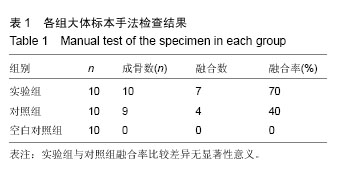
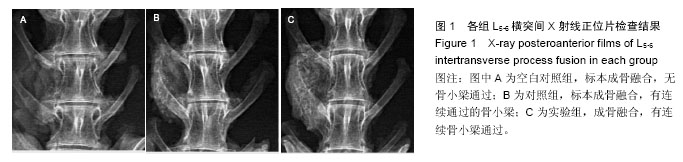
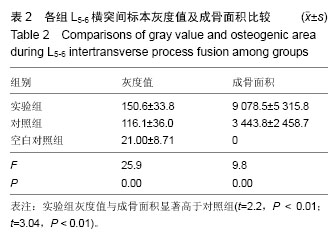
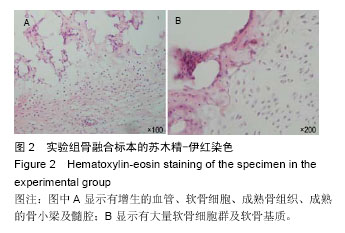
| [1] Younger EM,Chapman MW.Morbidity at bone graft donor site.Orthorp Trauma.1989;3:192-195.[2] Gerstenfed LC,Cullinanes DM,Barnes GL.Fracture healing as a postnatal developmental process: molecular,spatial,and temporal aspects of its regulation.J Cell Biochem.2003;88:873-884.[3] Suárez-González D, Lee JS, Diggs A,et al. Controlled multiple growth factor delivery from bone tissue engineering scaffolds via designed affinity.Tissue Eng Part A.2014; 20(15-16):2077-2087.[4] Samee M,Kasugai S,Kondo H,et al.Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) transfection to human periosteal cells enhances osteoblast differentiation and bone formation.J Pharmacol Sci. 2008;108(1):18-31. [5] Peng H,Wright V,Usas A,et al.Synynergistic enhancement of bone formation and healing by stem cell-expressed VEGF and bone morphogenetic protein-4.J Clin Invest. 2002;110(6):751-759.[6] Kawamura M,Urist MR.Human fibrin is a physiological delivery system for bone morphogenetic protein.Clin Orthop.1988;235:302-310. [7] Mandracchia VJ,Nelson SL,Barp EA.Current concepts of bone healing.Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2001;18:55-77.[8] David SM,Gruber HE,Meyer RA.Lumbar spine fusion using recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein in the canine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24: 1973-1979.[9] Laffargue P,Hildebrand HF,Rtaimate M.Evaluation of human recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2-loaded tricalcium phosphate implants in rabbits' bone defects.Bone.1999;25(2 Suppl):55S-58S.[10] Irie K,Alpaslan C,Takahashi K. Osteoclast differentiation in ectopic bone formation induced by recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 (rhBMP-2).J Bone Miner Metab. 2003;21(6):363-369.[11] Schimandle JH,Boden SD,Hutton WC.Experimental spinal fusion with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20(12):1326-337. [12] Boden SD,Schimandle JH,Hutton WC.1995 Volvo Award in basic sicences:The use of an osteoinductive growth factor for lumbar spinal fusion.Part Il:Study of dose,carrier,and species.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1995; 20(24):2633-2644. [13] Morone MA,Boden SD,Hair G,et a1.Gene expression during autograft lumbar spine fusion and the effect of bone morphogenetic protein-2.Clin Orthop. 1998;351: 252-265.[14] Park DK,Kim SS,Thakur N,et al.Use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 with local bone graft instead of iliac crest bone graft in posterolateral lumbar spine arthrodesis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(12):E738-747.[15] Barnes B,Boden SD,Louis-Ugbo J,et al.Lower dose of rhBMP-2 achieves spine fusion when combined with an osteoconductive bulking agent in non-human primates.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005;30(10): 1127-1133.[16] Glowacki J.Angiogenesis in fracture repair.Clin Orthop. 1998;355(Suppl.):S82-89.[17] Nakagawa M,Kaneda T,Arakawa T.Vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF) directly enhence osteoclastic bone resorption and survial mature osteoclasts.FEBS Lett.2000;4473:161-164.[18] Gerber HP,Vu TH,Ryan AM,et al.VEGF couples hypertrophic cartilage remodeling,ossification and angiogenesis during endochondral bone formation.Nat Med.1999;5:623-628. [19] Street J,Bao M,deGuzman L,et al.Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulate bone repair by promoting angiogenesis bone turnover.Proc Netl Sci USA. 2002; 99(15): 9656-9661.[20] Streeten EA,Brandi ML.Biology of bone endothelial cells.Bone Miner.1990;10:85-94. [21] Wang S,Miura M,Demura H,et al.Anablic effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on osteoblasts are enhanced by vascular endothelial growth factor produced by osteoblasts and by growth factors produced by endothelial cells.Endocrinology. 1997; 138:2953-2962.[22] Nakagawa M,Kaneda T,Arakawa T.Vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF) directly enhence osteoclastic bone resorption and survial mature osteoclasts.FEBS Lett.2000;4473:161-164.[23] Niida S,Kaku M,Amano H.Vascular endothelial growth factor can substitude for macrophage colony-stimulating factor in the support of osteoclastic bone resorption.J Exp Med.1999;190:293-298.[24] Street J,Winter D,Wang JH,Wakai A.Is human fracture hematoma inherently angiogenic? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(378):224-237.[25] Peng H,Wright V,UsasA,et al.Synynergistic enhancement of bone formation and healing by stem cell-expressed VEGF and bone morphogenetic protein-4.J Clin Invest.2002; 110(6):751-759. [26] Xiao C,Zhou H,Liu G,et al.Bone marrow stromal cells with a combined expression of BMP-2 and VEGF-165 enhanced bone regeneration.Biomed Mater. 2011; 6(1):015013.[27] Sukul M,Nguyen TB,Min YK,et al.Effect of Local Sustainable Release of BMP2-VEGF from Nano-Cellulose Loaded in Sponge Biphasic Calcium Phosphate on Bone Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A.2015;21(11-12):1822-3186.[28] Hay E,Lemonnier J,Fromigue O.Bone morphogenetic protein-2 promotes osteoblast apoptosis through a Smad-independent,protein kinase C-dependent signaling pathway.J Biol Chem.2001;276: 29028- 29036.[29] Bouletreau PJ,Warren SM,Spector JA,et al.Hypoxia and VEGF up-regulate BMP-2 mRNA and protein expression in microvascular endothelial cells: implications for fracture healing.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109(7):2348.[30] Deckers MM,van Benzoonijen RL,van der Horst G,et al.Bone morphogenetic proteins stimulate angiogenesis through osteoblast-derived vascular endothelial growth factor A.Endocrinology. 2002;143(4): 1545-553. [31] Matsubara H,Hogan DE,Morgan EF,et al.Vascular tissues are a primary source of BMP2 expression during bone formation induced by distraction osteogenesis. Bone.2012;51(1):168-180. [32] Zhang G,Drinnan CT,Geuss LR,et al.Vascular differentiation of bone marrow stem cells is directed by a tunable three-dimensional matrix.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(9):3395-403. [33] Ohira S,Doi K,Yaku H.Sutureless Technique to Fix the Great Saphenous Vein along the Atrioventricular Groove Using Fibrin Glue in Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting.Heart Surg Forum. 2016;19(2): E074-076. [34] Sakaguchi Y,Tsuji Y,Fujishiro M,et al.Triamcinolone Injection and Shielding with Polyglycolic Acid Sheets and Fibrin Glue for Postoperative Stricture Prevention after Esophageal Endoscopic Resection: A Pilot Study.Am J Gastroenterol.2016;111(4):581-583. [35] Hong KP,Kim DK,Kang KH.Staple Line Coverage with a Polyglycolic Acid Patch and Fibrin Glue without Pleural Abrasion after Thoracoscopic Bullectomy for Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax.Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2016;49(2):85-91. [36] Liu Z,Zhu Y,Zhu H,et al.Enhancement of posterolateral lumbar spine fusion using recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 and mesenchymal stem cells delivered in fibrin glue.J Biomater Appl.2016.pii: 0885328216643854.[Epub ahead of print][37] Cho AB,Paulos RG,Bersani G,et al.A reinforcement of the sutured microvascular anastomosis with fibrin glue application: A retrospective comparative study with the standard conventional technique.Microsurgery. 2016.doi:10.1002/micr.30054.[Epub ahead of print] |
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)