1.1 设计 随机对照动物实验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2015年1至12月在深圳大学医学院实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 SPF级8周龄雌性SD大鼠31只(10只用于制备骨髓间充质干细胞,21只用于建立脊髓损伤动物模型),体质量250-300 g,由广东省实验动物中心提供。
1.3.2 试剂和仪器 胎牛血清(Sigma公司);0.25% Trypsin-0.04%EDTA(Gibco公司);超净工作台、CO2培养箱、细胞计数仪(德国Thermo公司);流式细胞仪(美国Beckman Coulter公司);改良Allen撞击装置(中国,A21203);DAPI染色试剂盒(碧云天生物公司);Nestin抗体、GFAP抗体、NeuN抗体(美国Abcam公司);Shootin1 Rabbit Polyclonal IgG antibody(美国Abcam公司);Alexa Fluor 594 Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG( H+L)、Alexa Fluor 488 Goat Anti-Mouse IgG( H+L)、Alexa Fluor 594 Goat Anti-Mouse IgG( H+L) (Invitrogen公司)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 骨髓间充质干细胞的分离及纯化培养[3] 选取250 g成年大鼠,以腹腔注射过量2%戊巴比妥钠(0.6 mL)的方式处死,摘除双侧股骨,超净工作台内用PBS洗3次,用含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的L-DMEM培养液冲洗骨髓腔,接种于10 cm培养皿中,补充培养基至10 mL,置于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2的恒温培养箱中培养,24 h后更换培养液,弃除骨组织、软组织及血细胞等杂细胞。以后根据细胞生长情况,两三天更换1次培养液,8-10 d后细胞融合至80%左右进行传代。待细胞传代至第5代时形态几乎为长梭形,可以认为第5代以后的细胞即为较纯的骨髓间充质干细胞。应用流式细胞术鉴定大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞表型。
1.4.2 Shootin1质粒的构建与腺病毒包装 深圳Biowit公司构建质粒,并包装腺病毒。NCBI中检索了目的基因的基本信息,靶基因名称:Rattus norvegicus similar to 4930506M07Rik protein (RGD1311558),全长1 902 bp,其mRNA的Gene Bank Ref. ID: NM_001079705.3。使用的腺病毒穿梭载体为pDC316-mCMV-EGFP,带有氨苄Amp抗性,同时带有NheⅠ与NotⅠ酶切位点,因此可根据酶切位点设计引物pDC316-Shootin1-NheI-F,将靶基因Shootin1连接于pDC316-mCMV-EGFP载体上。
穿梭质粒载体pDC316-Shoootin1-mCMV-EGFP构建完成后,用纳米聚合物高效转染试剂polyfectin将病毒载体导入293T细胞进行腺病毒包装。获得了以下滴度浓度的腺病毒液:10 mg/L质粒 pDC316-mCMV-EGFP- rShootin1 10 μL,2×1013 PFU/L腺病毒rAV-mCMV- EGFP-rShootin1 1 mL,1×1013 PFU/L腺病毒rAV- mCMV-EGFP 1 mL。
1.4.3 Shootin1腺病毒转染骨髓间充质干细胞 将第5代纯化的骨髓间充质干细胞按照5×104/孔接种于预先铺好了直径为14 mm细胞爬片的24孔板中,待细胞充分贴壁铺展开后可进行腺病毒转染。该实验分为两组,每组2孔,一组进行rAV-EGFP-Shootin1腺病毒转染,一组进行rAV-EGFP腺病毒转染。另外,同时接种2个6 cm 培养皿,每皿接种5×105个细胞。一皿转染腺病毒rAV-EGFP,一皿转染腺病毒rAV-EGFP-Shootin1。
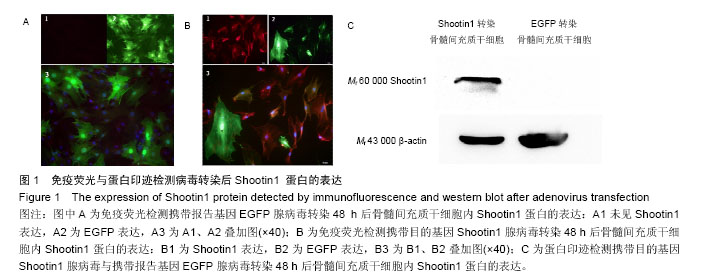
1.4.4 免疫荧光检测基因修饰后骨髓间充质干细胞中Shootin1蛋白表达情况 转染48 h待EGFP表达达到高峰时收获细胞。将腺病毒rAV-EGFP-Shootin1及rAV-EGFP转染的骨髓间充质干细胞铺板后进行Shootin1免疫荧光染色。Shootin1一抗(Abcam Rb Polyclonal IgG)按照1︰100稀释后每组的1个孔加入300 μL抗体,另1个孔加入PBS作为阴性对照,4 ℃孵育过夜。第2天室温放置30 min复温,PBS洗3次,去除非特异结合的一抗。荧光二抗Alexa Fluor 594(Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG)按照1︰100稀释后每孔加入300 μL抗体,避光孵育30 min,PBS洗3次,去除未结合游离的二抗。取出细胞爬片,轻轻倒扣于滴加DAPI封固剂(Southern Biotect DAPI Fluoromount-G)的载玻片上,完成封固后可进行荧光检测。
1.4.5 蛋白印迹检测基因修饰后骨髓间充质干细胞中Shootin1蛋白表达情况 收获细胞,制备样品,WB检测,配制分离胶,加样,电泳,转膜,加一抗:用封闭液按1︰1 000稀释一抗Shootin1(Abcam Rb Polyclonal IgG)及Anti β-actin(CWBIO Anti β-actin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody) 4 ℃过夜,然后用TBST漂洗3次× 5 min。加二抗:取封闭液按1︰2 000稀释二抗Goat anti Rb IgG-HRP(CWBIO)及Goat anti Ms IgG-HRP (CWBIO)室温振动孵育1 h,然后用TBST漂洗3次× 5 min。将ECL显色剂A、B按1︰1等体积混合(各1 mL)。取1 mL显色液滴入显影仪上,曝光3-10 min,观察结果。
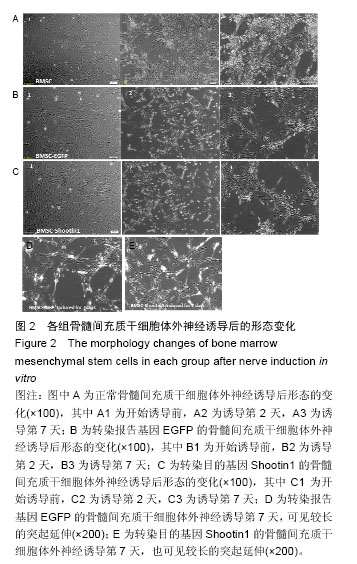
1.4.6 骨髓间充质干细胞体外神经诱导分化 实验分3组:A组:转染Shootin1的骨髓间充质干细胞组;B组:转染报告基因EGFP的骨髓间充质干细胞组;C组:骨髓间充质干细胞正常对照组。将经过腺病毒rAV-EGFP- Shootin1及rAV-EGFP转染的骨髓间充质干细胞按照5×104/孔接种于预先铺有细胞爬片的24孔板中,补齐培养液至1mL进行培养,24 h后待细胞完全贴壁进行体外神经诱导。先进行预诱导24 h,预诱导培养基:L-DMEM+体积分数为10%胎牛血清+100 μg/L碱性成纤维生长因子,然后改用诱导培养基诱导7 d,诱导培养基:L-DMEM+ 0.1%二甲基亚砜+2 mmol/L维甲酸+100 μg/L碱性成纤维生长因子+100 μg/L表皮生长因子+100 μg/L脑源性神经营养因子[4]。正常对照组骨髓间充质干细胞未转染,常规培养24 h后进行体外神经诱导。
1.4.7 免疫荧光检测各组Nestin、NeuN的表达差异 每孔细胞用PBS清洗,40 g/L多聚甲醛固定,再加入0.1% Triton X-100透化,然后用5% BSA封闭,加Nestin抗体(Abcam Mouse monoclonal)、NeuN抗体(Abcam Rabbit polyclonal),按照1︰100稀释,每孔300 μL,4 ℃孵育过夜。第2天室温放置30 min复温,PBS洗3次,去除非特异结合的一抗。加入荧光二抗Alexa Fluro 594 (Goat Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L))、Alexa Fluor(594 Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)),按照1︰500稀释,每孔300 μL,避光孵育30 min,PBS洗3次,去除未结合游离的二抗。取出细胞爬片,轻轻倒扣于滴加DAPI封固剂(Southern Biotect DAPI Fluoromount-G)的载玻片上,完成封固后可进行荧光检测。
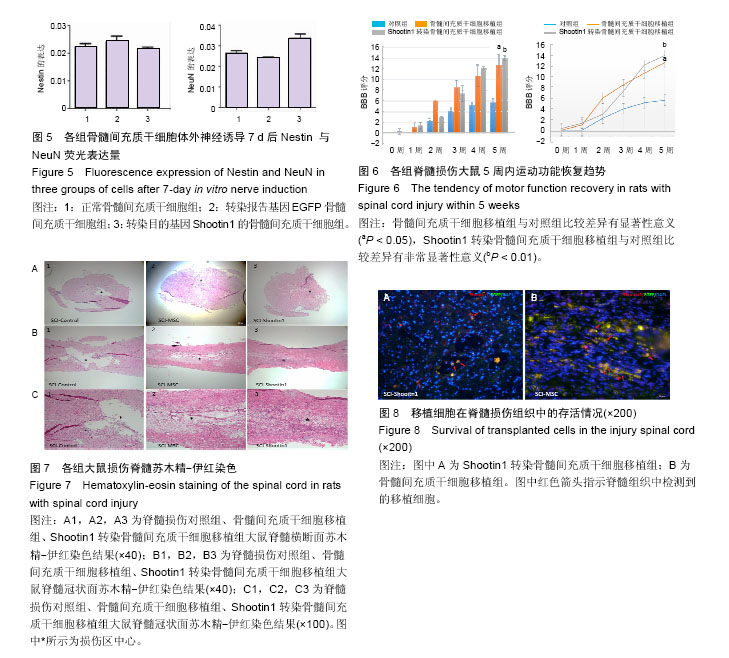
1.4.8 大鼠脊髓损伤模型的建立及细胞移植[5] 21只SD大鼠随机分3组,每组7只。脊髓损伤对照组仅进行脊髓损伤手术;骨髓间充质干细胞移植组造成脊髓损伤后进行神经诱导后的骨髓间充质干细胞移植;Shootin1转染骨髓间充质干细胞组造成脊髓损伤后进行Shootin1转染神经诱导后的骨髓间充质干细胞移植。
用2%戊巴比妥钠作腹腔麻醉后,按肋骨确定椎体序列以T9棘突为中心,背部正中切口,长3 cm,分离椎旁肌,显露T8-9棘突,咬骨钳咬除T8-9棘突,小心去除椎板,暴露T10段脊髓,用改良的Allen’s撞击装置制备脊髓损伤动物模型[6],用拉钩拉开脊髓两侧软组织,牵拉固定,使脊柱稳定,不受呼吸运动影响,将40 g的撞击棒从5 cm高度自由落体,致伤能量200 g•cm,撞击T10骨窗对应的脊髓,造成急性脊髓损伤。脊髓损伤模型撞击造模成功的标准[7-8]:撞击后的脊髓组织出现水肿、膨隆、出血,硬脊膜保持完整且呈紫红色,大鼠尾巴偶出现痉挛性摆动。脊髓损伤完成后,用胰岛素注射器吸取10 μL神经诱导后的骨髓间充质干细胞或Shootin1转染神经诱导后的骨髓间充质干细胞,细胞量为1×106,注射入脊髓损伤中心头侧2 mm处,留针1 min。常规分层缝合后回笼饲养。术后每日腹腔注射青霉素8×104 U,庆大霉素0.2×104 U,维持7 d。术后人工排尿,2次/d,直到动物自身恢复排尿反射能力。大鼠共计死亡2只,出现在脊髓损伤对照组。行为学评价时每组只统计5只大鼠。
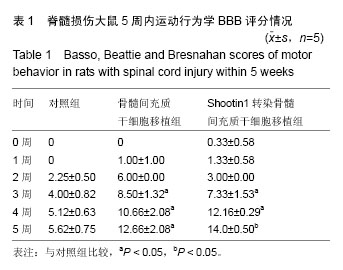
1.4.9 行为学检测各组大鼠运动功能恢复情况 参照BBB运动评分系统提出的脊髓损伤大鼠功能恢复评判标准即BBB评分法(共21级)[9],对各组动物进行评分并记录,它将大鼠后肢运动分为22个等级。后肢全瘫为0分,完全正常为21分,其基本内容为:活动关节的数目和运动范围,负重程度及前后肢协调性,前、后爪和尾部的运动情况。评分时使用双盲法对各组动物后肢运动能力进行评估,BBB评分观察期为5 min,动物应尽量保持在监测范围的中心区域活动。分别在脊髓损伤后1,2,3,4周记录大鼠双后肢运动功能恢复情况。
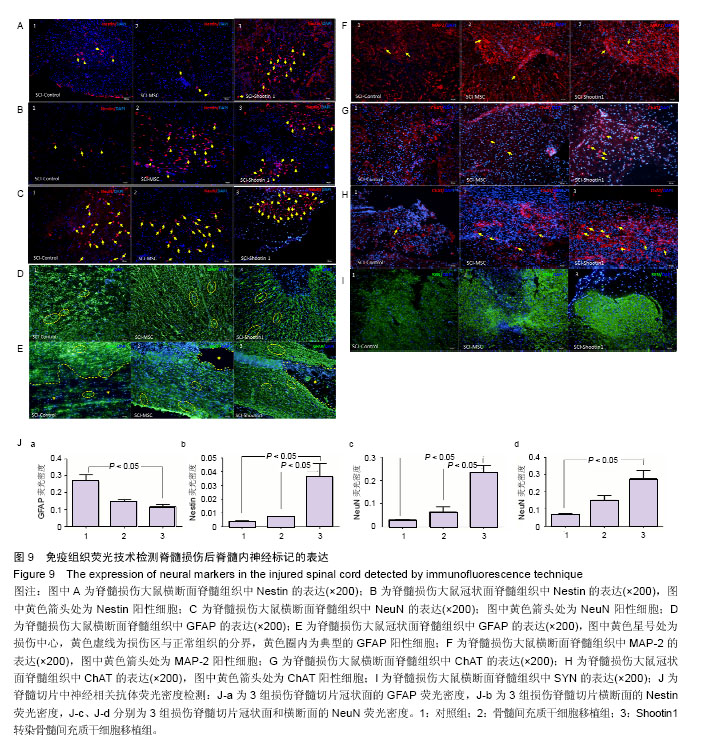
1.4.10 组织学检测 脊髓损伤5周后,麻醉大鼠,进行心脏灌注,取出以损伤区为中心,头尾侧各1 cm长度的脊髓段,置于40 g/L多聚甲醛中固定过夜。第2天按照10%、20%、30%梯度沉糖法兑换水分进行脱水处理,然后包埋,冰冻切片,进行苏木精-伊红染色检测脊髓组织结构,同时用免疫荧光检测脊髓组织神经相关标记:消除组织内过氧化物酶,封闭及细胞透化,加入一抗Nestin(Abcam Mouse monoclonal)1︰200、NeuN (Abcam Rabbit polyclonal) 1︰500、MAP-2(Cell Signaling Technology Rabbit polyclonal) 1︰200、GFAP(Abcam Mouse monoclonal) 1︰50、ChAT (Abcam Rabbit polyclonal) 1︰200,Synaptophysin (Millipore Mouse Monoclonal) 1︰100 置于4 ℃冰箱孵育过夜,复温PBS冲洗后滴加1︰500荧光二抗Alexa Fluro 594 (Goat Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L))、Alexa Fluor 594 (Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG)室温孵育1 h,封固后在荧光显微镜下进行观察。
1.5 主要观察指标 各组BBB评分以及脊髓组织中Nestin、GFAP、NeuN、MAP-2、ChAT、突触素等神经相关蛋白表达的差异。
1.6 统计学分析 荧光强度使用ImageJ 2×进行计算,数据以x±s表示,采用SPSS 16.0软件,细胞移植治疗组与对照组间的比较采用单因素方差分析及q 检验,两个细胞移植治疗组间比较采用t 检验。
.jpg)

.jpg)