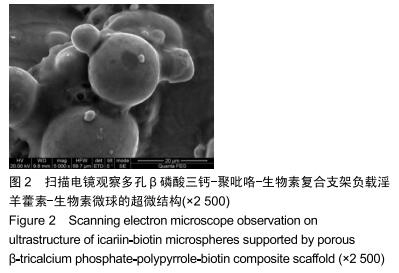
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (34): 5532-5537.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2347
• 复合支架材料 composite scaffold materials • 上一篇 下一篇
多孔β磷酸三钙-聚吡咯-生物素-淫羊藿素微球复合支架促进骨髓间充质干细胞的募集
刘 锌1,杜 斌1,孙光权1,曹金星2,江晓红2
1南京中医药大学附属医院,江苏省中医院,江苏省南京市 210029;2南京理工大学化工学院,江苏省南京市 210094
Porous beta-tricalcium phosphate-polypyrrole-biotin-icariin composite scaffold promotes recruitment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Liu Xin1, Du Bin1, Sun Guangquan1, Cao Jinxing2, Jiang Xiaohong2
1Jiangsu Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Institute of Chemical Industry, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
β磷酸三钙-聚吡咯-生物素:亲和素-生物素复合物是目前已知的最强非共价结合物,其结合不受温度、pH值及蛋白变性剂等影响,聚吡咯与磷酸三钙混合可赋予支架整体存在导电特性,其表面适合多种细胞黏附与生长。通过化学反应合成方法,以聚吡咯为亲和素,形成β磷酸三钙-聚吡咯-生物素结构,利用生物素多靶点结合能力提高支架与骨诱导因子的结合能力。
载药支架:骨组织工程支架负载药物能有效提高其修复性能。淫羊藿素是中药有效单体,其类似于雌激素的化学结构,易于与生物素产生非共价结合,从而达到更好地控释,且能保持成骨诱导作用。因此该载药方式可能将支架性能进一步理想化。
背景:淫羊藿素作为成骨诱导活性物质已被广泛负载于骨科支架材料中,然而现有研究基本均以淫羊藿素聚合微球形式直接放置于支架孔隙中,导致其释放与支架降解难以同步,且局部有效利用率较低。
目的:制备多孔β磷酸三钙-聚吡咯-生物素-淫羊藿素微球复合支架,初步探索该支架与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养的生物学特点。
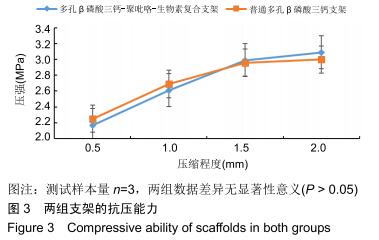
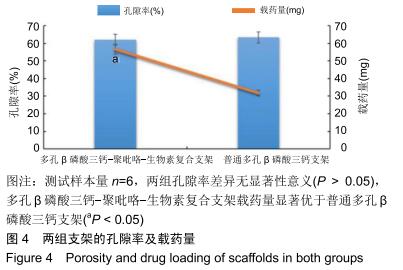
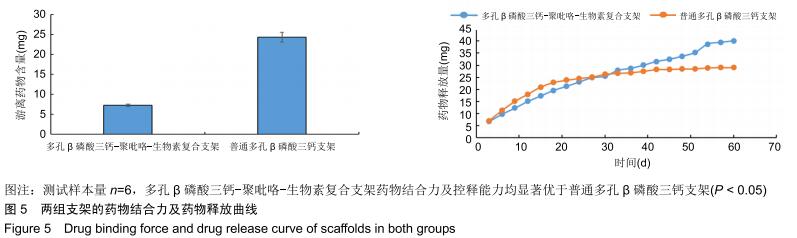
方法:以FeCl3为氧化剂,通过氧化化学合成聚吡咯,将聚吡咯、生物素与β磷酸三钙共混合并进行电化学合成,此后采用3D打印技术制备多孔β磷酸三钙-聚吡咯-生物素复合支架,运用HDDD反应制备淫羊藿素-生物素-聚乳酸微球,并将二者组合。将同样3D打印制备的负载淫羊藿素-聚乳酸微球的多孔β磷酸三钙支架设置为对照组。检测并对比两组支架的抗压强度、孔隙率、载药量、药物结合力及药物缓释性能,绘制淫羊藿素释放曲线,扫描电镜观察两组支架对骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学作用。
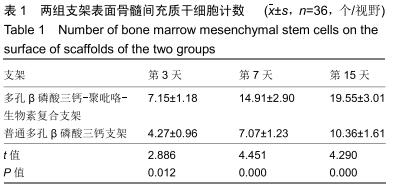
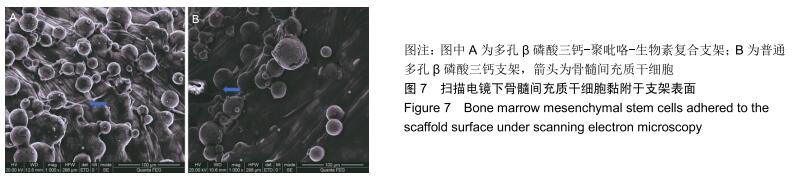
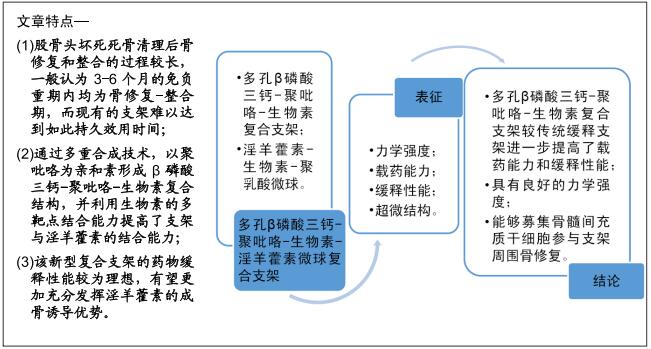
结果与结论:多孔β磷酸三钙-聚吡咯-生物素复合支架的载药量、药物结合力及药物缓释性能显著优于对照组(P < 0.05),扫描电镜下支架表面贴壁生长的骨髓间充质干细胞数量显著高于对照组(P < 0.05),两组支架抗压强度及孔隙率差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。结果表明,多孔β磷酸三钙-聚吡咯-生物素复合支架较传统缓释支架进一步提高了载药能力及缓释性能,并具有良好的力学强度,同时可能具有更好的募集骨髓间充质干细胞参与支架周围骨修复的作用。
ORCID: 0000-0001-8284-1994(刘锌)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: