实验对供试血液灌流器的血液相容性完成了全面检测,包括对凝血、血液学、血小板及补体系统影响的检测、血栓形成的检测。GB/T 16886.4-2003中溶血实验属于血液学中的一项。凝血、血液学、血小板及补体实验分别从接触模型、实验条件(接触面积/血液体积、接触时间)、检测指标、判定标准来详述。
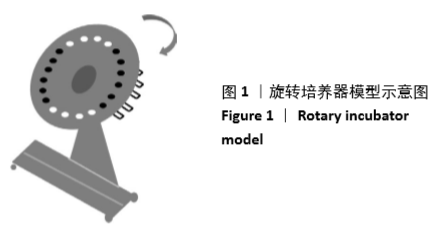
所用的旋转培养器接触模型是实验室原创,被广泛应用于多种医疗器械的血液相容性评价[7-9],为方便交流,称之为“许氏旋转培养器接触模型”。该接触模型组装简便,仅需一次性塑料采血管、旋转培养器、隔水培养箱;因旋转培养器有30°的倾斜角,血液与树脂微粒集中在采血管的底部,减少了血液与采血管不必要的额外接触;旋转培养器以30 r/min的速率旋转,与常用的振荡器水平震荡接触方式[10](图4)相比,此滚动式动态接触方式使树脂微粒与血液的接触非常轻柔又相当充分。
供试血液灌流器及对照血液灌流器均为广谱用灌流器,吸附剂均为聚苯乙烯二乙烯苯树脂,表面孔隙率及孔隙大小较为接近,因此实验中未考虑树脂微粒表面孔隙率和孔隙大小,仅对树脂微粒的直径进行测量。供试树脂微粒与对照树脂微粒的直径约为0.6 mm,相同体积的供试及对照树脂微粒其表面积也相同。采用的实验条件是0.5 mL树脂微粒与1.5 mL全血在37 ℃环境下接触20 mim。该实验条件的“血液体积/(接触时间×树脂微粒体积)”约相当于临床上血容量为4.5 L的患者用树脂微粒体积为250 mL的血液灌流器进行2 h的治疗。体外血液相容性实验与临床体内使用差别很大。通常体外实验条件会严于体内,但在灌流器及透析器类的血液相容性实验中,因吸附剂、中空纤维对血液的影响较大,一般会选择与临床使用相近的实验条件。因血液在体外缺少体内血液的缓冲和代偿作用,这样的体外实验条件与临床实际应用相比也是相对严格的。
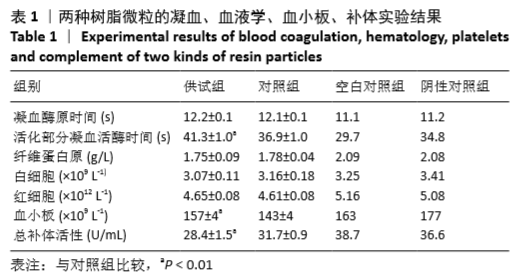
凝血、血细胞、血小板、补体实验所选择的检测指标中,凝血酶原时间、活化部分凝血活酶时间、纤维蛋白原的检测用凝血仪,白细胞、红细胞、血小板的检测用血细胞分析仪,总补体活性的检测用生化分析仪。整个实验,从采集血液到完成所有指标的检测可控制在3 h内。凝血酶原时间、活化部分凝血活酶时间、纤维蛋白原是临床凝血4项除凝血酶时间外的其他3项。凝血酶时间在血液相容性实验中非常不敏感,弃去不用。凝血酶原时间、活化部分凝血活酶时间分别反映外源性和内源性凝血系统的功能,相对比较敏感,常被联合应用于血液相容性中凝血系统的检测。纤维蛋白原在血液灌流器、血液透析器等与血液有大面积接触器械的血液相容性实验中非常敏感[8-9]。实验中供试和对照树脂微粒引起纤维蛋白原下降的程度>15%。3种血细胞中血小板在体外实验中相对敏感[9],红细胞、白细胞尤其是白细胞通常变化不大。总补体活性作为补体系统激活程度的检测指标,在体外实验中相对敏感[8-9]。实验中供试组和对照组引起总补体活性下降的程度>18%。
活化部分凝血活酶时间、凝血酶原时间被广泛应用于血液相容性的研究。但在许多文献中可以发现,在体外血液相容性实验中,因缺乏空白对照用做对比,研究者们错误地认为活化部分凝血活酶时间、凝血酶原时间的延长代表测试材料或器械具有一定的抗凝血作用[11-13]。活化部分凝血活酶时间、凝血酶原时间的检测均加入了过量激活剂及凝血所需的钙离子,它们分别反映了血浆中内源性凝血、外源性凝血路径中有活性的凝血因子含量。从此次实验以及实验室多年来的试验中可发现,在体外血液相容性实验中,测试材料或器械对凝血系统的激活作用越强,血浆中有效的内源性、外源性凝血因子被消耗越多,活化部分凝血活酶时间、凝血酶原时间就会越长。用于空白对照未经任何处理的血液,其活化部分凝血活酶时间、凝血酶原时间通常最短。
与空白对照相比,供试及对照树脂微粒与血液接触后均可引起活化部分凝血活酶时间、凝血酶原时间延长,纤维蛋白原减少,白细胞、红细胞、血小板减少,总补体活性降低。供试树脂微粒与对照树脂微粒的活化部分凝血活酶时间、血小板数量、总补体活性相比均有统计学差异,其中供试组血小板含量大于对照组,供试优于对照,供试相对于对照的百分比为109%;而供试组活化部分凝血活酶时间大于对照组,总补体活性小于对照组,供试均劣于对照,相对于对照的百分比分别为112%,89%。其他各指标,供试组与对照组均无统计学差异。
实验室所采用的灌流器和透析器的实验条件均与临床实际使用相近,灌流器凝血、血液学、血小板、补体实验的判定标准参照实验室建立的关于透析器血液相容性评价的判定标准[9]:如供试品的检测指标劣于对照品,其相对于对照品的百分比需在85%-115%范围内方可被接受。实验中供试品劣于对照品的检测指标为活化部分凝血活酶时间、总补体活性,供试品相对于对照品的百分比均在指定范围内。
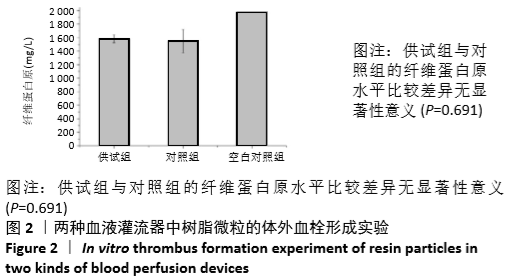
体外血栓形成实验方法是实验室原创,为方便交流可称之为“纤维蛋白原体外血栓形成法”。用半抗凝的兔血与实验材料接触一定时间后,加入肝素终止血液凝固过程,充分震荡混匀后静置一段时间使血液的凝固状态达到平衡,取血液离心,检测血浆中纤维蛋白原水平。以下分别从半抗凝兔血的选择、终止血液凝固方式及反映血液凝固程度的指标来详述。①之所以使用半抗凝的兔血,是考虑到若完全不予抗凝,血液在很短时间内凝固,与测试材料的作用时间太短。半抗凝血液的抗凝比例是实验室多次实验摸索的结果,3.8%枸橼酸钠溶液以1∶25的比例抗凝。②终止血液凝固过程的方式。实验室最初是用加入足量枸橼酸钠抗凝剂的方式来终止凝固过程,后来逐步优化到使用肝素。用肝素可以加入10 µL这样小的体积,对半凝固状态的血液影响较小,且有充分的终止血液凝固作用。加入肝素终止血液凝固过程后需充分震荡混匀并静置一定时间,使血液凝固状态达到平衡并稳定。这对后续平行样之间纤维蛋白原检测的精密度很重要。③用血浆纤维蛋白原水平来反映血液凝固的程度,是基于血液凝固过程的最后一步是纤维蛋白原在凝血酶作用下转化为纤维蛋白并交联形成血栓。纤维蛋白原剩余量越少说明血液凝固越严重。该体外血栓形成实验方法实验室曾用硅橡胶、聚乙烯和玻璃等基础材料做过验证[14]。实验中供试组与对照组的纤维蛋白原无统计学差异,说明在此实验条件下供试品与对照的血栓形成性能差异不大。
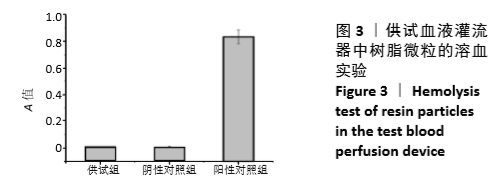
血液灌流器的溶血实验可以采用2种方法:①按照说明书将血液灌流器用生理盐水预冲后取出树脂微粒与血细胞直接作用的直接接触法;②完成预冲后在灌流器中充满生理盐水进行浸提,取浸提液与血细胞接触的浸提液法。考虑到血液灌流器中的树脂微粒在临床使用过程中与血液大面积接触,应选择相对较为严格的直接接触法。实验中供试血液灌流器中树脂微粒的溶血率为0.2%,小于5%。
综上,供试血液灌流器中树脂微粒的溶血率较低;与对照灌流器中的树脂微粒相比,体外血栓形成无统计学差异,对补体和凝血系统的激活相对较为严重,但与对照的相对百分比均在85%-115%之间,对血小板数量的影响相对较小,对白细胞数量、红细胞数量的影响与对照比无统计学差异。供试血液灌流器的血液相容性可被接受。
血液灌流器、血液透析器及氧合器等与血液大面积接触医疗器械的血液相容性检测非常重要。理想的体外血液相容性实验方法需要具备这几点:①方法明确且固定:包括样品的制备、实验条件、检测指标及测定方法的选择;②能检测出不同产品间的差别:血液相容性检测指标众多,不同厂家的产品间一定会有差异,实验条件的选择一定要能够将这些差异检测出来;③建立与临床应用的相关性,并据此制定判定标准。临床应用资料是最真实的产品血液相容性反应,依据其与体外实验方法相关性所制定的体外实验判定标准最为可靠。目前的血液相容性实验多以已经上市的同类产品作为对照,将供试产品与对照产品相比较,这是与临床应用的初步结合。与临床应用相结合,是体外实验未来发展的方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
 供试血液灌流器及对照血液灌流器均为广谱用灌流器,吸附剂均为聚苯乙烯二乙烯苯树脂,表面孔隙率及孔隙大小较为接近,因此实验中未考虑树脂微粒表面孔隙率和孔隙大小,仅对树脂微粒的直径进行测量。供试树脂微粒与对照树脂微粒的直径约为0.6 mm,相同体积的供试及对照树脂微粒其表面积也相同。采用的实验条件是0.5 mL树脂微粒与1.5 mL全血在37 ℃环境下接触20 mim。该实验条件的“血液体积/(接触时间×树脂微粒体积)”约相当于临床上血容量为4.5 L的患者用树脂微粒体积为250 mL的血液灌流器进行2 h的治疗。体外血液相容性实验与临床体内使用差别很大。通常体外实验条件会严于体内,但在灌流器及透析器类的血液相容性实验中,因吸附剂、中空纤维对血液的影响较大,一般会选择与临床使用相近的实验条件。因血液在体外缺少体内血液的缓冲和代偿作用,这样的体外实验条件与临床实际应用相比也是相对严格的。
供试血液灌流器及对照血液灌流器均为广谱用灌流器,吸附剂均为聚苯乙烯二乙烯苯树脂,表面孔隙率及孔隙大小较为接近,因此实验中未考虑树脂微粒表面孔隙率和孔隙大小,仅对树脂微粒的直径进行测量。供试树脂微粒与对照树脂微粒的直径约为0.6 mm,相同体积的供试及对照树脂微粒其表面积也相同。采用的实验条件是0.5 mL树脂微粒与1.5 mL全血在37 ℃环境下接触20 mim。该实验条件的“血液体积/(接触时间×树脂微粒体积)”约相当于临床上血容量为4.5 L的患者用树脂微粒体积为250 mL的血液灌流器进行2 h的治疗。体外血液相容性实验与临床体内使用差别很大。通常体外实验条件会严于体内,但在灌流器及透析器类的血液相容性实验中,因吸附剂、中空纤维对血液的影响较大,一般会选择与临床使用相近的实验条件。因血液在体外缺少体内血液的缓冲和代偿作用,这样的体外实验条件与临床实际应用相比也是相对严格的。