中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 1726-1732.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2541
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
肝脏三维重建技术较传统CT成像技术对肿瘤体积可提供更准确的术前评估
李 博1,林 杰2
- 1锦州医科大学附属第三医院,辽宁省锦州市 121002;2辽宁省肿瘤医院,辽宁省沈阳市 110042
Three-dimensional liver reconstruction provides a more accurate preoperative assessment of tumor size than traditional CT imaging technique
Li Bo1, Lin Jie2
- 1Third Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121002, Liaoning Province, China; 2Liaoning Cancer Hospital & Institute, Shenyang 110042, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
肝后下腔静脉:下腔静脉是体内最大的静脉干,为下腔静脉系的主干,在第5腰椎平面,由左、右髂总静脉合成,沿腹主动脉右侧上升,经肝的后方,穿膈的腔静脉孔入胸腔,进入右心房,收集下肢、盆腔和腹腔的静脉血。当下腔静脉阻塞时,在腹壁的两侧、脐平面以下可见到曲张血管。
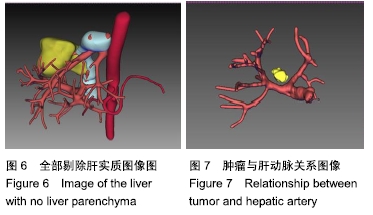
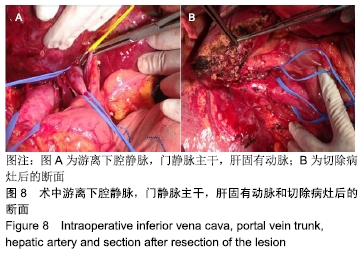
肝钳切肝法:肝钳切肝法是利用特制器械——肝钳钳夹将要切除之肝组织,阻断其血供后进行切肝的手术方法。适用于肝部分切除或左外叶切除,有时亦可用于右半肝切除。具体操作:先将欲要切除的肝叶或半肝充分游离,按此肝组织大小选择适合的钳翼,将钳翼套到相应肝组织上,收紧钳翼,使肝局部血供完全阻断,离钳翼一定间距(2 cm左右)切开肝包膜,分离肝实质,结扎切面上的所有管道结构,然后把相应肝组织切除。此法具有简便、术中出血少、省时及相当安全等优点,但不能用于肝中叶切除。对于要切除的肝组织较厚者,止血效果不够确切。
背景:在进行肝脏的精准治疗时,目前临床上常采取多排螺旋CT和高场强MRI对肝实质疾病、Child-Pugh分级、门静脉高压和ICG滞留率等参数分析,相对准确地评估剩余肝脏储备功能并确定个体患者肝切除的安全极限。
目的:探讨肝脏三维重建技术在精准肝脏外科临床应用上的优势。
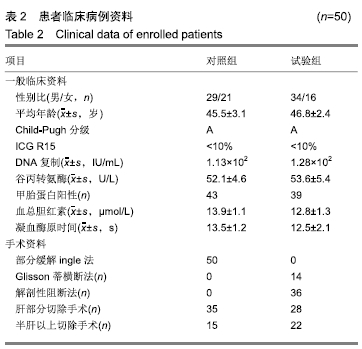
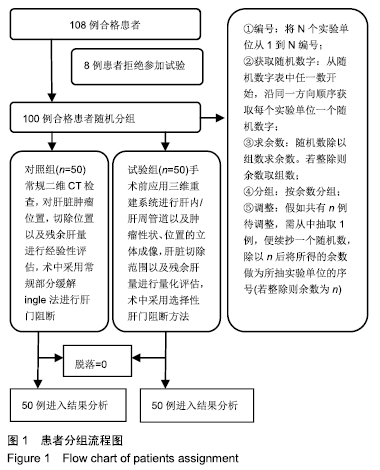
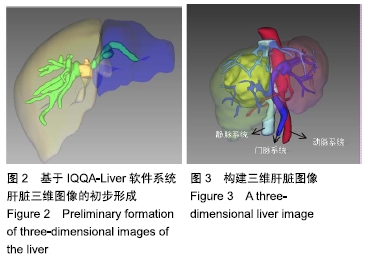
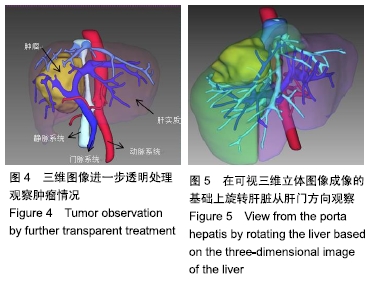
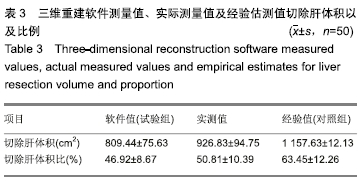
方法:随机选取辽宁省肿瘤医院肝胆外科接受肝脏切除手术治疗的原发性肝癌患者100例,分为2组。对照组:二维CT检查,对肝脏肿瘤位置、切除范围以及残余肝量进行经验性评估,术中采用部分缓解Pringle法进行肝门阻断;试验组:手术前应用三维重建系统进行肝内、肝周管道以及肿瘤性状位置的立体成像,肝脏切除范围以及残余肝量进行量化评估,术中采用选择性肝门阻断方法。比较两组术后肝切除体积与术前影像评估的差异,并观察术后患者的恢复情况。研究方案的实施符合辽宁省肿瘤医院的相关伦理要求,参与者及其家属对治疗过程完全知情同意。
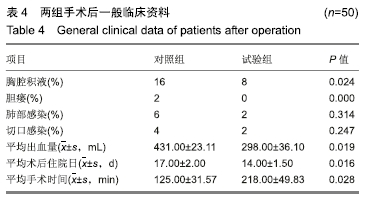
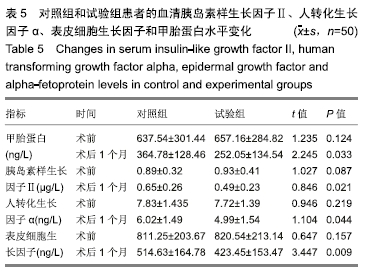
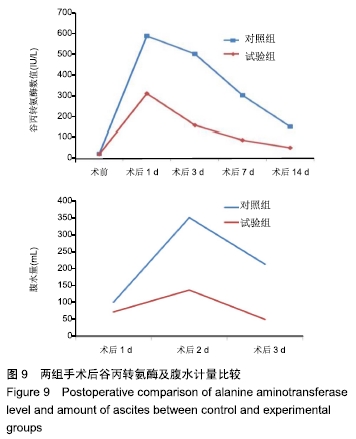
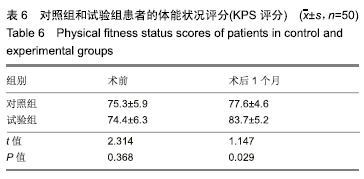
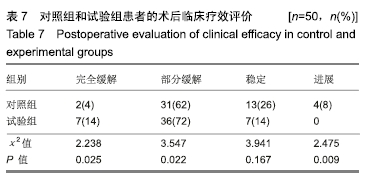
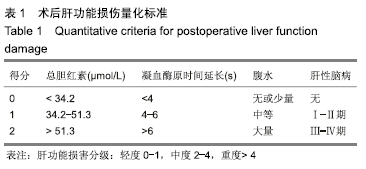
结果与结论: ①试验组术后切除肝肿瘤体积与术前计算比较无显著性意义;对照组有显著性意义(P < 0.05);对照组患者的住院时间和并发症的发生率明显高于试验组(P < 0.05);②术后1个月试验组患者的血清胰岛素样生长因子Ⅱ、人转化生长因子α、表皮细胞生长因子和甲胎蛋白水平较对照组均显著降低(P < 0.05);③与对照组相比,试验组谷丙转氨酶在术后第14天已经趋于正常,术后腹腔引流腹水计量两组逐渐减少,试验组明显低于对照组(P < 0.05);④术后1个月两组患者的KPS评分较术前均显著提高(P < 0.05),试验组明显高于对照组(P < 0.05);⑤对照组总有效率显著低于试验组(92%,100%,P < 0.05);⑥结果说明,与传统的CT成像技术比,肝脏三维重建技术可以在术前对肿瘤的体积提供更准确的术前评估,同时可以降低患者术中的手术风险、缩短患者的住院时间和降低术后并发症的发生率。
ORCID: 0000-0002-4039-242X(李博)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程中图分类号: