| [1] 沈晓明,王卫平,常立文,等.儿科学[M].7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2008:408-409.[2] 孙国军,赵文静,陈曦,等.脐血间充质干性的分离平培养及生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(14):2504-2507.[3] 赵霞,路希敬,刘国强,等.不同培养基培养人脐血间充质干细胞的差异[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(19): 3447-3455.[4] 周志刚,李志忠,林永新,等.人脐血间充质干细胞定向诱导分化成类神经元的实验研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015, 31(2):229-233.[5] 陈镭,陈冰,谢福堂.诱导脐血间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(23):4335-4338.[6] Divya MS, Roshin GE, Divya TS, et al. Umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells consist of a unique population of progenitors co-expressing mesenchymal stem cell and neuronal markers capable of instantaneous neuronal differentiation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;3(6):57.[7] 王向野,张志友,杨小明,等.神经干细胞侧脑室内移植治疗脑瘫鼠的实验研究[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2012, 17(6):354-357.[8] 谭洁璐,郑湘榕.脑性瘫痪动物模型的制作与鉴定研究进展[J].国际儿科学杂志,2010,37(5):494-496. [9] Wang Y, Liu Y, Liu Q. Ganglioside promotes the bridging of sciatic nerve defects in cryopreserved peripheral nerve allografts. Neural Regen Res. 2014; 9(20):1820-1823.[10] 李哲,王和强,刘兵,等.单唾液酸四己糖神经节苷脂钠注射液对痉挛性脑瘫的疗效[J].中国康复理论与实践,2015, 21(3):341-343.[11] 赵凯,贾宇臣.人脐血干细胞在局灶性脑缺血大鼠体内的迁移与分化[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2015,28(3): 286- 291.[12] 肖升平,马廉,罗敏洁,等.人脐带血间充质干细胞在缺氧缺血性脑病新生鼠脑内的定值[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2007, 22(21):1655-1657.[13] Castillo-Melendez M, Yawno T, Jenkin G, et al. Stem cell therapy to protect and repair the developing brain: a review of mechanisms of action of cord blood and amnion epithelial derived cells. Front Neurosci. 2013; 7:194.[14] Park SI, Lim JY, Jeong CH, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy promotes functional recovery of contused rat spinal cord through enhancement of endogenous cell proliferation and oligogenesis. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:362473.[15] Koh H,Hwang K,Lim HY,et al.Mononuclear cells from the cord blood and granulocyte- colony stimulating factor-mobilized peripheral blood: is there a potential for treatment of cerebral palsy? Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10 (12): 2018-2024.[16] Danby R, Rocha V. Improving engraftment and immune reconstitution in umbilical cord blood transplantation. Front Immunol. 20144;5:68.[17] Park HW, Moon HE, Kim HS, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve functional recovery through thrombospondin1, pantraxin3, and vascular endothelial growth factor in the ischemic rat brain. J Neurosci Res. 2015; 93(12): 1814-1825.[18] Koh SH, Kim KS, Choi MR, et al. Implantation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a neuroprotective therapy for ischemic stroke in rats. Brain Res. 2008;1229:233-248.[19] Cui B, Li E, Yang B, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Exp Ther Med. 2014;7(5):1233-1236.[20] Kim DH, Lee D, Chang EH, et al. GDF-15 secreted from human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells delivered through the cerebrospinal fluid promotes hippocampal neurogenesis and synaptic activity in an Alzheimer's disease model. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(20):2378-2390.[21] Zhu Y, Guan YM, Huang HL, et al. Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cell transplantation suppresses inflammatory responses and neuronal apoptosis during early stage of focal cerebral ischemia in rabbits. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014;35(5):585-591.[22] Chelluboina B, Klopfenstein JD, Pinson DM, et al. Stem cell treatment after cerebral ischemia regulates the gene expression of apoptotic molecules.Neurochem Res. 2014;39(8):1511-1521.[23] Park SI, Lim JY, Jeong CH, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy promotes functional recovery of contused rat spinal cord through enhancement of endogenous cell proliferation and oligogenesis. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:362473.[24] Fleiss B, Guillot PV, Titomanlio L, et al. Stem cell therapy for neonatal brain injury. Clin Perinatol. 2014; 41(1):133-148.[25] Koh SH, Kim KS, Choi MR, et al. Implantation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a neuroprotective therapy for ischemic stroke in rats. Brain Res. 2008;1229:233-248.[26] Rafieemehr H, Kheirandish M, Soleimani M. Improving the neuronal differentiation efficiency of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultivated under appropriate conditions. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015;18(11):1100-1106.[27] Hussain EK, Waheed IN. The Effects of Insulin Like Growth Factor -1 (IGF-1) on the Plasticity of Umbilical Cord Blood Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Colonies to In Vitro Neurogenic Differentiation. Journal of Biology, Agriculture and Healthcare. 2015; 5(4): 138-144.[28] Wang YD,Liu YG,Liu Q.Ganglioside promotes the bridging of sciatic nerve defects in cryopreserved peripheral nerve allografts. Neural Regen Res. 2014; 9(20): 1820-1823.[29] Nan C, Shi Y, Zhao Z, et al. Monosialoteterahexosyl ganglioside induces the differentiation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells into neuron-like cells. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(4): 1057-1062.[30] Zhang X, Zhang Q, Li W, et al. Therapeutic effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on neonatal rat hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Neurosci Res. 2014;92(1):35-45.[31] Tio M, Tan KH, Lee W, et al. Roles of db-cAMP, IBMX and RA in aspects of neural differentiation of cord blood derived mesenchymal-like stem cells. PLoS One. 2010;5(2):e9398.[32] Zhang ZJ, Li YJ, Liu XG, et al.Human umbilical cord blood stem cells and brain-derived neurotrophic factor for optic nerve injury: a biomechanical evaluation. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(7): 1134-1138.[33] Sypecka J, Sarnowska A. Mesenchymal cells of umbilical cord and umbilical cord blood as a source of human oligodendrocyte progenitors. Life Sci. 2015; 139:24-29. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
脐血间充质干细胞:脐血是胎儿出生时脐带内及近胎盘侧血管内血液,是胎儿血液循环的一部分。研究表明,脐血间充质干细胞含量丰富,约占有核细胞的0.98%,该细胞为较原始细胞,有分化为造血细胞、脂肪细胞、肌肉细胞、神经细胞等潜能。目前实验研究证明,脐血间充质干细胞移植能治疗血液病、心脏疾病、脑损伤、脊髓损伤等疾病。目前也有报道脐血间充质干细胞经侧脑室注射治疗脑性瘫痪的实验研究。
神经节苷酯:是含唾液酸的糖神经鞘脂,是神经细胞膜的组成成分,在神经发生、生长、分化过程中起必不可少的作用,包括促进神经再生、促进神经轴突生长和突触形成、恢复神经支配功能、改善神经传导、促进脑电活动及其他神经电生理指标的恢复、保护细胞膜、促进细胞膜各种酶活性恢复等作用。
文题释义:
脐血间充质干细胞:脐血是胎儿出生时脐带内及近胎盘侧血管内血液,是胎儿血液循环的一部分。研究表明,脐血间充质干细胞含量丰富,约占有核细胞的0.98%,该细胞为较原始细胞,有分化为造血细胞、脂肪细胞、肌肉细胞、神经细胞等潜能。目前实验研究证明,脐血间充质干细胞移植能治疗血液病、心脏疾病、脑损伤、脊髓损伤等疾病。目前也有报道脐血间充质干细胞经侧脑室注射治疗脑性瘫痪的实验研究。
神经节苷酯:是含唾液酸的糖神经鞘脂,是神经细胞膜的组成成分,在神经发生、生长、分化过程中起必不可少的作用,包括促进神经再生、促进神经轴突生长和突触形成、恢复神经支配功能、改善神经传导、促进脑电活动及其他神经电生理指标的恢复、保护细胞膜、促进细胞膜各种酶活性恢复等作用。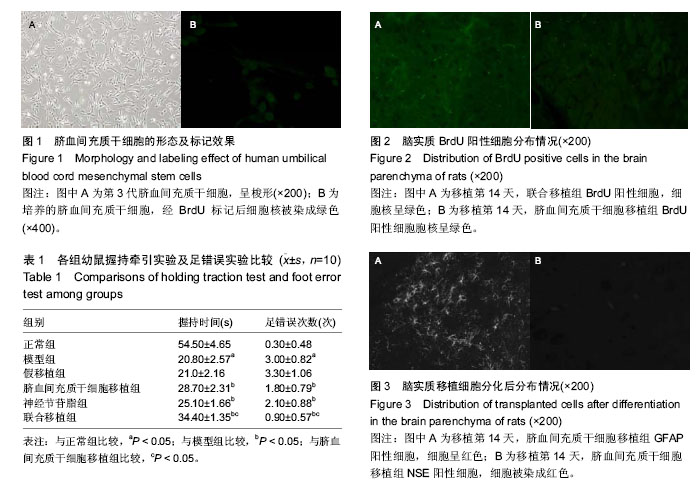
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
脐血间充质干细胞:脐血是胎儿出生时脐带内及近胎盘侧血管内血液,是胎儿血液循环的一部分。研究表明,脐血间充质干细胞含量丰富,约占有核细胞的0.98%,该细胞为较原始细胞,有分化为造血细胞、脂肪细胞、肌肉细胞、神经细胞等潜能。目前实验研究证明,脐血间充质干细胞移植能治疗血液病、心脏疾病、脑损伤、脊髓损伤等疾病。目前也有报道脐血间充质干细胞经侧脑室注射治疗脑性瘫痪的实验研究。
神经节苷酯:是含唾液酸的糖神经鞘脂,是神经细胞膜的组成成分,在神经发生、生长、分化过程中起必不可少的作用,包括促进神经再生、促进神经轴突生长和突触形成、恢复神经支配功能、改善神经传导、促进脑电活动及其他神经电生理指标的恢复、保护细胞膜、促进细胞膜各种酶活性恢复等作用。
文题释义:
脐血间充质干细胞:脐血是胎儿出生时脐带内及近胎盘侧血管内血液,是胎儿血液循环的一部分。研究表明,脐血间充质干细胞含量丰富,约占有核细胞的0.98%,该细胞为较原始细胞,有分化为造血细胞、脂肪细胞、肌肉细胞、神经细胞等潜能。目前实验研究证明,脐血间充质干细胞移植能治疗血液病、心脏疾病、脑损伤、脊髓损伤等疾病。目前也有报道脐血间充质干细胞经侧脑室注射治疗脑性瘫痪的实验研究。
神经节苷酯:是含唾液酸的糖神经鞘脂,是神经细胞膜的组成成分,在神经发生、生长、分化过程中起必不可少的作用,包括促进神经再生、促进神经轴突生长和突触形成、恢复神经支配功能、改善神经传导、促进脑电活动及其他神经电生理指标的恢复、保护细胞膜、促进细胞膜各种酶活性恢复等作用。