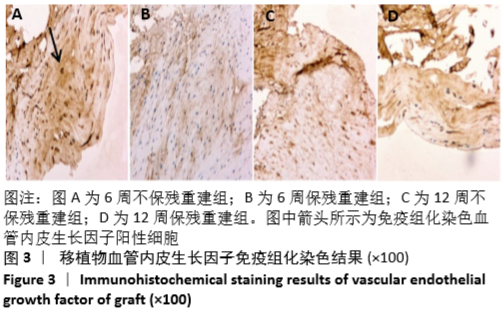
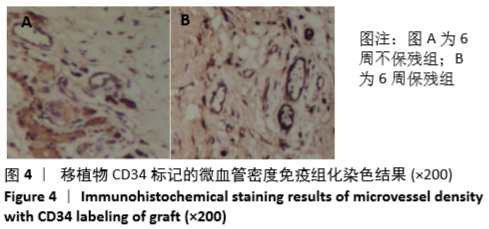
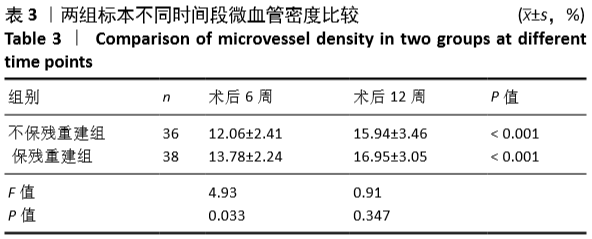
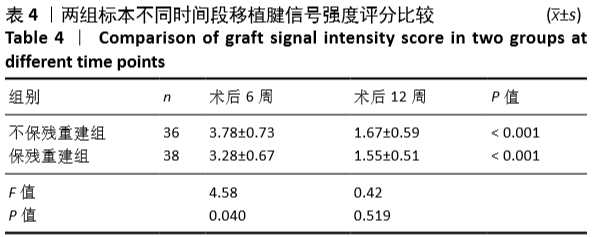
[1] GRASSI A, KIM C, MARCHEGGIANI MUCCIOLI GM, et al. What Is the Mid-term Failure Rate of Revision ACL Reconstruction? A Systematic Review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(10):2484-2499.
[2] 唐聪,黄长明,范华强.前交叉韧带损伤合并半月板损伤的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2015,4(4):309-314.
[3] LITTLE D, THOMPSON JW, DUBOIS LG, et al. Proteomic differences between male and female anterior cruciate ligament and patellar tendon. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96526.
[4] 王辉,王万明.前交叉韧带重建术后腱骨愈合影响因素研究进展[J].实用医学杂志,2014,30(14): 2343-2345.
[5] CHEN CH. Strategies to enhance tendon graft--bone healing in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Chang Gung Med J. 2009;32(5):483-493.
[6] AHN JH, WANG JH, LEE YS, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using remnant preservation and a femoral tensioning technique: clinical and magnetic resonance imaging results. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(8):1079-1089.
[7] TENSHO K, IWAASA T, SHIMODAIRA H, et al. Anatomical Remnant-Preserving Double-Bundle ACL Reconstruction With a New Remnant Augmentation Technique. Arthrosc Tech. 2020;9(2):e283-e290.
[8] SACCOMANNO MF, CAPASSO L, FRESTA L, et al. Biological enhancement of graft-tunnel healing in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Joints. 2016;4(3):174-182.
[9] HSU SL, WANG CJ. The use of demineralized bone matrix for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a radiographic, histologic, and immunohistochemical study in rabbits. J Surg Res. 2014;187(1):219-224.
[10] AL-BLUWI MT, AZAM MQ, SADAT-ALI M. The effect of bone growth factor in the tendon to bone healing in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: An experimental study in rabbits. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2016;6(1):23-27.
[11] ZHANG L, JIANG K, CHAI H, et al. A Comparative Animal Study of Tendon Grafts Healing After Remnant-Preserving Versus Conventional Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:3426-3437.
[12] HANKENSON KD, GAGNE K, SHAUGHNESSY M. Extracellular signaling molecules to promote fracture healing and bone regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2015;94: 3-12.
[13] CHENG P, HAN P, ZHAO C, et al. High-purity magnesium interference screws promote fibrocartilaginous entheses regeneration in the anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction rabbit model via accumulation of BMP-2 and VEGF. Biomaterials. 2016;81:14-26.
[14] Ntoulia A, Papadopoulou F, Ristanis S, et al. Revascularization Process of the Bone--Patellar Tendon--Bone Autograft Evaluated by Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging 6 and 12 Months After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(7):1478-1486.
[15] GÓMEZ-PUERTO MC, VERHAGEN LP, BRAAT AK, et al. Activation of autophagy by FOXO3 regulates redox homeostasis during osteogenic differentiation. Autophagy. 2016;12(10):1804-1816.
[16] MUINOS-LÓPEZ E, RIPALDA-CEMBORÁIN P, LÓPEZ-MARTÍNEZ T, et al. Hypoxia and Reactive Oxygen Species Homeostasis in Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells Define a Molecular Mechanism for Fracture Nonunion. Stem Cells. 2016;34(9):2342-2350.
[17] NEYBECKER P, HENRIONNET C, PAPE E, et al. In vitro and in vivo potentialities for cartilage repair from human advanced knee osteoarthritis synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):329.
[18] NGUYEN VT, CANCEDDA R, DESCALZI F. et al. Platelet lysate activates quiescent cell proliferation and reprogramming in human articular cartilage: involvement of Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018; 12(3):e1691-e1703.
[19] MAES C. Signaling pathways effecting crosstalk between cartilage and adjacent tissues: Seminars in cell and developmental biology:The biology and pathology of cartilage. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;62:16-33
[20] 李广周,吴伟.低氧环境对骨代谢影响的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(33):4963-4969.
[21] 王国祥,刘殿玉,刘晓莉,等.肌腱周围炎大鼠模型建立与针刺干预作用的实验研宄[J].辽宁中医杂志,2011,38(12):2310-2313
[22] MA C, WEI Q, CAO B, et al. A multifunctional bioactive material that stimulates osteogenesis and promotes the vascularization bone marrow stem cells and their resistance to bacterial infection. PLoS One. 2017;12(3): e0172499.
[23] LI M, DAI N, WANG D, et al. Distinct APE1 Activities Affect the Regulation of VEGF Transcription Under Hypoxic Conditions. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019;17:324-332.
[24] PALEOLOG EM. The vasculature in rheumatoid arthritis: cause or consequence?. Int J Exp Pathol. 2009;90(3):249-261.
[25] SUN L, ZHOU X, WU B, et al. Inhibitory effect of synovial fluid on tendon-to-bone healing: an experimental study in rabbits. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(9): 1297-1305.
[26] 时玉娟,蔡彦,陈强,李志勇.VEGF分泌量及分泌来源对肿瘤血管生长影响的数值模拟[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(6):629-635.
[27] Won Jin Cho, Jung-Soo Pyo. Immunohistochemical analysis of the impact of ischemic change in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Pathol Res Pract. 2020;216(1):152694.
[28] Kirizuki S, Matsumoto T, Ueha T, et al. The Influence of Ruptured Scar Pattern on the Healing Potential of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Remnant Cells. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(6):1382-1388.
[29] YOSHIKAWA T, TOHYAMA H, ENOMOTO H, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis in patellar tendon grafts in the early phase after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14(9):804-810.
[30] 李明,李君,付昆.骨碎补总黄酮对膝骨关节炎模型兔HIF-1α和VEGF表达的影响[J].中国药房,2018,29(18):2484-2488.
[31] NAYAK M, NAG HL, NAG TC, et al. Ultrastructural and histological changes in tibial remnant of ruptured anterior cruciate ligament stumps: a transmission electron microscopy and immunochemistry-based observational study. Musculoskelet Surg.2020;104(1):67-74.
[32] HASSELLUHN MC, KLEIN L, PATZAK MS, et al. Stromal Features of the Primary Tumor Are Not Prognostic in Genetically Engineered Mice of Pancreatic Cancer. Cells. 2019;9(1):58.
[33] INOKUCHI T, MATSUMOTO T, TAKAYAMA K, et al.Influence of the Injury-to-Surgery Interval on the Healing Potential of Human Anterior Cruciate Ligament-Derived Cells. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(6):1359-1369.
[34] AGA C, WILSON KJ, JOHANSEN S, et al. Tunnel widening in single- versus double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstructed knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(4):1316-1327.
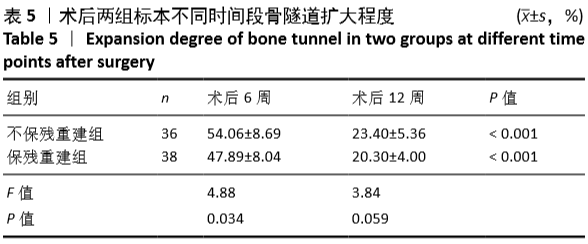
[35] 张磊,孙荣鑫,王少军,等.保留残端重建兔前交叉韧带术对其胫骨骨道扩大的预防作用[J].山东医药,2016,56(37):25-27.
[36] 刘书芳,矫玮,张晓辉,等.运动员前交叉韧带重建术后康复程序对其骨隧道的影响[J].中国康复,2015,30(2):109-111. |