中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 1701-1707.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2506
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
电针干预脊髓损伤大鼠受损节段缺氧诱导因子1α、血管内皮生长因子的表达
张鸿升1,魏卫兵2,周宾宾3,崔俊武3,李振兴3,王永清4
- 1广西中医药大学附属瑞康医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530000;2柳州市中医医院,广西壮族自治区柳州市 545001;3广西中医药大学第一附属医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530022;4天津市第四中心医院,天津市 300140
Effect of electroacupuncture intervention on expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor in injured segments of rats with spinal cord injury
Zhang Hongsheng1, Wei Weibing2, Zhou Binbin3, Cui Junwu3, Li Zhenxing3, Wang Yongqing4
- 1Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Liuzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 3First Affiliated Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530022, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 4Fourth Central Hospital of Tianjin, Tianjin 300140, China
摘要:
文题释义:
缺氧诱导因子1α:脊髓损伤可刺激作为血管生成的潜在因子包括血管内皮生长因子在内的多种因子的表达,提高组织对缺血缺氧状态的耐受性并重建立血氧微循环,在脊髓损伤后神经功能恢复的环节起关键作用。
血管内皮生长因子:在神经组织及血管生成区域表现活跃,调节脊髓损伤区内皮细胞增殖、分化和早期血管生成的生,是作为血管生成的调节剂的存在,起到修复受损脊神经和帮助重建血氧微环境的作用。
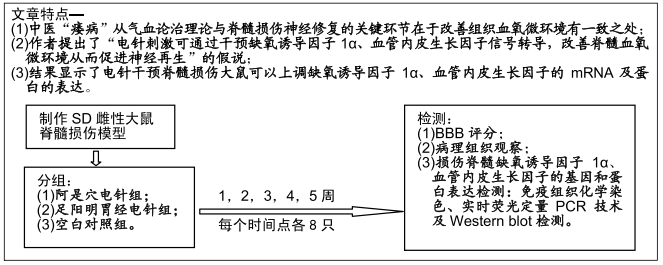
背景:作者发现,中医“痿病”从气血论治理论与脊髓损伤神经修复的关键环节在于改善组织血氧微环境有着惊人的相似,提出假设:电针刺激可通过干预缺氧诱导因子1α、血管内皮生长因子信号转导,改善脊髓血氧微环境从而促进神经再生。
目的:探讨电针干预对脊髓损伤大鼠受损节段缺氧诱导因子1α、血管内皮生长因子表达的影响。
方法:120只SD雌性大鼠以微型血管夹夹闭脊髓,保持夹闭状态20 s制作脊髓夹伤模型,随机分为3组:即阿是穴电针组、足阳明胃经电针组和空白对照组,每组40只。电针组造模后第3天开始接受每日1次的电针治疗,阿是穴电针组选择2个阿是穴、足阳明胃经电针组选择双侧伏兔、足三里穴,每周5次。于干预后1,2,3,4,5周对大鼠进行BBB评分之后分别取出损伤的脊髓组织标本,行病理组织观察,并采用免疫组织化学染色、实时荧光定量PCR 技术及Western blot检测损伤脊髓缺氧诱导因子1α、血管内皮生长因子的基因和蛋白表达。实验方案经广西中医药大学第一附属医院动物实验伦理委员会批准(批准号201712001)。
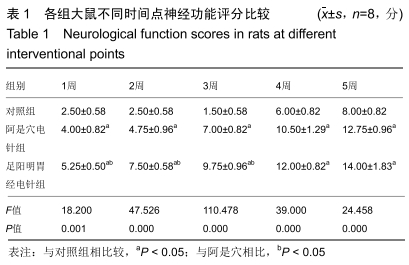
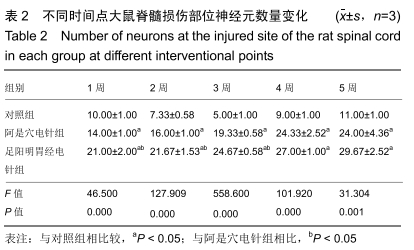
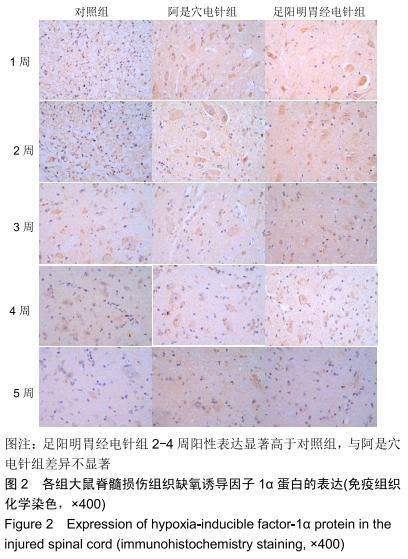
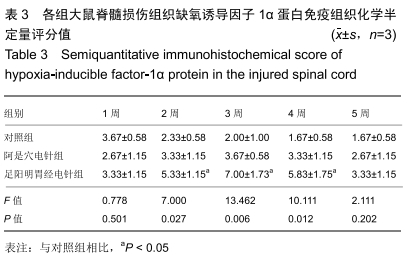
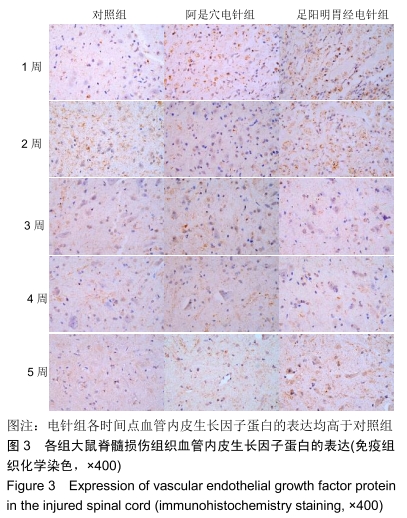
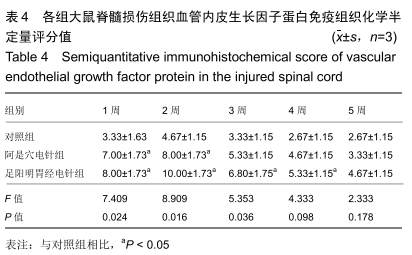
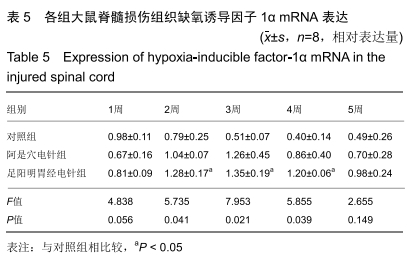
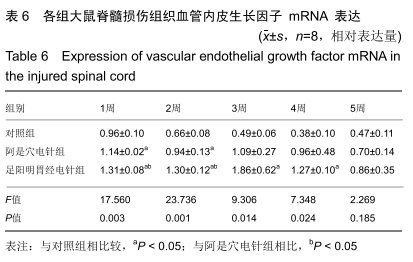
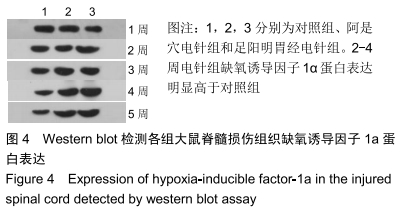
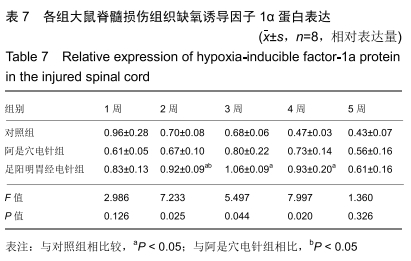
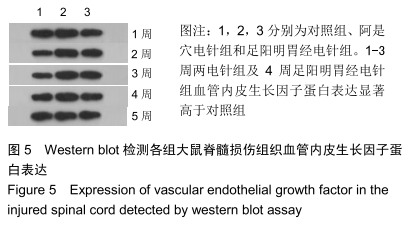
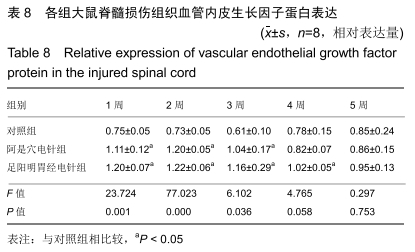
结果与结论:①阿是穴电针组及足阳明胃经电针组大鼠的下肢功能评分、缺氧诱导因子1α及血管内皮生长因子基因及蛋白表达明显高于未经电针干预的对照组;②随着干预时间的推移阿是穴电针组及足阳明胃经电针组的神经元数量均明显高于空白对照组;③结果说明,电针干预可以有效改善脊髓损伤大鼠的下肢功能评分、增加神经元的数量、上调缺氧诱导因子1α及血管内皮生长因子的mRNA及蛋白表达,从而有效促进脊髓神经功能的修复。
ORCID: 0000-0001-6069-4997(张鸿升)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: