| [1] Xu B,Xu H,Wu Y,et al.Intervertebral disc tissue engineering with natural extracellular matrix-derived biphasic composite scaffolds.PLoS One.2015;10(4): e0124774. [2] 马新芳,张静莹.骨组织工程支架材料的研究现状与应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(30):4895-4899. [3] Holzwarth JM, Ma PX.Biomimetic nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2011;32(26):9622-9629. [4] Ruiz-Hitzky E,Darder M,Aranda P,et al.Advances in biomimetic and nanostructured biohybrid materials. Adv Mater.2010;22(3):323-326. [5] Xie J,Peng C,Zhao Q,et al.Osteogenic differentiation and bone regeneration of iPSC-MSCs supported by a biomimeticnanofibrous scaffold.Acta Biomater.2016;29: 365-379. [6] Qu T,Liu X.Nano-structured gelatin/bioactive glass hybrid scaffolds for the enhancement of odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells.J Mater Chem B Mater Biol Med.2013;1(37):4764-4772. [7] Liu X,Ma PX.Phase separation, pore structure, and properties of nanofibrous gelatin scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2009;30(25):4094-4103. [8] Liu X,Smith LA,Hu J,et al.Biomimetic nanofibrous gelatin/apatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2009;30(12):2252-2258. [9] Rey-Rico A,Silva M,Couceiro J,et al.Osteogenic efficiency of in situ gelling poloxamine systems with and without bone morphogenetic protein-2. Eur Cell Mater.2011; 21(4):317-340. [10] Lieberman JR,Daluiski A,Einhorn TA.The role of growth factors in the repair of bone. Biology and clinical applications.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84-A(6):1032-1044. [11] Bouxsein ML,Turek TJ,Blake CA,et al.Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 accelerates healing in a rabbit ulnar osteotomy model.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2001; 83-A(8): 1219-1230. [12] Vo TN,Kasper FK,Mikos AG,et al.Strategies for controlled delivery of growth factors and cells for bone regeneration.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(12):1292- 1309. [13] 马立坤,叶鹏,黄文良,等.骨形态发生蛋白2/聚乳酸缓释微球的制备及表征[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(3): 395-400. [14] 王玮,尹庆水,张余.负载重组人骨形态发生蛋白-2壳聚糖纳米微球的制备及异位成骨活性研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(2):147-152. [15] Carreira AC,Lojudice FH,Halcsik E,et al.Bone morphogenetic proteins: facts, challenges, and future perspectives.J Dent Res.2014;93(4):335-345. [16] Lee J,Yoo JJ,Atala A,et al.The effect of controlled release of PDGF-BB from heparin-conjugated electrospun PCL/gelatin scaffolds on cellular bioactivity and infiltration.Biomaterials.2012;33(28):6709-6720. [17] Seib FP, Herklotz M, Burke KA, et al. Multifunctional silk-heparin biomaterials for vascular tissue engineering applications.Biomaterials. 2014;35(1): 83-91. [18] Zuo Q,Guo R,Liu Q,et al.Heparin-conjugated alginate multilayered microspheres for controlled release of bFGF. Biomed Mater.2015;10(3):035008. [19] Lu Q,Li M,Zou Y,et al. Delivery of basic fibroblast growth factors from heparinized decellularized adipose tissue stimulates potent de novo adipogenesis.J Control Release. 2014;174:43-50. [20] Bhakta G,Rai B,Lim ZX,et al.Hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels functionalized with heparin that support controlled release of bioactive BMP-2. Biomaterials. 2012;33(26): 6113-6122. [21] 刘秀英,张超灿,徐卫林,等.甲苯胺蓝分光光度法测定肝素钠的研究[J].化学试剂,2009, 31(4):271-274. [22] Lin H,Zhao Y,Sun W,et al.The effect of crosslinking heparin to demineralized bone matrix on mechanical strength and specific binding to human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Biomaterials. 2008;29(9): 1189-1197. [23] Karageorgiou V,Kaplan D.Porosity 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2005;26(27): 5474-5491. [24] Banwart JC,Asher MA,Hassanein RS.Iliac crest bone graft harvest donor site morbidity. A statistical evaluation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1995;20(9): 1055-1060. [25] Florczyk SJ,Leung M,Li Z,et al.Evaluation of three-dimensional porous chitosan–alginate scaffolds in rat calvarial defects for bone regeneration applications. J Biomed Mater Res. 2013;101(10): 2974-2983. [26] De Long Jr WG,Einhorn TA,Koval K,et al.Bone grafts and bone graft substitutes in orthopaedic trauma surgery. A critical analysis.J Bone Joint Surg A. 2007; 89(3): 649-658. [27] Xiao W,Fu H,Rahaman MN,et al.Hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres: a novel bioactive and osteoconductive carrier for controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein-2 in bone regeneration.Acta Biomater. 2013; 9(9): 8374-8383. [28] Hollister SJ. Porous scaffold design for tissue engineering. Nat Mater.2005;4(7): 518-524. [29] Bueno EM,Glowacki J.Cell-free and cell-based approaches for bone regeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5(12):685-697. [30] 谢兴文,姜徽,李宁,等.重组人骨形态发生蛋白2诱导骨修复的应用及前景[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(7): 1319-1323. [31] Galimberti F,Lubelski D,Healy AT,et al.A systematic review of lumbar fusion rates with and without the use of rhBMP-2.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(14):1132-1139. [32] Zhao B,Katagiri T,Toyoda H,et al.Heparin potentiates the in vivo ectopic bone formation induced by bone morphogenetic protein-2.J Biol Chem.2006;281(32): 23246-23253. [33] Li Z,Qu T,Ding C,et al.Injectable gelatin derivative hydrogels with sustained vascular endothelial growth factor release for induced angiogenesis.Acta Biomater. 2015;13:88-100. [34] 李娟,吴英锋,杨新林.肝素功能化生物材料的研究进展[J].有机化学,2010,30(3):359-367. [35] 马寅孙,蔡玉荣,刘琳,等.肝素化丝素支架作为骨形态发生蛋白-2缓释载体的研究[J].化学学报,2012, 70(4): 479-484. [36] Jeon O,Song SJ,Kang SW,et al.Enhancement of ectopic bone formation by bone morphogenetic protein-2 released from a heparin-conjugated poly(L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold.Biomaterials. 2007;28(17):2763-2771. [37] Xu X,Jha AK,Duncan RL,et al.Heparin-decorated, hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel particles for the controlled elease of bone morphogenetic protein 2.Acta Biomater.2011; 7(8):3050-3059. [38] Sachar A,Strom TA,Serrano MJ,et al.Osteoblasts responses to three-dimensional nanofibrous gelatin scaffolds.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(11): 3029-3041. [39] Sun Y,Jiang Y,Liu Q,et al.Biomimetic Engineering of Nanofibrous Gelatin Scaffolds with Noncollagenous Proteins for Enhanced Bone Regeneration.Tissue Eng Part A.2013; 19(15-16):1754-1763. [40] Ma PX,Zhang R.Synthetic nano-scale fibrous extracellular matrix. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;46(1):60-72. |
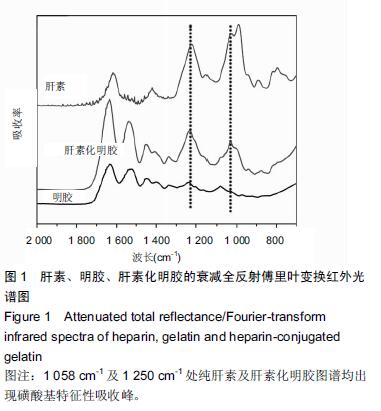
.jpg)

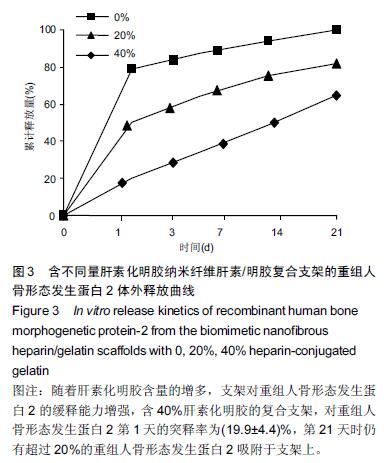
.jpg)