| [1] 刘忠厚.骨质疏松学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1998:529.
[2] Honig S. Osteoporosis - new treatments and updates. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2010;68(3):166-170.
[3] 盛柩,谢培凤,王新祥.原发性骨质疏松症从脾论治及相关机制探讨[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(7):1922- 1926.
[4] 章伟文.中西医结合治疗老年性骨质疏松症35例疗效观察[J].云南中医中药杂志,2012, 33(10):41-42.
[5] 张毅,曾平,李宁华.北京崇文区中老年原发性骨质疏松症的发生及其影响因素:分层多阶段整群抽样调查[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(27):5332- 5335.
[6] Vural P, Akgul C, Canbaz M. Effects of hormone replacement therapy on plasma pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines and some bone turnover markers in postmenopausal women. Pharmacol Res. 2006;54(4):298-302.
[7] Uemura H, Kamada M, Maegawa M, et al. Effect of hormone replacement therapy on the production of bone-resorbing cytokines by peripheral blood cells in postmenopausal women. Horm Metab Res. 2005; 37(4):226-230.
[8] Papanicolaou DA, Wilder RL, Manolagas SC, et al. The pathophysiologic roles of interleukin-6 in human disease. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128(2):127-137.
[9] 罗南萍,刘恒国.骨质疏松症与相关细胞因子的研究[J]. 放射免疫学杂志,2007,20(2):132-136.
[10] Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Björk-Eriksson T, et al. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med. 1998;4(11):1313-1317.
[11] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[12] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.
[13] Zhu Y, Liu T, Song K, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell: a better stem cell than BMSC. Cell Biochem Funct. 2008;26(6):664-675.
[14] 蔡玉霞,张剑宇.补骨脂水煎剂对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(2):268-271.
[15] 吴建斌.不同填充材料及脂肪源干细胞移植对骨质疏松大鼠的影响[D].广州:南方医科大学,2013.
[16] 郭成龙,张晓刚,宋敏,等.骨质疏松症药物治疗的研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2010,18(6):65-68.
[17] 文天林,孙天胜,王玲.骨质疏松的流行病学、病因和分类[J].人民军医,2010,53(9):662-663.
[18] 胡军,张华,牟青.骨质疏松症的流行病学趋势与防治进展[J].临床荟萃,2011,26(8):729-731.
[19] Kumar S, Mahendra G, Nagy TR, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of recombinant adeno-associated virus 2-transduced murine mesenchymal stem cells and development of an immunocompetent mouse model for ex vivo osteoporosis gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 2004;15(12):1197-1206.
[20] 马伟,牟慧琴,马占洋.绝经后骨质疏松症中医病因病机研究概况[J].中医杂志,2012,53(13):1152-1154.
[21] 郭晓黎.中医学对骨质疏松症病因病机认识[J].中医学报, 2012,27(10):1289-1290.
[22] 胡志俊,王世伟,刘文波,等.骨质疏松的中医辨证分型研宄[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2012, 20(1):23-25.
[23] 贾经汉,邱新建,陈志坚.骨质疏松动物模型的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2007,22(8):765-768.
[24] 邓娟,裴必伟,徐胜前,等.类风湿关节炎患者全身骨质疏松和局部骨侵烛的关系研究[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2012, 16(10): 674-678.
[25] 唐鹏,孟国林,王军,等.长期应用双膦酸盐类药物对老年性骨质疏松骨折愈合过程的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2012,18(4):317-322.
[26] 于文广,张鲁阳,张学顺.类风湿关节炎患者骨质疏松健康教育相关因素调查分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012, 18(7):623-627.
[27] 尚庆,刘宗超,鲁晓波.骨质疏松动物模型特点的综述[J].中国实用医药,2008,3(13):193-195.
[28] 崔双,薛昊罢.绝经后女性骨质疏松患者骨密度与血脂和护骨素的相关性[J].中国老年学杂志,2012, 32(10): 2051-2053.
[29] 张颖,张博,张治国,等.从肝脾肾三脏探讨绝经后骨质疏松症的发病机理[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2012,18(1): 36-37.
[30] 李雪琳.中西医结合治疗绝经妇女骨鹿疏松症30例[J].实用中医药杂志,2012,28(4): 285-286.
[31] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.
[32] Nakao N, Nakayama T, Yahata T, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells facilitate hematopoiesis in vitro and in vivo: advantages over bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Pathol. 2010;177(2):547-554.
[33] Yañez R, Lamana ML, García-Castro J, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells have in vivo immunosuppressive properties applicable for the control of the graft-versus-host disease. Stem Cells. 2006;24(11):2582-2591.
[34] Schäffler A, Büchler C. Concise review: adipose tissue-derived stromal cells--basic and clinical implications for novel cell-based therapies. Stem Cells. 2007;25(4):818-827.
[35] Niemeyer P, Kornacker M, Mehlhorn A, et al. Comparison of immunological properties of bone marrow stromal cells and adipose tissue-derived stem cells before and after osteogenic differentiation in vitro. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(1):111-121.
[36] 陶晖,杨会营,余美春,等.异体脂肪源干细胞移植对糖皮质激素性骨质疏松大鼠的影响[J].解剖学报,2011,4(2): 220-225.
[37] 李良,李冬菊,吴江,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松发病机理中潜在的作用[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2006,23(1):129-135.
[38] Coelho MJ, Fernandes MH. Human bone cell cultures in biocompatibility testing. Part II: effect of ascorbic acid, beta-glycerophosphate and dexamethasone on osteoblastic differentiation. Biomaterials. 2000;21(11): 1095-1102.
[39] Gruber R. Cell biology of osteoimmunology. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2010;160(17-18):438-445.
[40] Justesen J, Stenderup K, Kassem MS. Mesenchymal stem cells. Potential use in cell and gene therapy of bone loss caused by aging and osteoporosis. Ugeskr Laeger. 2001;163(40):5491-5495.
[41] 刘晓青,崔燎,吴铁.双侧卵巢切除大鼠不同时间段骨形态计量学参数的观察[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2005, 11(4): 427-429. |
.jpg)
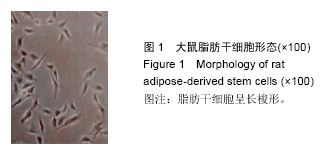
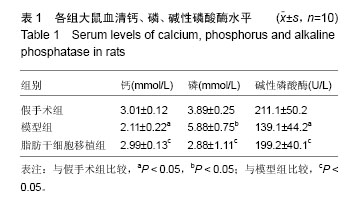
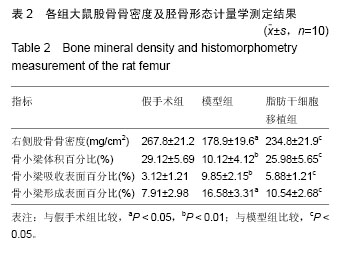
.jpg)