| [1] Kunz RI, Coradini JG, Silva L, et al. Effects of immobilization and remobilization on the ankle joint in wistar rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014;47(10):842-849.
[2] Lamb SE, Marsh JL, Hutton JL, Nakash R, Cooke MW. Mechanical supports for acute, severe ankle sprain: a pragmatic, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;373:575-581.
[3] Jones RK, Chapman GJ, Findlow AH, et al. A new approach to prevention of knee osteoarthritis: reducing medial load in the contralateral knee. J Rheumatol. 2013;40(3):309-315.
[4] Stumpfe ST, Pester JK, Steinert S, et al. Is there a correlation between biophotonical, biochemical, histological, and visual changes in the cartilage of osteoarthritic knee-joints? Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2013;3(3):157-165.
[5] Brandt KD. Response of joint structures to inactivity and to reloading after immobilization. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49(2):267-271.
[6] Arakaki K, Kitamura N, Kurokawa T, et al. Joint immobilization inhibits spontaneous hyaline cartilage regeneration induced by a novel doublenetwork gel implantation. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22:417-425.
[7] Bedi A, Feeley BT, Williams RJ III. Management of articularcartilage defects of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92:994-1009.
[8] Vanwanseele B, Eckstein F, Knecht H, et al. Knee cartilage of spinal cord-injured patients displays progressive thinning in the absence of normal joint loading and movement. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46(8): 2073-2078.
[9] Haapala J, Arokoski J P, Ronkko S, et al. Decline after immobilisation and recovery after remobilisation of synovial fluid IL1, TIMP, and chondroitin sulphate levels in young beagle dogs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60(1):55-60.
[10] Trudel G, Himori K, Uhthoff HK. Contrasting alterations of apposed and unapposed articular cartilage during joint contracture formation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86(1):90-97.
[11] 顾延,戴克戎,裘世静,等.应力降低导致关节软骨退变机理的形态学研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1995,15(9):631-633.
[12] Mollon B, Kandel R, Chahal J, et al. The clinical status of cartilage tissue regeneration in humans. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21:1824-1833.
[13] Gu XI, Leong DJ, Guzman F, et al. Development and validation of a motion and loading system for a rat knee joint in vivo. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010;38:621-631.
[14] Convery FR, Akeson WH, Keown GH. The repair of large osteochondral defects. An experimental study in horses. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972;82:253-262.
[15] 马信龙,马剑雄.可调节动物实验用全环外固定架:中国, CN203468785U[P].2014-03-12.
[16] Wakitani S, Goto T, Pineda SJ, et al. Mesenchymal cell-based repair of large, full-thickness defects of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(4): 579-592.
[17] van der Sluijs JA, Geesink RG, van der Linden AJ, et al. The reliability of the Mankin score for osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(1):58-61.
[18] Angele P, Yoo JU, Smith C, et al. Cyclic hydrostatic pressure enhances the chondrogenic phenotype of human mesenchymal progenitor cells differentiated in vitro. J Orthop Res,2003,21(3):451-457.
[19] Harada Y, Tomita N, Wakitani S, et al. Use of controlled mechanical stimulation in vivo to induce cartilage layer formation on the surface of osteotomized bone. Tissue Eng. 2002;8(6):969-978.
[20] Loening AM, James I E, Levenston M E, et al. Injurious mechanical compression of bovine articular cartilage induces chondrocyte apoptosis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000;381(2):205-212.
[21] van Valburg AA, van Roy HL, Lafeber FP, et al. Beneficial effects of intermittent fluid pressure of low physiological magnitude on cartilage and inflammation in osteoarthritis. An in vitro study. J Rheumatol. 1998; 25(3):515-520.
[22] Mobasheri A, Mobasheri R, Francis MJ, et al. Ion transport in chondrocytes: membrane transporters involved in intracellular ion homeostasis and the regulation of cell volume, free [Ca2+] and pH. Histol Histopathol. 1998;13(3):893-910.
[23] Hung SC, Nakamura K, Shiro R, et al. Effects of continuous distraction on cartilage in a moving joint: an investigation on adult rabbits. J Orthop Res. 1997; 15(3): 381-390.
[24] Leong DJ, Gu XI, Li Y, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-3 in articular cartilage is upregulated by joint immobilizationand suppressed by passive joint motion. Matrix Biol. 2010;29:420-426.
[25] Billinghurst RC, Dahlberg L, Ionescu M, et al. Enhanced cleavage of type II collagen by collagenases in osteoarthritic articular cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1997; 99(7):1534-1545.
[26] Qi C, Changlin H, Zefeng H. Matrix metalloproteinases and inhibitor in knee synovial fluid as cartilage biomarkers in rabbits: the effect of high-intensity jumping exercise. J Surg Res. 2007;140(1):149-157.
[27] 刘志翔,张柳,张楠.降钙素对兔骨关节炎软骨基质金属蛋白酶1的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(22):1741-1743.
[28] Ando A, Suda H, Hagiwara Y, et al. Reversibility of immobilization-induced articular cartilage degeneration after remobilization in rat knee joints. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2011;224:77-85.
[29] Sowers MF, Karvonen-Gutierrez CA, Yosef M, et al. Longitudinal changes of serum COMP and urinary CTX-II predict X-ray defined knee osteoarthritis severity and stiffness in women. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(12):1609-1614.
[30] Lohmander LS, Atley LM, Pietka TA, Eyre DR. The release of crosslinked peptides from type II collagen into human synovial fluid is increased soon after joint injury and in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48(11):3130-3139.
[31] Catterall JB, Stabler TV, Flannery CR, Kraus VB. Changes in serum and synovial fluid biomarkers after acute injury (NCT00332254). Arthritis Res Ther. 2010; 12(6):R229. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
Ilizarov外固定器:Ilizarov装置是一种复杂的环形支架系统,通过多平面的水平穿透骨骼和肢体的克氏针与支架相连,它包含许多组件,在延长的同时可以矫正成角和旋转畸形;同时还有加压、延长和横向移位的功能。
关节制动:是经常用于骨骼肌肉损伤中来治疗关节疼痛以及关节损伤的一种方法,研究发现制动和其他治疗方法相比能减少受损滑膜关节的疼痛,减小关节应力,阻止受损关节的骨性关节炎进程。
文题释义:
Ilizarov外固定器:Ilizarov装置是一种复杂的环形支架系统,通过多平面的水平穿透骨骼和肢体的克氏针与支架相连,它包含许多组件,在延长的同时可以矫正成角和旋转畸形;同时还有加压、延长和横向移位的功能。
关节制动:是经常用于骨骼肌肉损伤中来治疗关节疼痛以及关节损伤的一种方法,研究发现制动和其他治疗方法相比能减少受损滑膜关节的疼痛,减小关节应力,阻止受损关节的骨性关节炎进程。.jpg) 文题释义:
Ilizarov外固定器:Ilizarov装置是一种复杂的环形支架系统,通过多平面的水平穿透骨骼和肢体的克氏针与支架相连,它包含许多组件,在延长的同时可以矫正成角和旋转畸形;同时还有加压、延长和横向移位的功能。
关节制动:是经常用于骨骼肌肉损伤中来治疗关节疼痛以及关节损伤的一种方法,研究发现制动和其他治疗方法相比能减少受损滑膜关节的疼痛,减小关节应力,阻止受损关节的骨性关节炎进程。
文题释义:
Ilizarov外固定器:Ilizarov装置是一种复杂的环形支架系统,通过多平面的水平穿透骨骼和肢体的克氏针与支架相连,它包含许多组件,在延长的同时可以矫正成角和旋转畸形;同时还有加压、延长和横向移位的功能。
关节制动:是经常用于骨骼肌肉损伤中来治疗关节疼痛以及关节损伤的一种方法,研究发现制动和其他治疗方法相比能减少受损滑膜关节的疼痛,减小关节应力,阻止受损关节的骨性关节炎进程。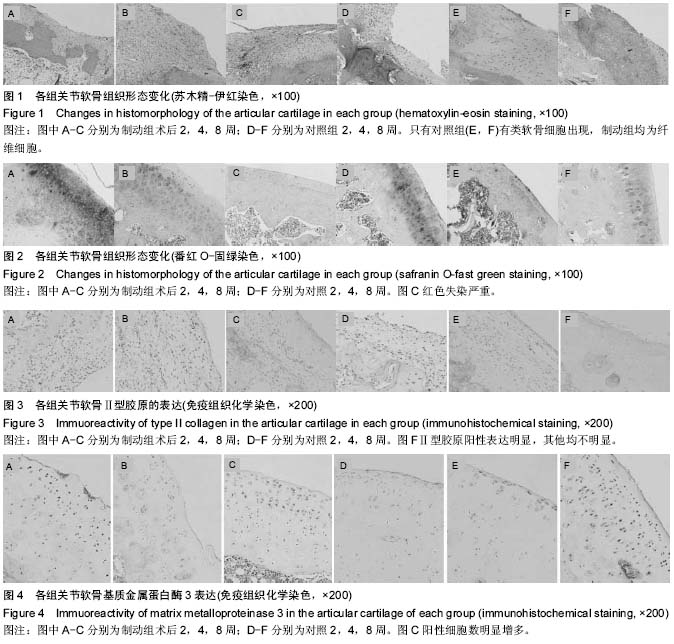
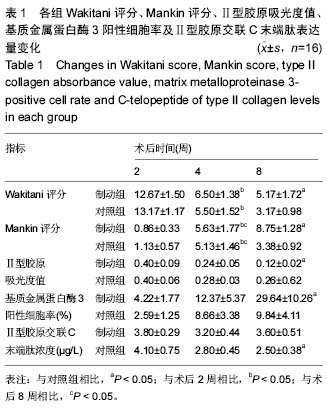
.jpg) 文题释义:
Ilizarov外固定器:Ilizarov装置是一种复杂的环形支架系统,通过多平面的水平穿透骨骼和肢体的克氏针与支架相连,它包含许多组件,在延长的同时可以矫正成角和旋转畸形;同时还有加压、延长和横向移位的功能。
关节制动:是经常用于骨骼肌肉损伤中来治疗关节疼痛以及关节损伤的一种方法,研究发现制动和其他治疗方法相比能减少受损滑膜关节的疼痛,减小关节应力,阻止受损关节的骨性关节炎进程。
文题释义:
Ilizarov外固定器:Ilizarov装置是一种复杂的环形支架系统,通过多平面的水平穿透骨骼和肢体的克氏针与支架相连,它包含许多组件,在延长的同时可以矫正成角和旋转畸形;同时还有加压、延长和横向移位的功能。
关节制动:是经常用于骨骼肌肉损伤中来治疗关节疼痛以及关节损伤的一种方法,研究发现制动和其他治疗方法相比能减少受损滑膜关节的疼痛,减小关节应力,阻止受损关节的骨性关节炎进程。