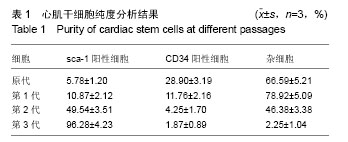
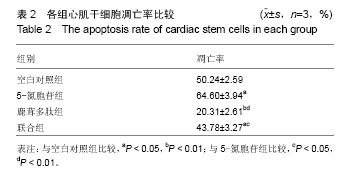
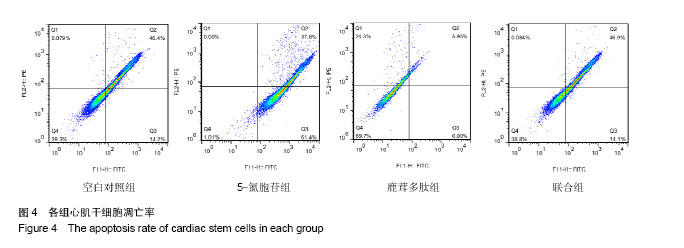
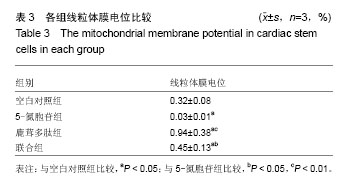
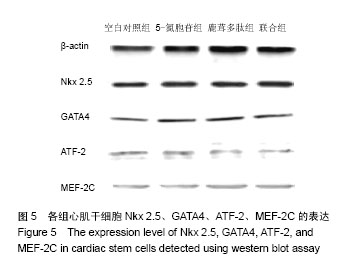
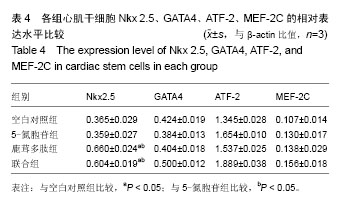
| [1] Lin JH, Deng LX, Wu ZY, et al. Pilose antler polypeptides promote chondrocyte proliferation via the tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. J Occup Med Toxicol. 2011;6(1):139-150.[2] Chen XD, Lin JH. Role of pilose antler polypeptides on replicative senescence of rat chondrocyte. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2008;21(7):515-518.[3] 姚震,陈林.我国心血管疾病现状与展望[J].海南医学,2013, 24(13):1873-1876.[4] 张航向,宁晓暄,王晓明.女性心血管疾病的研究进展[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2015,17(1):95-97.[5] Bearzi C, Rota M, Hosoda T, et al. Human cardiac stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(35):14068-14073.[6] 李航,孙佳明,张林林,等.鹿茸化学成分及生物活性概述[J].吉林中医药,2013,33(5):493-495.[7] 宗颖,刘侗,王志颖,等.鹿茸多肽成分及其药理作用研究[J].吉林中医药,2013,33(11):1135-1137,1145.[8] 高成森,任小斐,孟祥峰.温阳益气方治疗冠心病慢性心力衰竭临床观察[J].光明中医,2014,29(11):2302-2304.[9] 何璐.大鼠心肌干细胞的分离培养与鉴定及鹿茸多肽对其分化的诱导作用[D].长春:吉林大学,2016.[10] 徐岩,李朝政,李智萌,等.鹿茸多肽诱导心肌干细胞分化为心肌细胞研究进展[J].长春中医药大学学报,2016,32(3):653-655.[11] 王艳玲,黄晓巍,李哲,等.鹿茸多肽诱导心肌干细胞向心肌细胞分化的机制研究[J].中国药房,2016,27(34):4780-4783.[12] 王洁.心肌细胞自噬在创伤后迟发性心脏损伤中的作用研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2012.[13] 熊燕,张梅,陈菲,等.线粒体功能障碍与心血管疾病[J].中国病理生理杂志,2013,29(2):364-370.[14] 刘晓婷,王延让,张明.线粒体介导细胞凋亡的研究进展[J].环境与健康杂志,2013,30(2):182-185.[15] 马淇,刘垒,陈佺.活性氧、线粒体通透性转换与细胞凋亡[J].生物物理学报,2012,28(7):523-536.[16] Kim YK, Kim KS, Chung KH, et al. Inhibitory effects of deer antler aqua-acupuncture, the pilose antler of Cervus Korean TEMMINCK var mantchuricus Swinhoe, on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2003;3(7):1001-1010.[17] Lin JH, Deng LX, Wu ZY, et al. Pilose antler polypeptides promote chondrocyte proliferation via the tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. J Occup Med Toxicol. 2011;6:27.[18] Kim KW, Song KH, Lee JM, et al. Effects of TGFbeta1 and extracts from Cervus korean TEMMINCK var. mantchuricus Swinhoe on acute and chronic arthritis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;118(2):280-283.[19] Cheng K, Shen D, Smith J, et al. Transplantation of platelet gel spiked with cardiosphere-derived cells boosts structural and functional benefits relative to gel transplantation alone in rats with myocardial infarction. Biomaterials. 2012;33(10): 2872-2879. [20] 黄穗花,陈剑,郑韶欣,等.不同方法培养SD大鼠心肌干细胞的比较[J].广东医学,2011,32(18):2363-2366.[21] 赵天一,姜彤伟,张永和.鹿茸多肽对缺血动物模型心肌细胞线粒体凋亡相关基因蛋白Bcl-2/Bax的影响[J].吉林中医药,2013, 33(3):281-282.[22] 李朝政,许佳明,王烨,等.鹿茸多肽诱导心肌干细胞分化作用及对心肌细胞特征性MHC基因表达的影响[J].吉林中医药,2014, 34(8):825-828.[23] 杨威.不同强度运动对大鼠心肌细胞膜胆固醇平衡及稳定性的影响研究[D].武汉:湖北大学,2014.[24] 于妍,王硕仁,聂波,等.黄芪注射液在逆转心肌细胞肥大过程中对心肌细胞线粒体结构和功能的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2012, 37(7):979-984.[25] 门秀丽,张丽萍,吴静,等.线粒体形态与细胞凋亡的关系[J].生理科学进展,2012,43(5):356-360.[26] 郭茜,郭家彬,李梨,等.PGC-1α与线粒体生成调控在心血管疾病中的作用[J].中国药理学通报,2013,29(1):1-5.[27] Di Felice V, Ardizzone NM, De Luca A, et al. OPLA scaffold, collagen I, and horse serum induce an higher degree of myogenic differentiation of adult rat cardiac stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2009;221(3):729-739.[28] 施展,刘明颖,李辉. Nkx2-5在单纯性先天性心脏病中的突变及表达研究[J].中国优生与遗传杂志,2011,19(3):15-17.[29] 胡易池,杨毅宁.NKX2.5和TBX5与先天性心脏病的研究进展[J].医学综述,2012,18(13):1986-1989.[30] 蔡花,付四清.Nkx2.5基因与先天性心脏病[J].中国优生与遗传杂志,2014,22(4):1-3.[31] 刘玲珑,吴卓,赵文婧,等.间充质干细胞分化为心肌细胞过程中细胞形态变化与Nkx2.5表达相关性的初步研究[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2015,34(2):234-239.[32] 程波,李利,王林杰,等.MEF2基因家族的研究进展[J].中国畜牧杂志,2012,48(15):70-74.[33] 彭昌,张维华,潘博,等.组蛋白乙酰化酶对心脏发育核心转录因子Mef2c的动态调控作用[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2014,16(4): 418-423.[34] 邹育海,吴源锋,李慧娣,等.UCP3在心脏缺血/再灌注损伤中的研究进展[J].医学综述,2016,22(22):4385-4388.[35] 陈炜.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞转染Nkx2.5、GATA4、TBX5启动心肌细胞分化机制的实验研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2012. |
.jpg)

.jpg)