| [1] 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组缺血性脑卒中二级预防指南撰写组.中国缺血性脑卒中和短暂性脑缺血发作二级预防指南2010[J].中华神经科杂志,2010,43(2): 154-160.
[2] Nakagawara J, Minematsu K, Okada Y, et al. Thrombolysis with 0.6 mg/kg intravenous alteplase for acute ischemic stroke in routine clinical practice: the Japan post-Marketing Alteplase Registration Study (J-MARS). Stroke. 2010;41(9):1984-1989.
[3] Cannon CP, Rhee KE, Califf RM, et al. Current use of aspirin and antithrombotic agents in the United States among outpatients with atherothrombotic disease (from the REduction of Atherothrombosis for Continued Health [REACH] Registry). Am J Cardiol. 2010;105(4):445-452.
[4] Ansara AJ, Nisly SA, Arif SA, et al. Aspirin dosing for the prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke: an indication-specific review of the literature. Ann Pharmacother. 2010;44(5):851-862.
[5] Bath PM, Cotton D, Martin RH, et al. Effect of combined aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole versus clopidogrel on functional outcome and recurrence in acute, mild ischemic stroke: PRoFESS subgroup analysis. Stroke. 2010;41(4):732-738.
[6] Lee JS, Hong JM, Moon GJ, et al. A long-term follow-up study of intravenous autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with ischemic stroke. Stem Cells. 2010;28(6):1099-1106.
[7] Ferrero E, Ferri M, Viazzo A, et al. Early carotid surgery in patients after acute ischemic stroke: is it safe? A retrospective analysis in a single center between early and delayed/deferred carotid surgery on 285 patients. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010;24(7):890-899.
[8] Stanca DM, M?rginean IC, Sori??u O, et al. Plasmatic markers for early diagnostic and treatment decisions in ischemic stroke. J Med Life. 2015;8 Spec Issue:21-25.
[9] Jin R, Yang G, Li G. Molecular insights and therapeutic targets for blood-brain barrier disruption in ischemic stroke: critical role of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue-type plasminogen activator. Neurobiol Dis. 2010; 38(3):376-385.
[10] 鹿寒冰,董瑞国,李晓宾,等.大鼠实验性脑梗死后AQP4表达与MRI变化的相关性研究[J].卒中与神经疾病,2011, 18(6):348-352.
[11] 彭晓琴,张兆辉,何国厚.依达拉奉联合银杏达莫治疗急性脑梗死的Meta分析[J].卒中与神经疾病,2012,19(3): 159-163.
[12] Wang GH, Jiang ZL, Li YC, et al. Free-radical scavenger edaravone treatment confers neuroprotection against traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 2011;28(10):2123-2134.
[13] 李丽红.加用依达拉奉治疗急性脑梗死的疗效观察[J].中国医药指南,2010,8(15):104-105.
[14] 黄杰,陈燕,张斌,等.依达拉奉治疗急性脑梗死45例疗效分析[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2010,13(10):18-20.
[15] van Velthoven CT, Kavelaars A, van Bel F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell treatment after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury improves behavioral outcome and induces neuronal and oligodendrocyte regeneration. Brain Behav Immun. 2010;24(3):387-393.
[16] 孙春霞,孙善卫,张瑞彪.依达拉奉对进展性脑卒中患者血清hs-CRP及TNF-α水平的影响及临床意义[J],河北医药, 2010,32(18):2351-2352.
[17] 丁忠阳.依达拉奉对创伤性脑水肿大鼠 AQP4 表达的影响[J].山东医药,2011,51(49):32-33.
[18] 刘信东,张利娟,赵丽君.依达拉奉治疗大面积脑梗死的临床疗效观察[J].四川医学,2012,33(3):431-433.
[19] 张敏,张月,吕辉,等.依达拉奉注射液联合苦碟子注射液治疗急性脑梗死的疗效观察[J].中国医院用药评价与分析,2012,12(3):249-251.
[20] 叶冠龙.低分子肝素钙与依达拉奉联合治疗对进展性脑梗死的疗效及血清一氧化氮的影响[J].中国医院用药评价与分析,2010,10(4):335-336.
[21] 赵彬,刘斌,张玉芹.依达拉奉对脑出血大鼠血肿周围组织Caspase-3和Pdcd-5蛋白表达的影响[J].天津医药, 2012, 40(5):483-485.
[22] 吴睿,罗世坚,李振东,等.环孢素A抑制炎症改善大鼠脑缺血神经功能[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志,2015,41(5): 299-303.
[23] 曹红元,刘雨辉,李惠允,等.急性脑梗死后炎症因子的动态变化及其与神经功能的相关性研究[J].解放军医药杂志, 2014,26(3):51-54.
[24] 桂千,程庆璋.炎症因子与急性脑梗死的相关性研究[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2015,18(20):42-43.
[25] Liu N, Chen R, Du H, et al. Expression of IL-10 and TNF-alpha in rats with cerebral infarction after transplantation with mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Mol Immunol. 2009;6(3):207-213.
[26] 郭靖,李晓宾,李传玲,等.急性脑梗死后血清TNF-α水平与NIHSS评分的相关性及依达拉奉的干预作用[J].山东医药,2013,53(41):16-18.
[27] Myers TJ, Granero-Molto F, Longobardi L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells at the intersection of cell and gene therapy.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010;10(12):1663- 1679.
[28] Wang L, Ott L, Seshareddy K, et al. Musculoskeletal tissue engineering with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells. Regen Med. 2011;6(1): 95-109.
[29] Li J, Zhu H, Liu Y, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation protects against cerebral ischemic injury and upregulates interleukin-10 expression in Macacafascicularis. Brain Res. 2010; 1334:65-72.
[30] Eglitis MA, Mezey E. Hematopoietic cells differentiate into both microglia and macroglia in the brains of adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(8):4080- 4085.
[31] 张洪连,吴晓牧.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死及存在问题[J].中华脑血管病杂志(电子版),2010,4(4):300- 307.
[32] Anbari F, Khalili MA, Bahrami AR, et al. Intravenous transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes neural regeneration after traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(9):919-923.
[33] Xin H, Li Y, Liu Z, et al. MiR-133b promotes neural plasticity and functional recovery after treatment of stroke with multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in rats via transfer of exosome-enriched extracellular particles. Stem Cells. 2013;31(12):2737-2746.
[34] Yu HB, Chen PD, Yang ZX, et al. Electro-acupuncture at Conception and Governor vessels and transplantation of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treating cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014; 9(1):84-91.
[35] Peng Y, Zhang QM, You H, et al. Growth-associated protein 43 and neural cell adhesion molecule expression follow-ing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a rat model of ischemic brain injury. Neural Regen Res.2010;5(13): 975-980.
[36] Li Y, Hua XM, Hua F, et al. Are bone marrow regenerative cells ideal seed cells for the treatment of cerebral ischemia? Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(13): 1201-1209.
[37] Du J, Gao XQ, Deng L, et al. Transfection of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene promotes neuronal differentiation. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(1): 33-40.
[38] 何国美,戴薇.依达拉奉对脑梗死患者IL-6、IL-1 3及ET-1表达的影响[J],实用医学杂志,2010,26(6):1043-1044.
[39] Lapchak PA. A critical assessment of edaravone acute ischemic stroke efficacy trials: is edaravone an effective neuroprotective therapy? Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010;11(10):1753-1763.
[40] Sharma P, Sinha M, Shukla R, et al. A randomized controlled clinical trial to compare the safety and efficacy of edaravone in acute ischemic stroke. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2011;14(2):103-106.
[41] 赵燕民,范仲鹏,陈品.依达拉奉治疗急性大面积脑梗死患者的疗效观察[J].临床神经病学杂志,2008,21(5):381- 383.
[42] 欧阳锦华.依达拉奉治疗急性脑梗死的临床研究[J].中国医药,2010,5(9):833-834.
[43] 陈景红,李娜,孙素娟,等.依达拉奉对急性脑梗死患者血清血管内皮生长因子和肿瘤坏死因子水平的影响[J].临床神经病学杂志,2012,25(6):425-427.
[44] Balu S. Differences in psychometric properties, cut-off scores, and outcomes between the Barthel Index and Modified Rankin Scale in pharmacotherapy-based stroke trials: systematic literature review. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009;25(6):1329-1341.
[45] Watanabe T, Tanaka M, Watanabe K, et al. Research and development of the free radical scavenger edaravone as a neuroprotectant. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2004;124(3):99-111.
[46] Naritomi H, Moriwaki H. Prevention of post-stroke disuse muscle atrophy with a free radical scavenger. Front Neurol Neurosci. 2013;32:139-147.
[47] Kikuchi K, Miura N, Kawahara KI, et al. Edaravone (Radicut), a free radical scavenger, is a potentially useful addition to thrombolytic therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Biomed Rep. 2013;1(1):7-12.
[48] 赵燕民,范仲鹏,陈品.依达拉奉治疗急性大面积脑梗死患者的疗效观察[J].临床神经病学杂志,2008,21(5):381- 383.
[49] 欧阳锦华.依达拉奉治疗急性脑梗死的临床研究[J].中国医药,2010,5(9):833-834.
[50] 陈景红,李娜,孙素娟,等.依达拉奉对急性脑梗死患者血清血管内皮生长因子和肿瘤坏死因子水平的影响[J].临床神经病学杂志,2012,25(6):425-427.
[51] 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南撰写组.中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2010 [J].中华神经科杂志,2010,43(2):146-153.
[52] 李忠音,张军.依达拉奉对急性脑梗死患者血清炎性因子及神经功能的影响[J].河北医学,2015,21(1):122-125. |
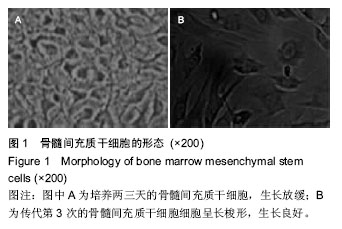
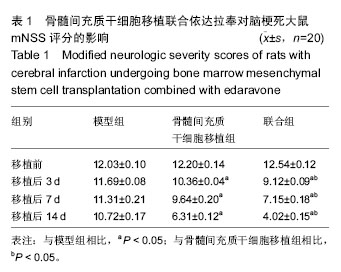
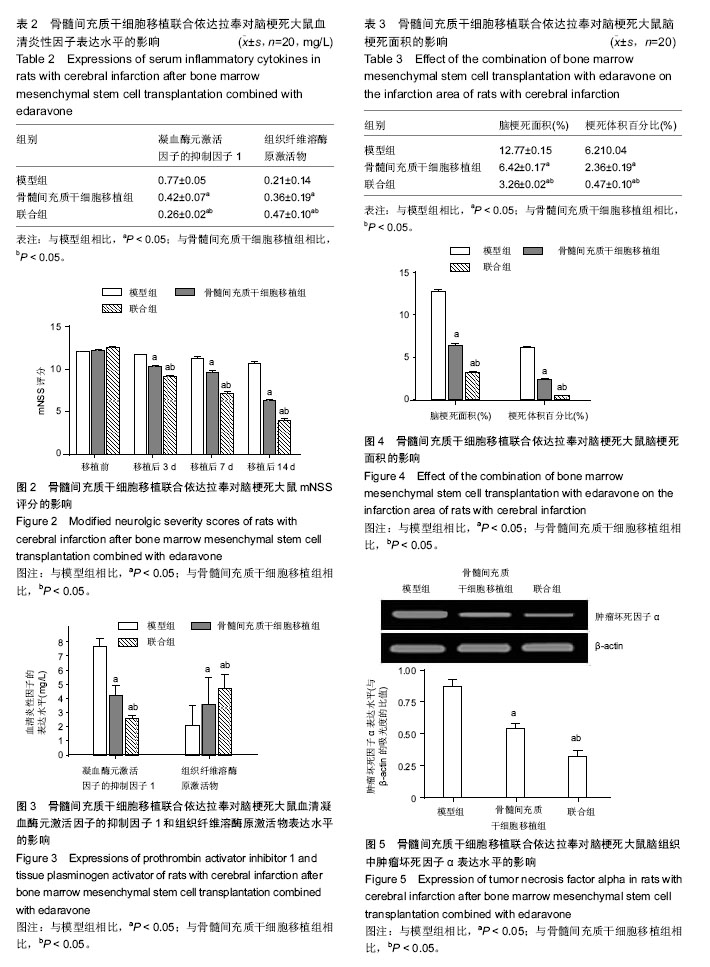
.jpg)
.jpg)