中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (19): 2857-2863.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.19.018
• 干细胞培养与分化 stem cell culture and differentiation • 上一篇 下一篇
神经干细胞在新型复合支架中的生长和分化
邢 冉1,2,陈旭义2,朱 祥1,2,李瑞欣3,涂 悦2
- 1天津中医药大学,天津市 300193
2武警后勤学院附属医院脑科医院脑创伤与神经疾病研究所天津市神经创伤修复重点实验室,天津市 300162
3军事医学科学院卫生装备研究所,天津市 300161
Neural stem cells on a novel composite scaffold: growth and differentiation
Xing Ran1, 2, Chen Xu-yi2, Zhu Xiang1, 2, Li Rui-xin3, Tu Yue2
- 1Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300193, China
2Brain Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Logistics University of People’s Armed Police Force, Institute of Brain Trauma and Neurological Disorders, Neurotrauma Repair Key Laboratory of Tianjin, Tianjin 300162, China
3Medical Equipment Institute of Military Medical Sciences Academy, Tianjin 300161, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 3-D打印技术:指在计算机控制下,根据物体的计算机辅助设计模型或计算机断层扫描等数据,通过材料的精确3-D堆积,快速制造任意复杂形状3-D物体的新型数字化成型技术。 神经干细胞:神经干细胞可以自我更新,分化为神经胶质细胞和神经元,其可以补充凋亡的神经元和胶质细胞,从而重新形成新的有功能的神经回路,是中枢神经组织工程理想的种子细胞。
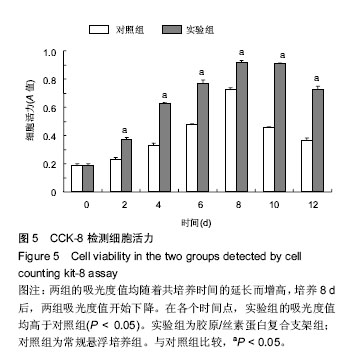
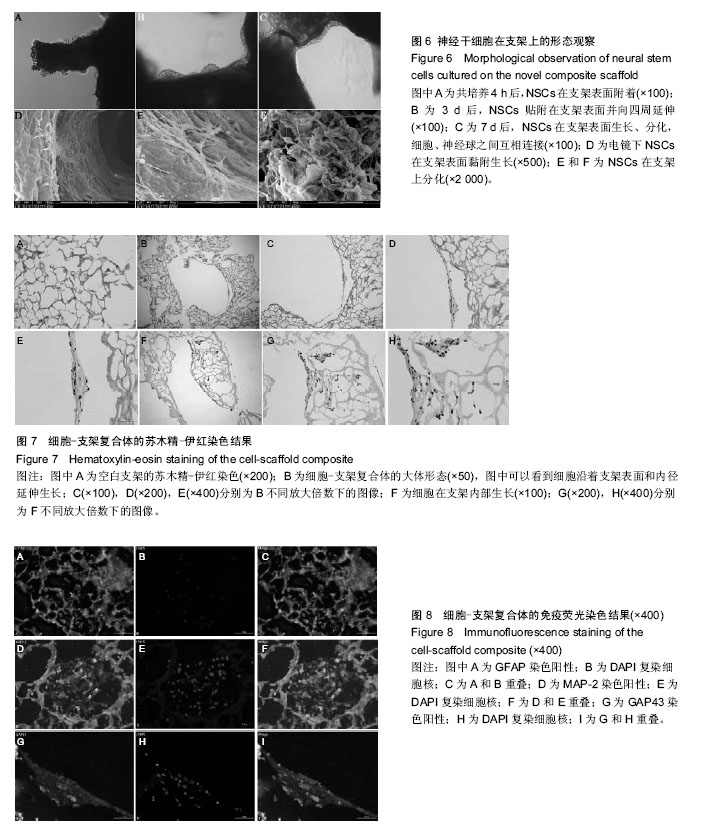
摘要 背景:神经干细胞具有自我增殖和多向分化潜能,是中枢神经组织工程理想的种子细胞。胶原蛋白和丝素蛋白作为生物支架材料已得到广泛应用,但是两者单独使用时均具有不足。那么能否将二者结合起来构建一个新的神经组织工程支架?该新型支架对神经干细胞的生长和分化又会有什么影响呢? 目的:观察新型复合支架中神经干细胞的生长和分化情况。 方法:将大鼠胚胎神经干细胞接种于新型复合支架中,通过光镜和扫描电镜观察其在支架中生长和分化情况。以常规悬浮培养作为对照组,使用CCK-8检测两组中神经干细胞的活力。对神经干细胞与新型复合支架的三维空间复合体进行石蜡切片,并进行苏木精-伊红染色和免疫荧光染色,观察神经干细胞在材料表面及内部的生长、分化情况。 结果与结论:①新型复合支架中的神经干细胞可以很好地生长、分化,细胞与细胞之间形成突触;②CCK-8检测显示,神经干细胞在支架中生长良好,新型复合支架中神经干细胞活力要优于对照组(P < 0.05);③石蜡切片的苏木精-伊红染色和免疫荧光染色进一步证明神经干细胞在支架中能够很好的生长和分化;④结果说明,制备的新型复合支架具有良好的生物相容性,有利于神经干细胞生长及分化,有良好的应用前景。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0001-5312-7118(邢冉)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)