded 3D-printed mesoporous silica/calcium phosphate cement porous scaffolds with enhanced vascularization and osteogenesis properties. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41331.[18] Lee SJ, Lee D, Yoon TR, et al. Surface modification of 3D-printed porous scaffolds via mussel-inspired polydopamine and effective immobilization of rhBMP-2 to promote osteogenic differentiation for bone tissue engineering. Acta biomaterialia.2016;40:182-91. [19] Huang KH, Lin YH, Shie MY, et al. Effects of bone morphogenic protein-2 loaded on the 3D-printed MesoCS scaffolds.J Formos Med Assoc. 2018;117(10):879-887.[20] Chen TH,Ghayor C,Siegenthaler B,et al.Lattice microarchitecture for bone tissue engineering from calcium-phosphate compared to titanium. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(19-20):1554-1561. [21] Grimsrud CD, Romano PR, D'Souza M, et al. BMP signaling stimulates chondrocyte maturation and the expression of Indian hedgehog. J Orthop Res. 2001;19(1):18-25.[22] De Luca F, Barnes KM, Uyeda JA, et al. Regulation of growth plate chondrogenesis by bone morphogenetic protein-2. Endocrinology. 2001;142:430-436. [23] Minina E, Kreschel C, Naski MC,et al. Interaction of FGF, Ihh/Pthlh, and BMP signaling integrates chondrocyte proliferation and hypertrophic differentiation. Dev cell. 2002;3:439-449. [24] Kobayashi T, Lyons KM, McMahon AP, et al. BMP signaling stimulates cellular differentiation at multiple steps during cartilage development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Dec 13;102(50):18023-18027. [25] Komatsu Y, Kaartinen V, Mishina Y. Cell cycle arrest in node cells governs ciliogenesis at the node to break left-right symmetry. Development.2011;138:3915-3920. [26] Hayashi M,Muneta T,Ju YJ,et al.Weekly intra-articular injections of bone morphogenetic protein-7 inhibits osteoarthritis progression. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(5):R118. 16:03 2019-1-7[27] Sekiya I,Tang T,Hayashi M,et al.Periodic knee injections of BMP-7 delay cartilage degeneration induced by excessive running in rats. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(8):1088-1092. [28] Takahashi T, Muneta T, Tsuji K, et al. BMP-7 inhibits cartilage degeneration through suppression of inflammation in rat zymosan-induced arthritis. Cell Tissue Res.2011;344:321-332. [29] Ozeki N, Muneta T, Koga H, et al. Transplantation of Achilles tendon treated with bone morphogenetic protein 7 promotes meniscus regeneration in a rat model of massive meniscal defect. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(11):2876-2886. [30] Blaney Davidson EN, Vitters EL, et al. Inducible chondrocyte-specific overexpression of BMP2 in young mice results in severe aggravation of osteophyte formation in experimental OA without altering cartilage damage. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(6):1257-1264. [31] Simson JA, Strehin IA, Lu Q, et al. An adhesive bone marrow scaffold and bone morphogenetic-2 protein carrier for cartilage tissue engineering.Biomacromolecules. 2013;14:637-643. [32] Duprez D,Bell EJ,Richardson MK,et al. Overexpression of BMP-2 and BMP-4 alters the size and shape of developing skeletal elements in the chick limb. Mech Dev. 1996;57(2):145-157. [33] Kutz WE, Wang LW, Dagoneau N, et al. Functional analysis of an ADAMTS10 signal peptide mutation in Weill-Marchesani syndrome demonstrates a long-range effect on secretion of the full-length enzyme.Human Mutat.2008;29:1425-1434. [34] Lee KS, Hong SH, Bae SC. Both the Smad and p38 MAPK pathways play a crucial role in Runx2 expression following induction by transforming growth factor-beta and bone morphogenetic protein. Oncogene.2002;21:7156-7163. [35] Afzal F, Pratap J, Ito K,et al.Smad function and intranuclear targeting share a Runx2 motif required for osteogenic lineage induction and BMP2 responsive transcription. J Cell Physiol. 2005;204(1):63-72. [36] Franceschi RT,Xiao G.Regulation of the osteoblast-specific transcription factor, Runx2: responsiveness to multiple signal transduction pathways. J Cell Biochem. 2003;88(3):446-454. [37] Wang M, Jin H, Tang D, et al. Smad1 plays an essential role in bone development and postnatal bone formation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(6):751-762. [38] Keller B, Yang T, Chen Y,et al. Interaction of TGFbeta and BMP signaling pathways during chondrogenesis. PloS one.2011;6:e16421. [39] Retting KN,Song B,Yoon BS,et al. BMP canonical Smad signaling through Smad1 and Smad5 is required for endochondral bone formation.Development. 2009;136:1093-1104. [40] Shore EM, Xu M, Feldman GJ,et al.A recurrent mutation in the BMP type I receptor ACVR1 causes inherited and sporadic fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Nature genetics.2006;38:525-527. [41] Shen Q, Little SC, Xu M, et al. The fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva R206H ACVR1 mutation activates BMP-independent chondrogenesis and zebrafish embryo ventralization. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(11):3462-3472. [42] Medici D, Shore EM, Lounev VY, et al. Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells. Nature Med. 2010; 16:1400-1406. [43] Hatsell SJ, Idone V, Wolken DM, et al. ACVR1R206H receptor mutation causes fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva by imparting responsiveness to activin A. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(303):303ra137. [44] van Dinther M,Visser N,de Gorter DJ,et al.ALK2 R206H mutation linked to fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva confers constitutive activity to the BMP type I receptor and sensitizes mesenchymal cells to BMP-induced osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(6):1208-1215. [45] Hao J, Ho JN, Lewis JA,et al. In vivo structure-activity relationship study of dorsomorphin analogues identifies selective VEGF and BMP inhibitors.ACS chemical biology 2010;5:245-253. [46] Yu PB, Deng DY, Lai CS, et al. BMP type I receptor inhibition reduces heterotopic [corrected] ossification. Nature medicine. 2008;14: 1363-1369. [47] Yang C, Yang L, Wan M, et al. Generation of a mouse model with expression of bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor lacking the cytoplasmic domain in osteoblasts. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192: 286-291. [48] Mishina Y, Starbuck MW, Gentile MA, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein type IA receptor signaling regulates postnatal osteoblast function and bone remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(26): 27560-27566. [49] Yoon BS, Ovchinnikov DA, Yoshii I,et al. Bmpr1a and Bmpr1b have overlapping functions and are essential for chondrogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(14):5062-5067. [50] Zou H, Wieser R, Massague J, et al. Distinct roles of type I bone morphogenetic protein receptors in the formation and differentiation of cartilage. Genes Dev. 1997;11(17):2191-2203. [51] Sahni V, Mukhopadhyay A,Tysseling V,et al. BMPR1a and BMPR1b signaling exert opposing effects on gliosis after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 2010;30(5):1839-1855. [52] Miyazono K.Signal transduction by bone morphogenetic protein receptors: functional roles of Smad proteins. Bone.1999;25:91-93. [53] Itoh F, Asao H, Sugamura K, et al. Promoting bone morphogenetic protein signaling through negative regulation of inhibitory Smads. EMBO J. 2001;20(15):4132-4142. [54] Bai S,Shi X,Yang X,et al. Smad6 as a transcriptional corepressor. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(12):8267-8270. [55] Luo K,Stroschein SL,Wang W, et al.The Ski oncoprotein interacts with the Smad proteins to repress TGFbeta signaling. Genes Dev. 1999; 13(17):2196-2206. [56] Wang W,Mariani FV,Harland RM,et al. Ski represses bone morphogenic protein signaling in Xenopus and mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(26):14394-14399. [57] Lana DP, Leferovich JM, Kelly AM,et al. Selective expression of a ski transgene affects IIb fast muscles and skeletal structure. Dev Dyn. 1996;205(1):13-23. [58] Guehenneux F, Duret L, Callanan MB, et al. Cloning of the mouse BTG3 gene and definition of a new gene family (the BTG family) involved in the negative control of the cell cycle. Leukemia. 1997;11(3): 370-375. [59] Ajima R,Ikematsu N, Ohsugi M, et al. Cloning and characterization of the mouse tob2 gene.Gene 2000;253:215-220. [60] Yoshida Y,Tanaka S,Umemori H,et al.Negative regulation of BMP/Smad signaling by Tob in osteoblasts. Cell. 2000;103:1085-1097. [61] Zhu H, Kavsak P, Abdollah S, et al. A SMAD ubiquitin ligase targets the BMP pathway and affects embryonic pattern formation. Nature.1999; 400:687-693. [62] Zhang Y, Chang C, Gehling DJ,et al. Regulation of Smad degradation and activity by Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(3):974-979. [63] Zimmerman LB, De Jesus-Escobar JM, Harland RM. The Spemann organizer signal noggin binds and inactivates bone morphogenetic protein 4.Cell. 1996;86:599-606. [64] Aspenberg P,Jeppsson C, Economides AN. The bone morphogenetic proteins antagonist Noggin inhibits membranous ossification. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16(3):497-500. [65] Gazzerro E, Du Z, Devlin RD,et al. Noggin arrests stromal cell differentiation in vitro. Bone.2003;32:111-119. [66] Bachiller D,Klingensmith J,Kemp C,et al.The organizer factors Chordin and Noggin are required for mouse forebrain development. Nature. 2000;403:658-661. [67] Fainsod A, Deissler K, Yelin R,et al. The dorsalizing and neural inducing gene follistatin is an antagonist of BMP-4. Mech Dev. 1997; 63(1):39-50. [68] Zohar R,McCulloch CA,Sampath K,et al.Flow cytometric analysis of recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 (BMP-7) responsive subpopulations from fetal rat calvaria based on intracellular osteopontin content. Matrix Biol. 1998;16(6):295-306. |
.jpg)
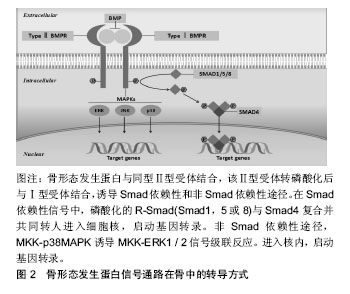
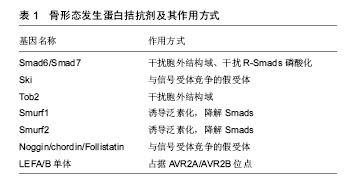
.jpg)
.jpg)